Vectron
Vectron (Vector-Polygon) is a Procedural uber primitive, providing infinite procedurally-generated scenes, volumes, and geometry, which bypass Meshes and Volumes. Vectrons have zero-memory footprints, driving increased efficiencies when compared to meshes or volumes generated on CPUs. This enables Vectron to provide procedurally-generated scenes on the GPU without using VRAM. Vectron provides tools in your workflow, and it helps render triangle-free geometry with the OctaneRender® built-in OSL (Open Shader Language) support and OSL texture shaders.
Procedural primitives using OSL vector geometry nodes let you create complex shapes, surfaces, volumes, warps, operators, and effects. By vectorizing meshes and volumes into Vectron objects, you can manipulate Vectron nodes in new ways. Examples include: spheres, strands, sound waves, infinite planes, liquids, clouds, oceans, flow field, and more.
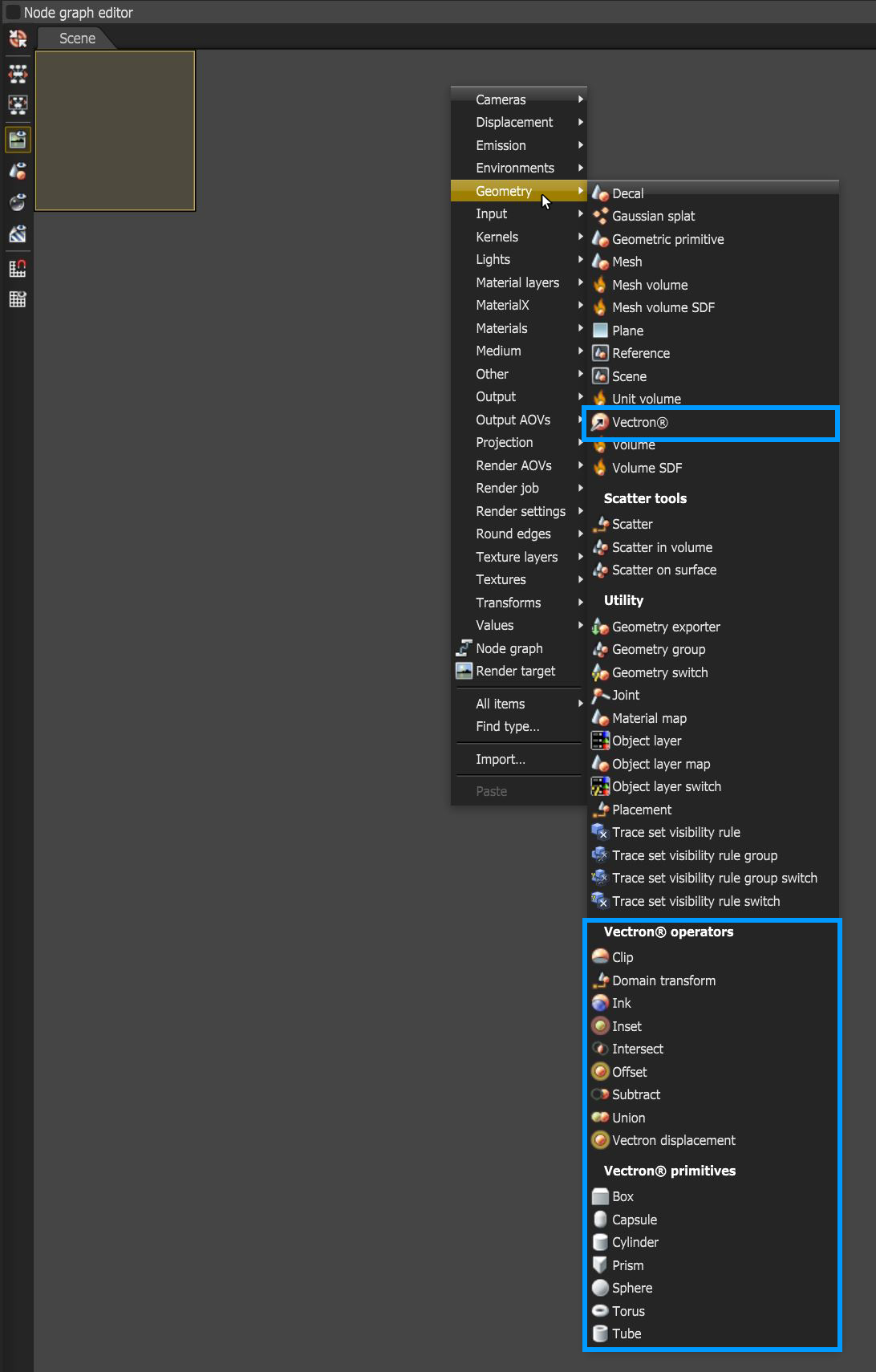
To start using the Vectron primitives, click on Geometry , then select any number of the Vectron nodes to create a Vectron asset in the Graph Editor (Figure 1).
