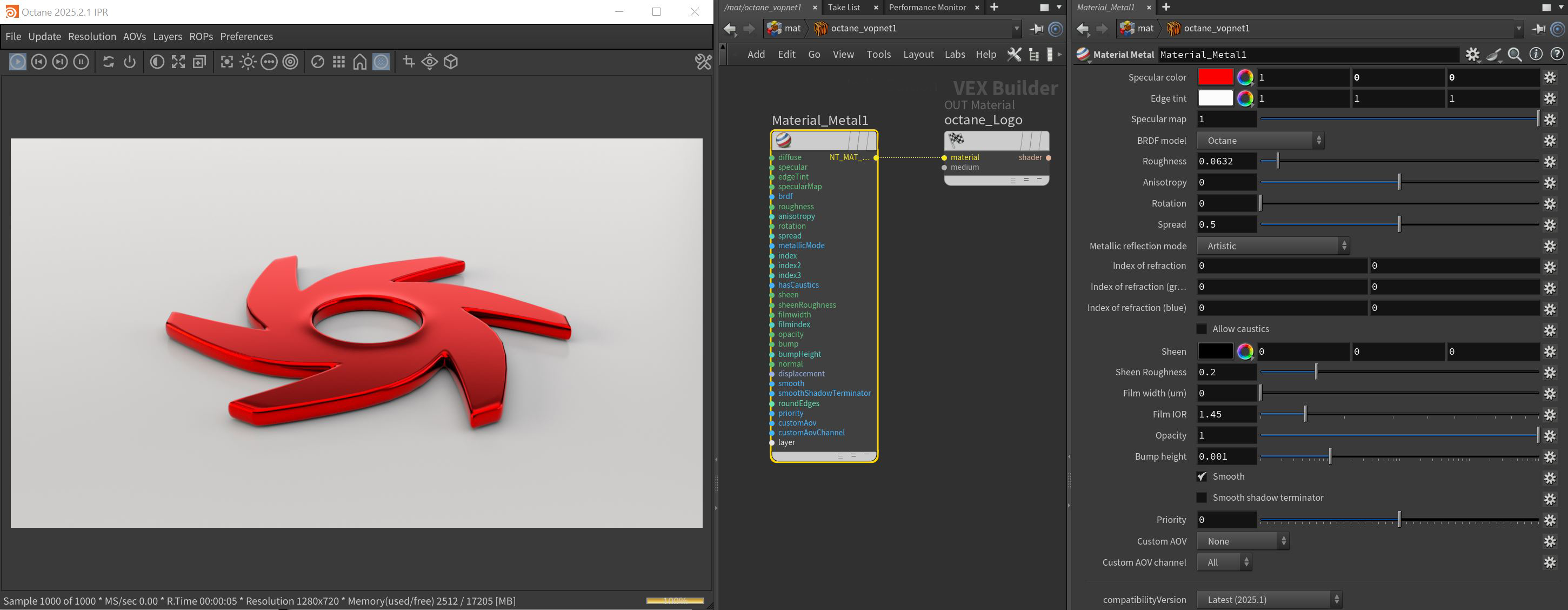
Material Metal
The Metallic material is used to create a more realistic and physically-accurate metal (conductors). The Metallic material is clearly distinguished from the Glossy material both in terms of specular and IOR. In the real world, the reflection properties of metals are very high; and it is determined according to the characteristics of the light reflected back, due to way that metals absorb certain wavelengths of light.(Figure 1).
|
|
Material Metal
|
Figure 1: The Metallic material and it's associated parameters
Metallic Material Parameters
Diffuse Pin - The Diffuse parameter gives the material its color. In computer graphics, this is also referred to as base color or albedo. You can set Diffuse color using the color picker or by connecting a texture (Procedural or Image-based).
Specular Color - Determines the intensity of Specular reflections that appear on the surface. Specular reflections are reflections of light sources on the surface. The Specular input accepts color values and textures. In most cases, specular highlights are white or colorless. However, to simulate metallic surfaces, the Specular color should be a color similar to the Diffuse parameter. Think of the bright yellow-orange highlights seen on the surface of a polished copper kettle.
Edge Tint - The edge of the metal's color, only used in artistic and IOR+color mode.
Specular Map - Mixes the Diffuse and Specular components.
BRDF Model - The BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) determines the amount of light that a material reflects when light falls on it. For Glossy materials, you can choose from six BRDF models. Specific geometric properties (the micro-facet distribution) of the surface affects each BRDF, which describes the surface's microscopic shape (i.e. micro-facet normals) and scales the brightness of the BRDF's reflections.
|
|
BRDF Models
|
Figure 3: Examples of the BRDF types
Roughness - Determines how much the specular reflection spreads across the surface. In CG terminology, this is referred to as reflection blur. A value of 0 simulates a smooth reflective surface, such as a mirror. Increasing the value simulates microfacets in the surface, which causes the reflective highlights to spread. For example, to create the look of worn plastic, increase the Roughness value. This parameter accepts a value or texture map (Procedural or Image-based).
