Materials Overview
There are several types of materials in OctaneRender® that can apply to surfaces to achieve a variety of appearances and rendering effects.
- Clipping - Allows one object to become a clipping volume for other objects in a scene.
- Composite - Mixes several materials using masks.
- Diffuse - Used for rough, non-reflecting materials, as well as light emitting meshes.
- Glossy - Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals.
- Hair - Designed for hair and fur objects.
- Layer - Constructs complex materials that consist of a base layer and several material layers.
- Metal - Similar to the Glossy material, except by default it exhibits more metal-like characteristics.
- Mixer - Mixes any two Material types.
- Null - Used for mesh objects that should be invisible but contain a medium.
- Portal - Designates openings in scenes to allow the render kernel to better sample light from those areas.
- Specular - Used for transparent materials such as glass and water.
- Standard Surface - This material closely aligns with the Autodesk Standard Surface shader specification for cross-application interoperability.
- Toon - Designs hand-drawn looking surfaces.
- Toon Ramp - Controls shading on the model. To use this material, you also need to use Toon lighting in the scene.
- Universal - Brings substance maps and PBR outputs into OctaneRender.
- Shadow Catcher - Captures shadows.
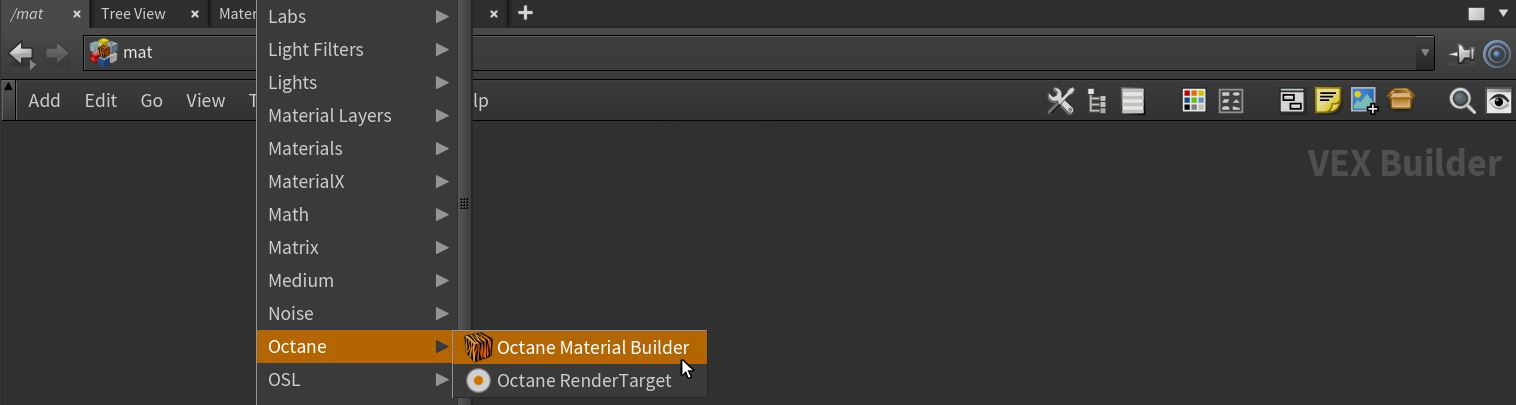
The material nodes have been transitioned to the MAT network, although the material types can still be accessed from the SHOP network. The preferred method is to access materials in a scene's MAT network. You can right-click or press the Tab key in the MAT work area and choose Octane > Octane Material Builder (Figure 1).
