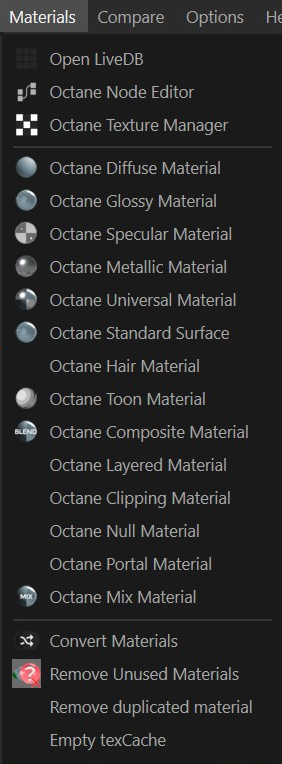
Materials Menu
The Materials Menu is how you can add OctaneRender® materials to your Cinema 4D scenes. This menu can also be used to:
- Access the LiveDB online Octane materials database
- Access the Octane Node Editor
- Open the Octane Texture Manager
- Convert Cinema 4D Materials into Octane Materials
- Remove Unused Materials (which saves VRAM)
- Remove Duplicated Materials (also saves VRAM)
- Empty Tex Cache (helpful with stability issues)
You can find detailed information on Octane Materials in the Using Materials section of documentation. Other links are provided for each topic below:
|
|
materials menu
|
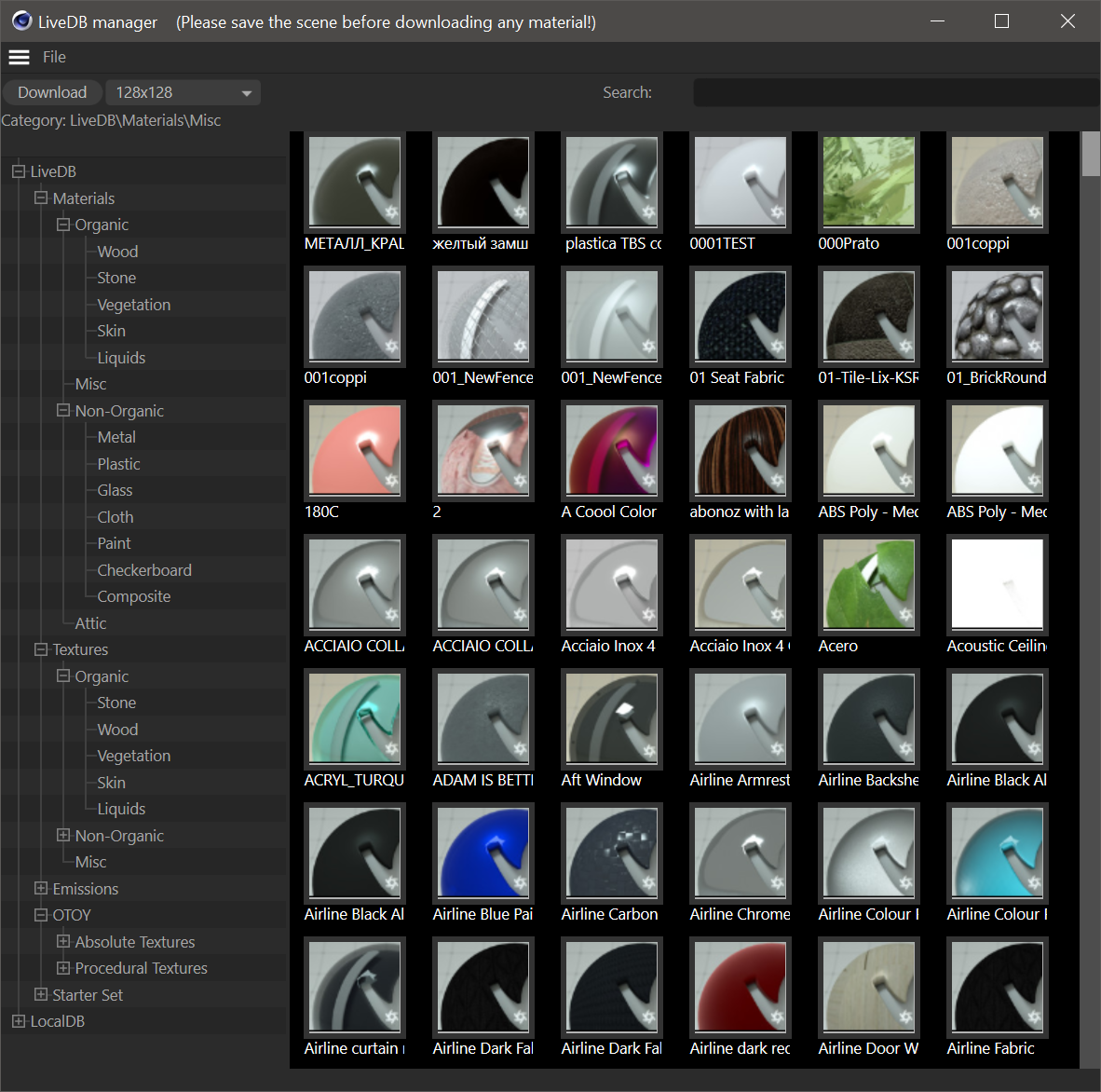
Open LiveDB
Live DataBase is the online material / texture database of Octane. Use Live DB to download and use pre-made Octane materials from Otoy and the Octane user community. Note that the scene into which the material is to be used my first be saved before the material can be downloaded from LiveDB.
|
|
live database (live DB)
|
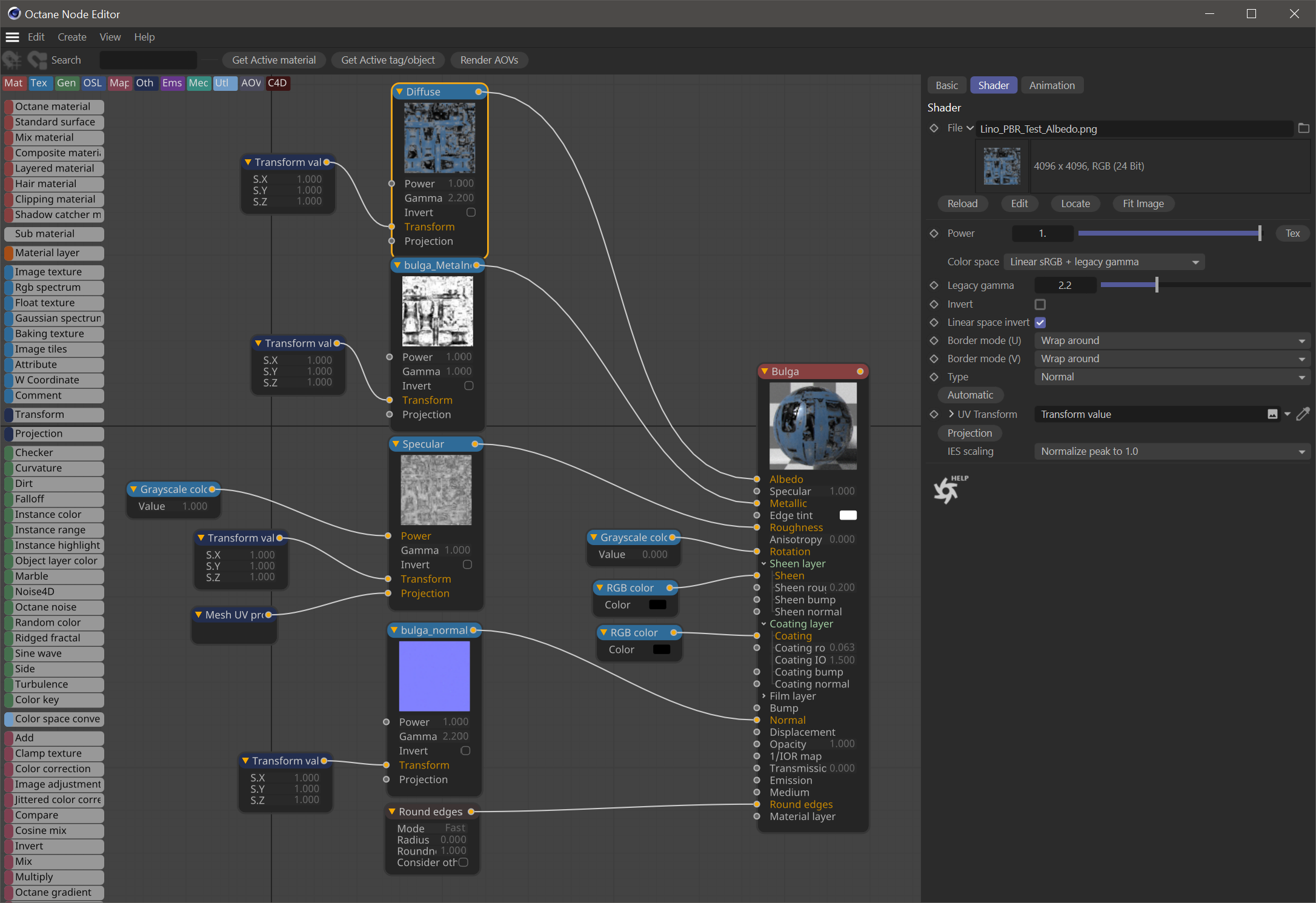
Octane Node Editor