|
|
vectron nodes
|
Figure 1: Accessing the Vectron nodes in the Node Graph Editor window
The Vectron Operators allow the Procedural OSL geometry node graph's workflow to follow the same structure as OSL texture node graphs with 4D mixing, blending, and boundary operator nodes for skinning, Metaballs, and procedural resurfacing. Boolean operations are also enabled in Vectrons.
The initial Vectron node generates a Sphere object with four default pins:
- Geometry Material - Material for the Vectron object.
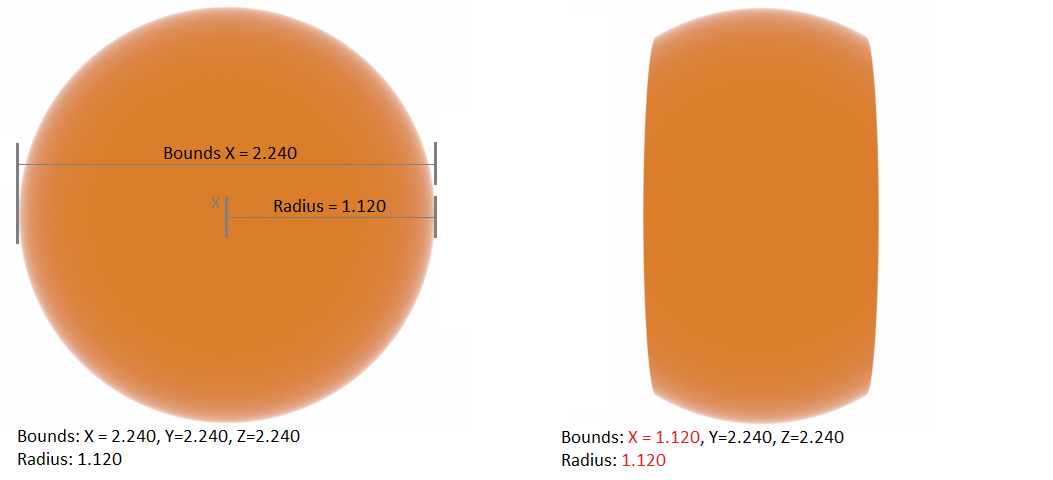
- Bounds - Bounds of the Procedural geometry in meters. These affect the geometry's shape, since they calculate pixels that can appear within those bounds in the XYZ plane. Bounds values that are less than the radius are cut off (Figure 2).
- Radius - The Vectron's radius.
- Translate - The Vectron object's translation.
|
|
Bound Values
|
Figure 2: Bound values
The Vectron node has an OSL script with the following lines of code:
#include <octane-oslintrin.h>
shader Vectron(
float radius = 1 [[float min = 0, float slidermax = 1e4, float sliderexponent = 4]],