Anisotropy - This attribute adjusts the amount of change in a surface's reflectance, depending on viewing direction.
Rotation - This attribute controls the orientation of the Anisotropy effect.
Spread - Determines the tail spread for the specualr BSDF (Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function) model of the specular layer.
Metallic Reflection Mode - This attribute, along with the IOR attributes, provide options for controlling the Index of Refraction across a surface.
- Artistic: This mode will only use the albedo color.
- IOR + Color: This mode uses the albedo color and further adjusts the brightness of the surface using the IOR.
- RBG IOR: This is the most commonly used mode. It uses the 3 IOR values only and ignores the albedo color altogether.
IOR attributes associated with the Metallic Refl. Modes. Complex-valued Index Of Refraction controlling the Metallic reflection's Fresnel effect, where n = the refractive index, and k = the extinction coefficient. For the following parameters, the left field is the value for "n" and the right field is the value for "k."
- IOR: Complex-valued Index Of Refraction (n-k*i) which controls the Fresnel effect of the specular reflection for metallic materials. For RGB IOR mode, this serves as the Index Of Refraction for the red light (650nm).
- IOR (Green): For RGB IOR mode, this is the Index Of Refraction for the green light (550nm).
- IOR (Blue): For RGB IOR mode, this is the Index Of Refraction for the blue light (450nm).
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through the object.
Sheen - This attribute provides control for applying a soft luster to a surface.
Sheen Roughness - Determines how much the sheen spreads across the surface, similar to the Roughness control for the specular characteristics.
Film Width - This controls the thickness of the optical, thin film on the material. This is useful in creating rainbow or oil slick effects.
Film IOR - This controls the Index Of Refraction of the thin film.
Opacity - Determines what parts of the surface are visible in the render. Dark values indicate transparent areas, and light values determine opaque areas. Values in between light and dark create the look of semi-transparent areas. You can lower the Opacity value to fade the overall visibility of an object, or use a texture map to vary the opacity across the surface. For example, if you wanted to make a simple polygon plane look like a leaf, you would connect a black-and-white image of the leaf’s silhouette to the Opacity channel.
Bump Pin - Creates fine details on the material’s surface using a Procedural or Image texture. When you connect a grayscale texture to this parameter, light areas of the texture give the appearance of protruding bumps, and dark areas create the appearance of indentation. You can adjust the strength of the Bump map by adjusting the Power or Gamma values on the Image texture node. These attributes are covered in more detail under the Texture Overview category.
Normal Pin - The Normal parameter also creates fine details on the surface. A Normal map is a special type of image texture that uses red, green, and blue color values to perturb the normals of the surface at render time, thus giving the appearance of added detail. They can be more accurate than Bump maps, but require specific software, such as ZBrush®, Mudbox®, Substance Designer, XnormalTM, or others to generate.
Displacement Pin - Adjusts the height of the vertices of a surface at render time using a texture map. Displacement maps differs from bump or normal maps in that the geometry is altered by the texture, as opposed to just creating the appearance of detail. Displacement mapping is more complex than using a bump or normal map, and the results can be more realistic, in particular along the surface's silhouette. Displacement mapping is covered in more detail under the Displacement Overview category.
Smooth - The Smooth parameter smooths the transition between surface normals. If you disable this option, the edges between the polygons of the surface are sharp, giving the surface a faceted look.
Smooth Shadow Terminator - If enabled, self-intersecting shadows for low polygon objects is smoothed according to the polygon's curvature.
Round Edges Pin - This creates a shader effect at render time that rounds the sharp edges of objects without modifying and reloading the geometry. Higher values will round the edges more. This is useful to bevel hard edges during render time, like when using low-polygon models. See the Round Edges section for more information.
Priority - Used to resolve the ambiguity in overlapping surfaces, the surface priority control allows artists to control the order of preference for surfaces. A higher number suggests a higher priority for the surface material, which means it is preferred over a lower priority surface material if a ray enters a higher priority surface and then intersects a lower priority surface while inside the higher priority surface medium.
Custom AOV - Writes a mask to the specified custom AOV.
Custom AOV Channel - Determines whether the custom AOV is written to a specific color channel (R, G, or B) or to all the color channels.
Layer Pin - Adds a Material Layer above the base material. See the Material Layers topic in this manual for more details.
Compatibility Version The Octane version that the behavior of this node should match.
- Latest (2025.1) - Default.
- 2023.1.1 - In artisitc metallic mode, a real-valued IOR is used instead of a falloff.
- 2023.1 - The slope of bump maps is calculated slightly differently, making it more sensitive to the orientation of the UV mapping.
- 2022.1 - Legacy behavior for bump map strength is active and bump map height is ignored. This applies in addition to 2023.1 compatibility mode behavior.