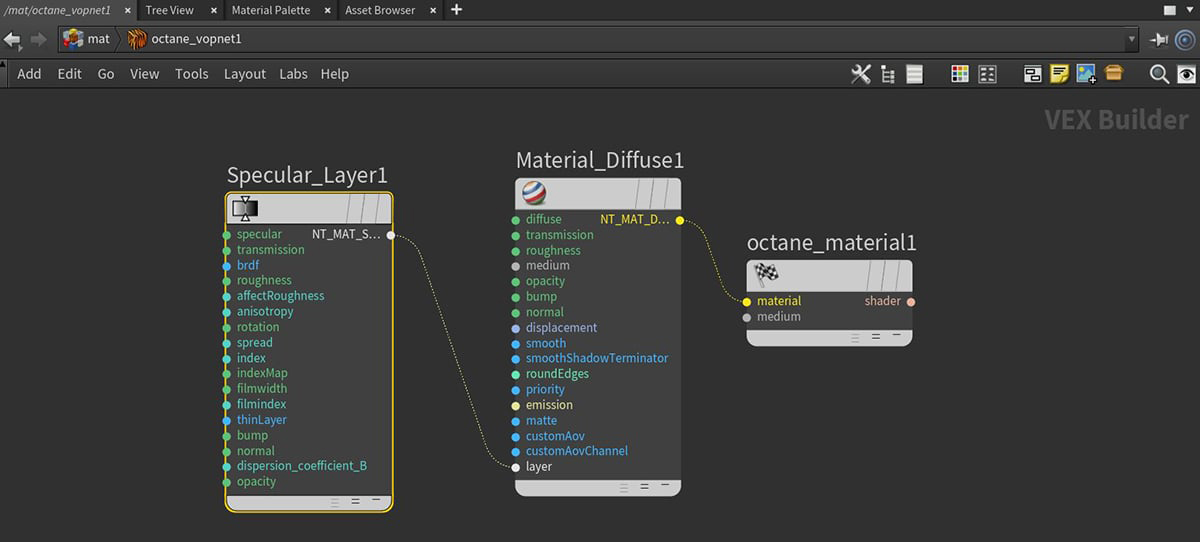
Specular Layer
The Specular layer is used for shiny materials like plastics, or clear materials like glass.
|
|
Specular Layer
|
Figure 1: A Specular Layer mode connected to the Layer pin on a Diffuse Material node
Specular Layer Parameters
Specular - The layer's coating color.
Transmission - The layer's transmission color.
BRDF - The BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) determines the amount of light that a material reflects when light falls on it. For Glossy materials, you can choose from six BRDF models. Specific geometric properties (the micro-facet distribution) of the surface affects each BRDF, which describes the surface's microscopic shape (i.e. micro-facet normals) and scales the brightness of the BRDF's reflections.
Roughness - The layer's roughness.
Affect Roughness - The percentage of roughness affecting subsequent layer roughness.
Anisotropy - The layer's anisotropy. A value of -1 is horizontal, while 1 is vertical. A value of 0 is Isotropic.
Rotation - The rotation of the specular anisotropic reflection.
Spread - Determines the tail spread for the specualr BSDF (Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function) model of the specular layer.
IOR - Controls the Fresnel effect of the reflection and refraction of light when it enters or exits the material. You can find standard values of Index Of Refraction (IOR) by searching the internet. Glass has a value of 1.53, and water has a value of 1.33.
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through the object.
Film Width - Sets the film coating's thickness.
Film IOR - Sets the film coating's Index Of Refraction.
Thin Layer - Makes the layer very thin so it reflects, or goes straight though the layer.
Bump Pin - Creates fine details on the material’s surface using a Procedural or Image texture. When you connect a grayscale texture to this parameter, light areas of the texture give the appearance of protruding bumps, and dark areas create the appearance of indentation. You can adjust the bump map strength by setting the Power or Gamma values on the Image texture node. These attributes are covered in more detail under the Texture Overview section.
Bump Height - Determines the height represented by a normalized value of 1.0 in the bump texture. A vaule of 0 disables the bump map and a negative value will invert the bump map.
Normal Pin - Creates the look of fine detail on the surface. A normal map is a special type of image texture that uses red, green, and blue color values to perturb the normals of the surface at render time, thus giving the appearance of added detail. They can be more accurate than Bump maps, but require specific software such as ZBrush®, Mudbox®, Substance Designer, XnormalTM, or others to generate.
Dispersion Coefficient - The dispersion in Octane is based on Cauchy’s equation which has two terms: A, which is the index of refraction; and B, which is the dispersion coefficient. Increasing the value increases the amount of coloration and dispersion in the object and in caustics.
Layer Opacity - Controls the layer opacity with a slider or greyscale texture.
Compatibility Version The Octane version that the behavior of this node should match.
- Latest (2023.1.1) - Default.
- 2023.1 - The slope of bump maps is calculated slightly differently, making it more sensitive to the orientation of the UV mapping.
- 2022.1 - Legacy behavior for bump map strength is active and bump map height is ignored. This applies in addition to 2023.1 compatibility mode behavior.