vector translate = 0,
output _sdf out = _SDFDEF)
{
out.dist = distance(P, translate) - radius;
}
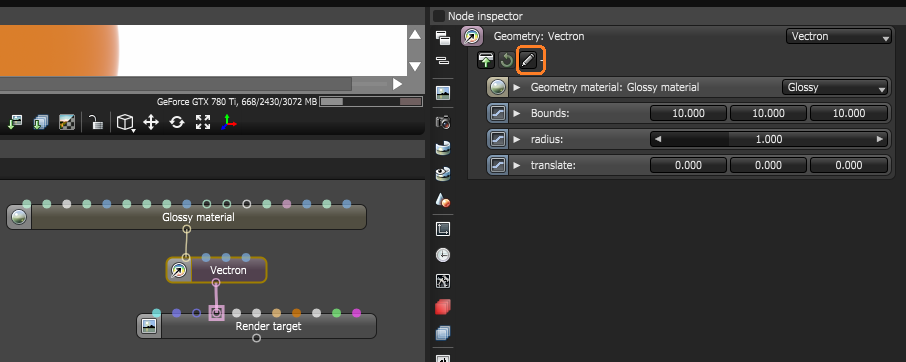
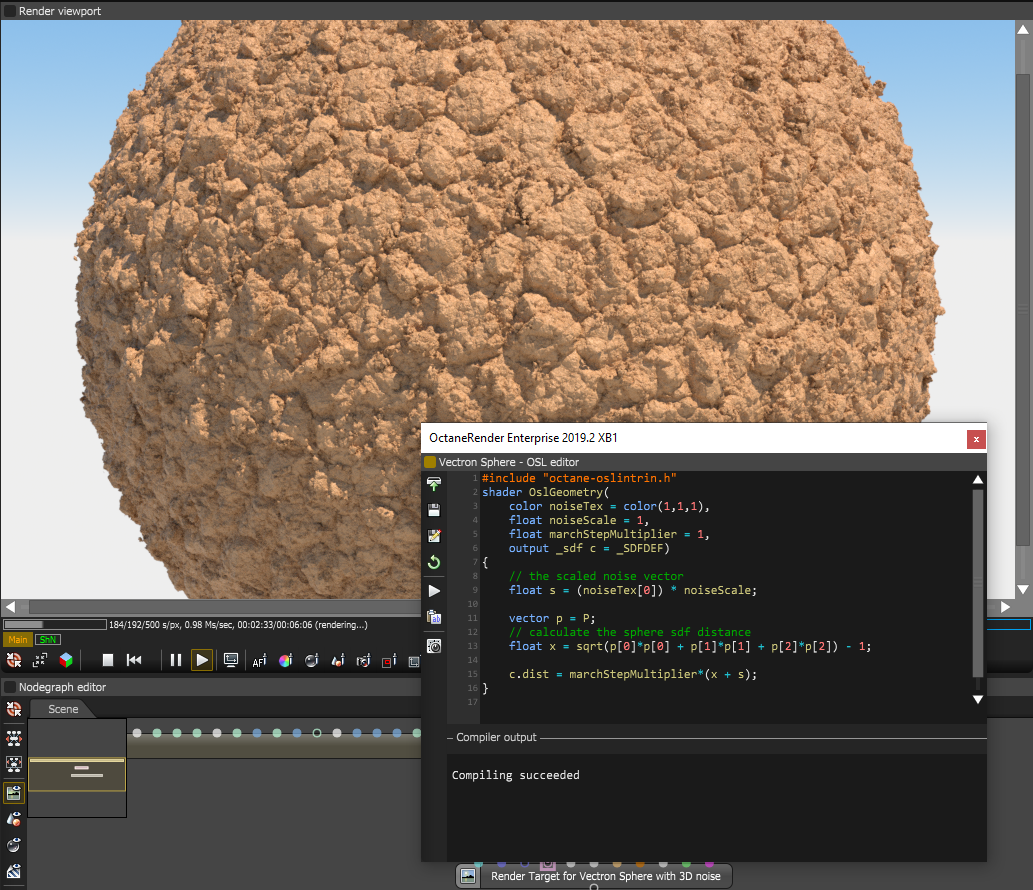
To edit the OSL script, select the node from the Nodegraph Editor window, and then click the Open In Editor icon in the Node Inspector window (Figure 3). Then recompile the script to view the new shape of the Vectron object (Figure 4), and manipulate the new node's attributes generated by the script.
|
|
Object Layer Color
|
Figure 3: The Open In Editor icon
Figure 4: The Compile icon
|
|
OSL Script
|
Figure 5: A Vectron node with a modified OSL script
You can download the example of the Vectron node in Figure 5 to see it in action here: VectronSphere.orbx
You can also download a collection of Vectron examples here: Fun_With_Vectron (4).orbx
|
NOTE OctaneRender includes some basic operators under Geometry > Vectron, which can subtract and merge Vectron items |
There are also two additional nodes for use with Vectron objects. The Vectron Subtract and Vectron Union nodes can be used to place boolean operations onto two or more Vectron objects.