There are two ways to edit materials in Octane: the classic Cinema 4D material editor and the Octane node editor. Node editor provides advanced control compared to the classic Cinema 4D editor, allowing you to build very sophisticated materials. More detailed information is provided in the Node Editor section.
|
|
octane node editor
|
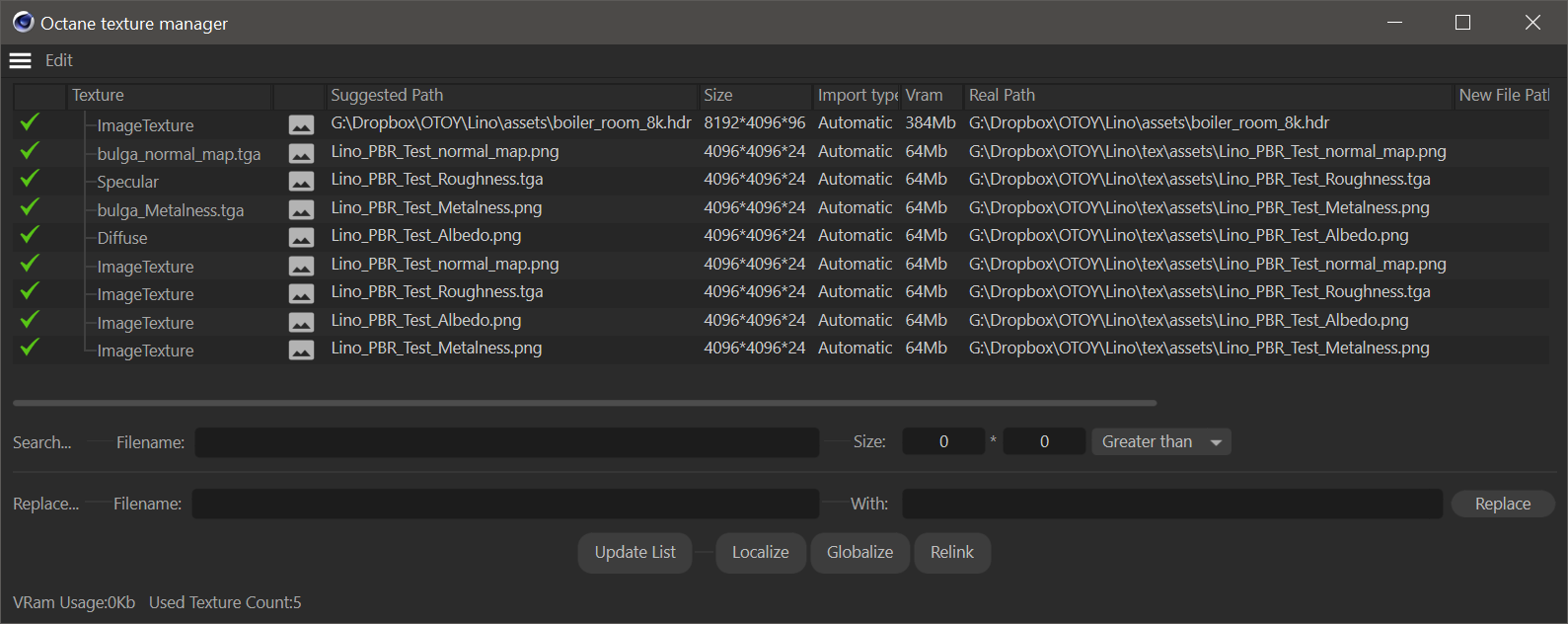
Octane Texture Manager
Use the Octane Texture Manager to review texture material assignments, how much VRAM is consumed by the selected texture, and the installation path of the texture. See Octane Texture Manager for more information.