|
|
MAT Network
|
Figure 1: Accessing Octane materials from the MAT network window
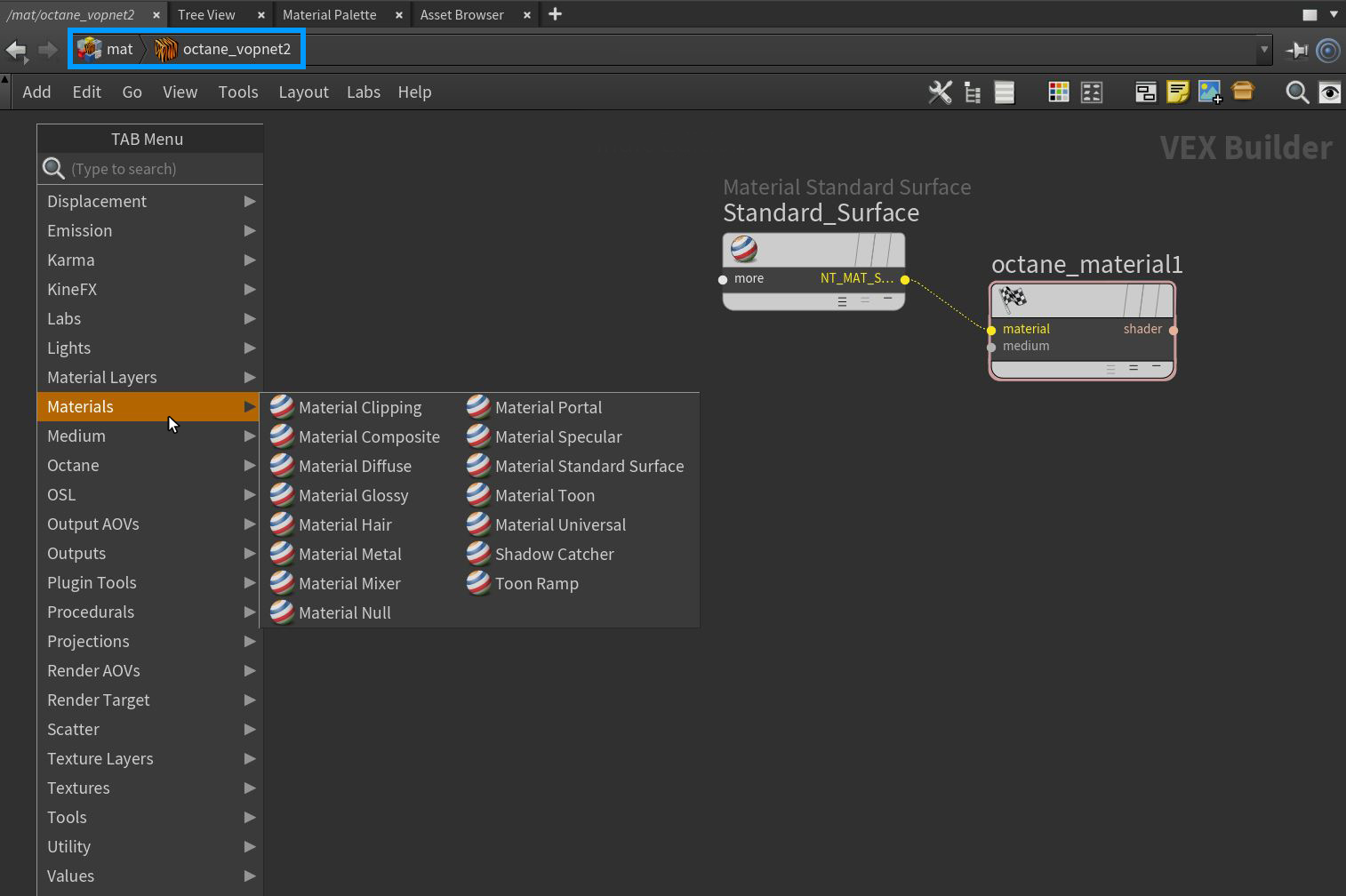
This will create an Octane VOP NET where complex materials can be designed (Figure 2). All of the Octane material-related nodes can be found outside of the Octane VOP NET node but they are more difficult to locate at the top level of the MAT network due to being mixed with all other render engine nodes. An OUT Material node is also present and vital to Octane material design. This node is discussed in the OUT Material section.