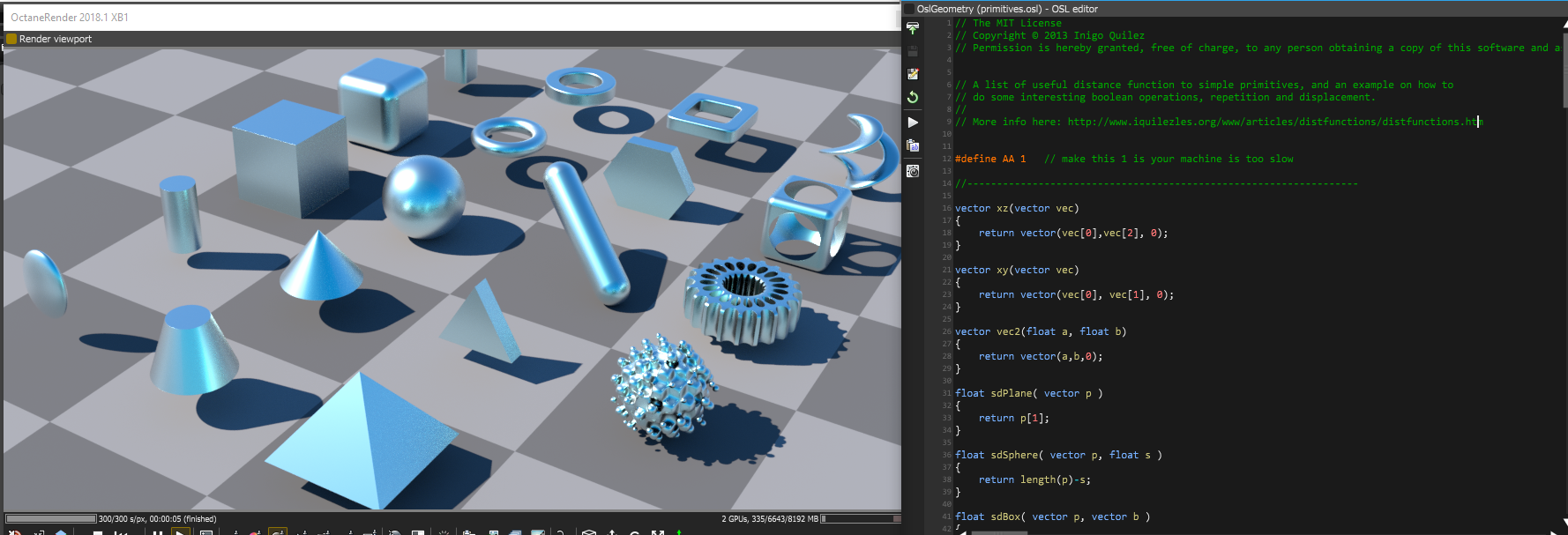
Applications Of The Vectron Primitive And SDF Surfaces
OctaneRender can render defined SDF surfaces using OSL shaders without the need to convert them to a Mesh first. You can change the surfaces with input variables without having to wait for any processing, and you can also create networks of set operations such as unions, subtractions, intersection, and their smooth variants - none of which need to be meshed before rendering, and all compiled using OSL.
|
|
Input Variables
|
