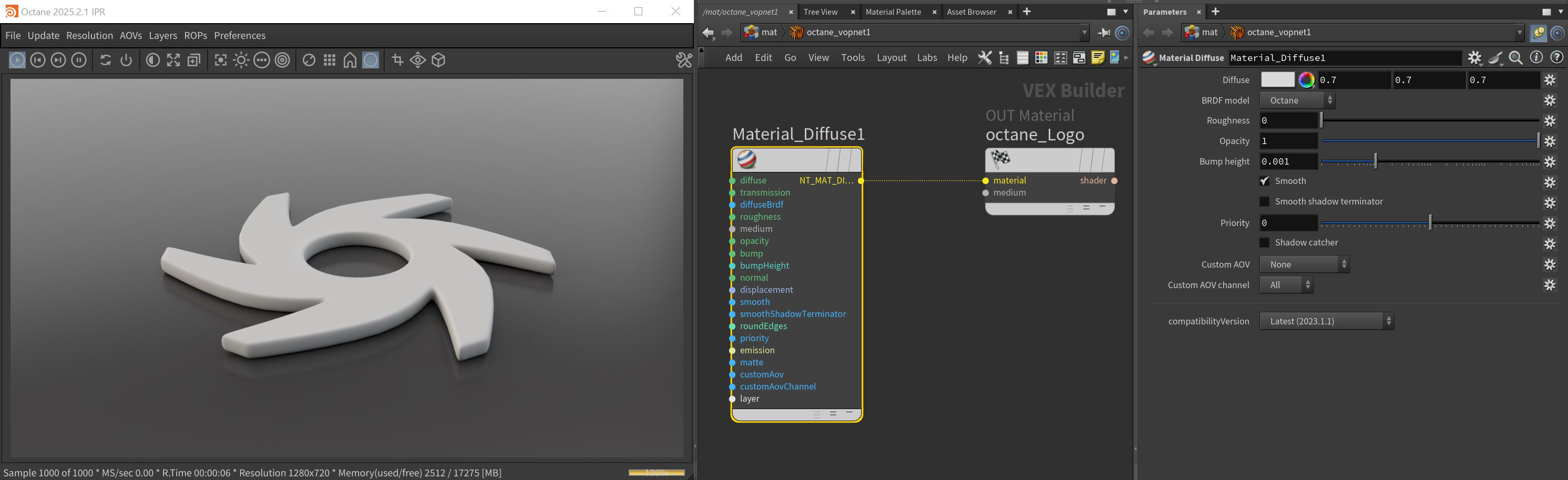
Material Diffuse
The Diffuse material is used for dull, non-reflecting materials or light-emitting surfaces (figure 1). Diffuse materials simulate a rough surface that reflects light back into the environment in all directions. Specular highlights and reflections do not appear on diffuse surfaces.
|
|
Material Diffuse
|
Figure 1: The Diffuse material and it's associated parameters
Diffuse Material Parameters
Diffuse - This gives the material its color. It accepts a value or an image-based texture.
Transmission Pin - Allows light to pass from the object, giving it a sense of internal illumination. This effect can be used to cheat sub-surface scattering and is particularly suited to do so for single-sided objects, but for anything else, a medium node should be used instead.This parameter uses a color or texture that is mixed with the material’s Diffuse color, and is most noticeable in areas affected by indirect lighting.
BRDF Model - Provides three models for diffuse light reflectance. Lambertian reflects light equally in all directions and does not support roughness. The Octane option creates a sheen effect much like velvet. And, the Oren-Nayar option behaves more like clay.
Roughness - Simulates very rough surfaces like sandpaper or clay. It accepts a value, color, or image-based texture.
Medium Pin - There are three primary types of mediums used with materials: Absorption, Random Walk, and Scattering. Details can be found in the Mediums and Volumes section.
Opacity - Sets the material's transparency. Although this parameter has the option to accept values and colors as inputs, a texture map is the most appropriate input parameter.
Bump Pin - Creates fine details on the material’s surface using a Procedural or Image texture. When you connect a grayscale texture to this parameter, light areas of the texture give the appearance of protruding bumps, and dark areas create the appearance of indentation. You can adjust the bump map strength by setting the Power or Gamma values on the Image texture node. These attributes are covered in more detail under the Texture Overview section.
Normal Pin - Creates the look of fine detail on the surface. A normal map is a special type of image texture that uses red, green, and blue color values to perturb the normals of the surface at render time, thus giving the appearance of added detail. They can be more accurate than Bump maps, but require specific software such as ZBrush®, Mudbox®, Substance Designer, XnormalTM, or others to generate.
Bump Height - Determines the height represented by a normalized value of 1.0 in the bump texture. A vaule of 0 disables the bump map and a negative value will invert the bump map.
Displacement Pin - Allows adjustment for the height of points on a surface based on an image value. Displacement differs from Bump or Normal mapping by providing true displacement of an objects surface. Displacement mapping is covered in more detail under the Displacement Overview section.
Smooth - Refers to Normal Smoothing, which determines whether or not to smooth the normals of all meshes sharing that material. When off, the materials can be faceted and polygonal.
Smooth Shadow Terminator - If enabled, self-intersecting shadows for low polygon objects is smoothed according to the polygon's curvature.
Round Edges Pin - This creates a shader effect at render time that rounds the sharp edges of objects without modifying and reloading the geometry. Higher values will round the edges more. This is useful to bevel hard edges during render time, like when using low-polygon models. See the Round Edges section for more information.
Priority - Used to resolve the ambiguity in overlapping surfaces, the surface priority control allows artists to control the order of preference for surfaces. A higher number suggests a higher priority for the surface material, which means it is preferred over a lower priority surface material if a ray enters a higher priority surface and then intersects a lower priority surface while inside the higher priority surface medium.
Emission Pin - Accepts either a Blackbody emission or a Texture emission node. This parameter makes the material emit light and creates mesh emitters. These node types are covered in more detail under the Mesh Emitter section.
Shadow Catcher/Matte Pin - Creates a shadow catching material. When active, the material renders shadows cast onto it, and is transparent everywhere else across a surface.
Custom AOV - Writes a mask to the specified custom AOV.
Custom AOV Channel - Determines whether the custom AOV is written to a specific color channel (R, G, or B) or to all the color channels.
Layer Pin - Adds a Material Layer above the base material. See the Material Layers section in this manual for more details.
Compatibility Version The Octane version that the behavior of this node should match.
- Latest (2023.1.1) - Default.
- 2023.1 - The slope of bump maps is calculated slightly differently, making it more sensitive to the orientation of the UV mapping.
- 2022.1 - Legacy behavior for bump map strength is active and bump map height is ignored. This applies in addition to 2023.1 compatibility mode behavior.