|
|
octane texture manager
|
Octane Diffuse Material
The Diffuse material is best for relatively simple materials without defined reflections — in this model, light hits the surface and distributes the color value evenly. It does not have specific Reflective or Refractive features. For a more detailed description, see the Diffuse Material section.
|
|
diffuse material — path tracer
|
Octane Glossy Material
The Glossy material is best for simpler shiny surfaces. In this model, the light is reflected when it hits the surface (the reflection is equal to the incident angle of the light). You can create materials like metals and plastics with this model. For a more detailed description, see the Glossy Material section.
|
|
glossy material — Photon tracer
|
Octane Specular Material
The Specular material is used to create typically transparent or translucent materials — in this model, when light hits the surface, it continues to travel through the medium. You can create materials such as glass, frosted glass and water in this model. For a more detailed description, see the Specular Material section.
|
|
specular material — Photon Tracer
|
Octane Metallic Material
The Metallic material is specifically designed to create realistic metal. Unlike the glossy material, the Metallic material breaks out complex IOR values, offering the most realistic results. For a more detailed description, see the Metallic Material section.
|
|
metallic material — photon tracer
|
Octane Universal Material
The Universal material is the Octane über material, as it includes all of material channels within Octane (with the exception of the special-use hair and toon materials). The other material types are designed for specific needs, whereas the Universal material can do it all. It is more complex and a little slower to render, but many consider the versatility to be worthwhile. The Universal material is also the go-to material for PBR support for Substance and other PBR systems. For a more detailed description, see the Universal Material section.
Octane Hair Material
The Octane Spectral Hair Material is a sophisticated hair shading model that is a significant upgrade from previous versions. Far more realistic and natural, this hair material is simple to work with and renders quickly. See the Hair Material section for more information.
Octane Toon Material
This material is designed to create toon shading, and requires toon lights to work properly. For more detailed description, see the Toon Material section.
|
|
toon material
|
Octane Mix Material
The Mix material used to mix two different Octane materials together, with the option to use a texture or Float to determine the mix value. For more detailed description, see the Mix Material section.
Octane Composite Material
The Composite material enables multiple Octane sub-materials to be mixed together. Standard Octane materials cannot be used by the Composite material; to mix standard Octane materials, use the Mix material instead. For a more detailed information, see the Composite Material section.
Octane Layered Material
The Octane Layered material allows you to build customized, specific materials, tuning the results and performance. The layered material uses an Octane sub-material as a base input, and Octane Material layers added as needed. See the Layered Material section for more.
Octane Standard Surface Material
The Standard Surface material is based upon the Autodesk specification, and is similar to the Octane Universal material: it has transparency, subsurface scattering, layering and more. Read more about it in the Standard Surface section.
|
|
standard surface material — photon tracer
|
|
|
standard surface material — Photon Tracer
|
Octane Clipping Material
The Clipping material removes portions of objects with this material applied from other objects in the scene. See the Clipping Material section for more information.
|
|
clipping material
|
Octane Portal Material
The Portal material is intended for interiors, where noise can accumulate with path tracing. The Portal material is assigned to "portal objects," which are simple meshes intended to cover small openings in a given structure. The combination of the mesh objects and the Portal material can assist the core engine to handle light paths more efficiently and with less noise. See the Portal Material section for more information.
Convert Materials
See the Material Tools section.
Remove Unused Materials
See the Material Tools section.
Remove Duplicated Material
See the Material Tools section.