|
|
VOP NET
|
Figure 2: Accessing Octane-specific nodes from the MAT network window, inside an Octane VOP NET node
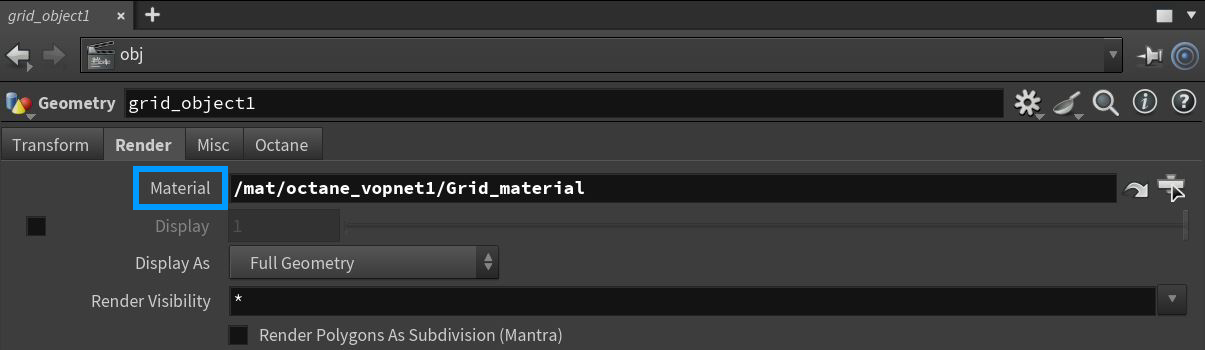
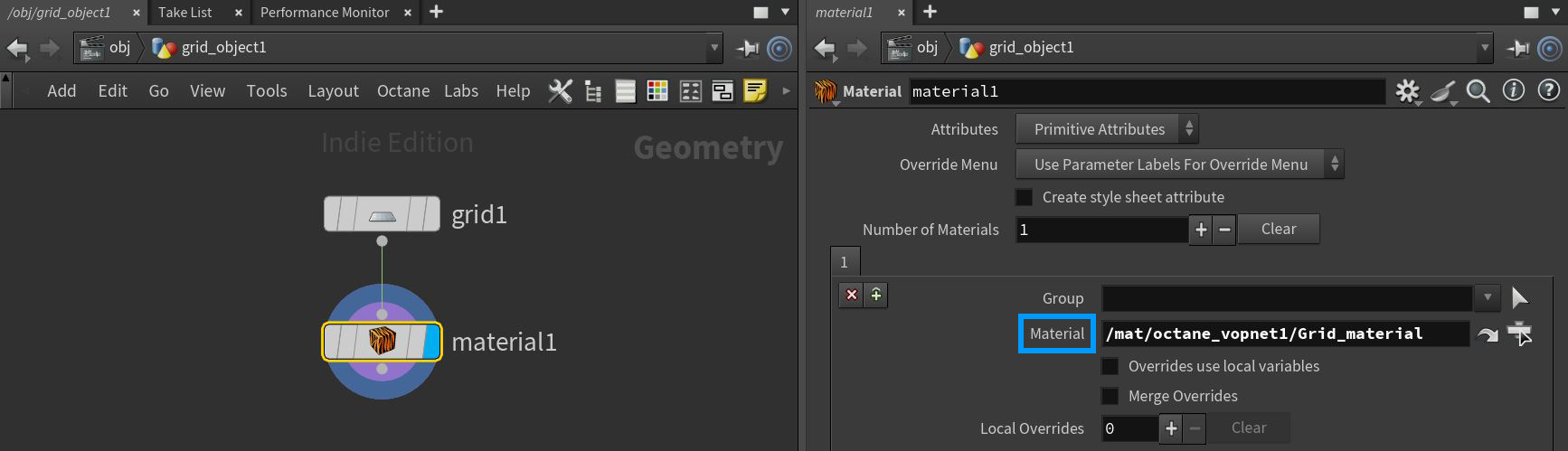
The materials can be applied to the scene objects two ways. The first method is to apply the material at the OBJ level (figure 3). The second method is to apply the material at the SOP level using a Material SOP node (figure 4).
|
|
OBJ Level
|
Figure 3: Assiging a material from the OBJ level
|
|
SOP Level
|
Figure 4: Assigning a material from the SOP level