Figure 6: Example of OSL shaders with input variables to manipulate the shape of Vectron objects
|
|
Vectron Set Operations
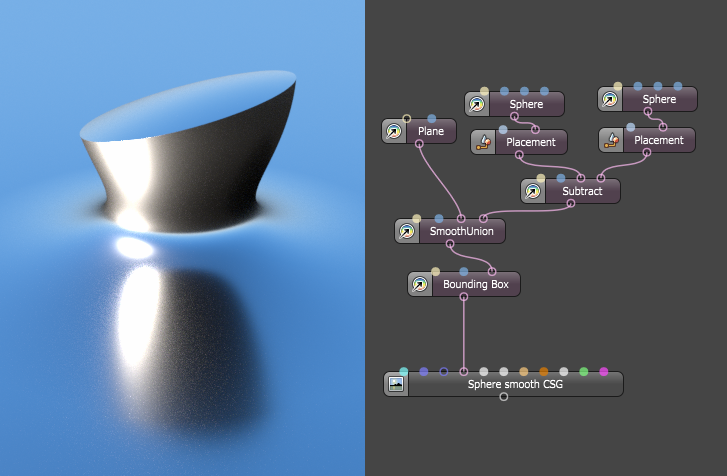
|
Figure 7: Example of a more complex network of set operations (unions, subtractions, intersection, and their smooth variants)
|
|
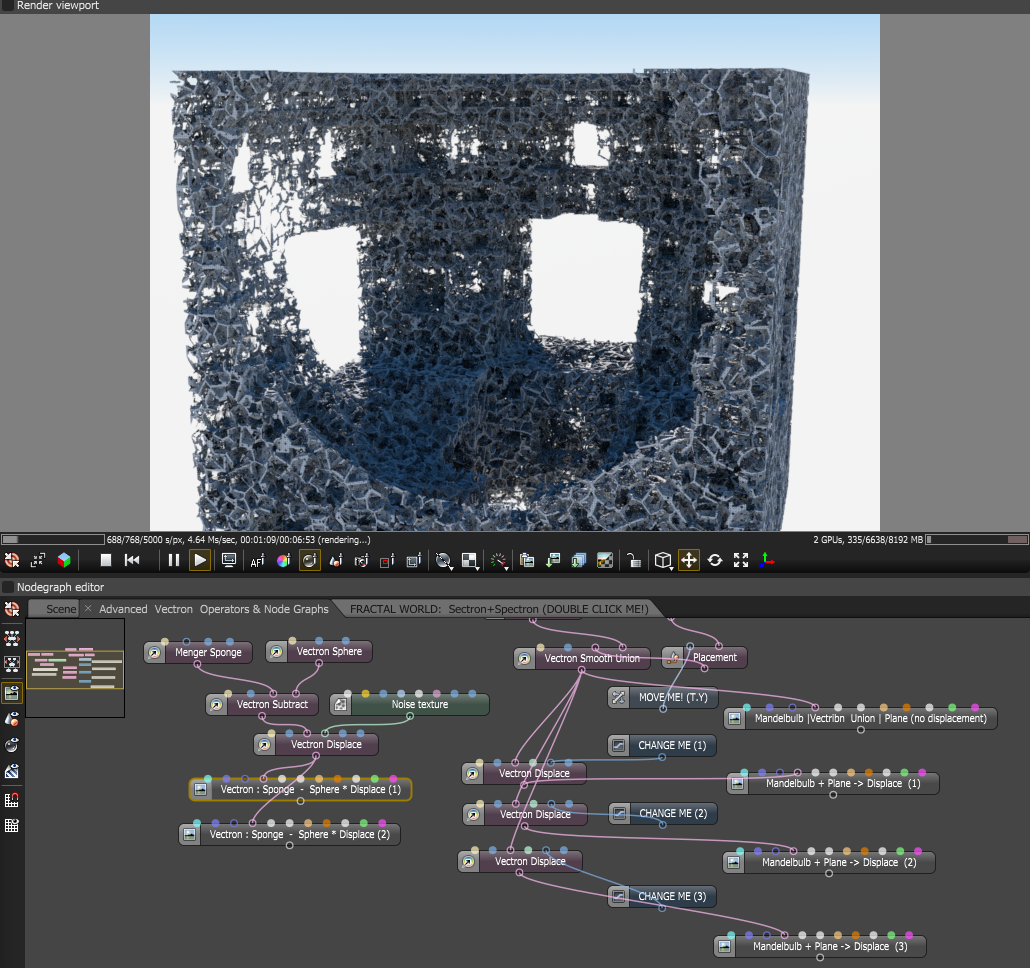
Shadertoy Samples
|
Figure 8: Samples from shadertoy being fed into the OSL vectron geometry node
|
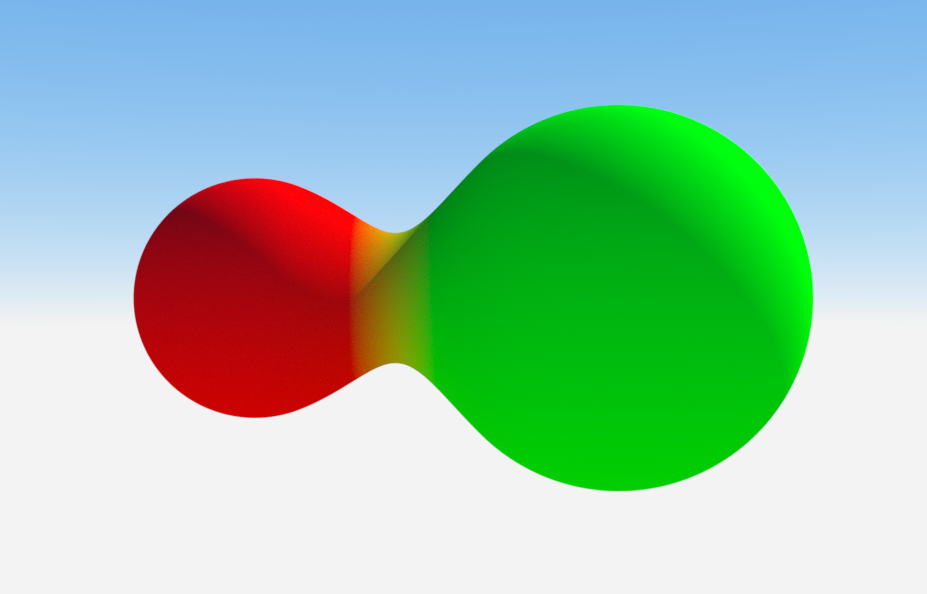
|
SDF Smooth Union
|
Figure 9: An example of an SDF smooth union with a Mix material implemented as part of the union