Photon Tracing Kernel
The Photon Tracing kernel is designed to render caustics approximately 1000x faster and with less noise than the existing PMC kernel using a novel GPU photon mapping and path guide approach. (figure 1).
|
|
Photon Tracing Kernel
|
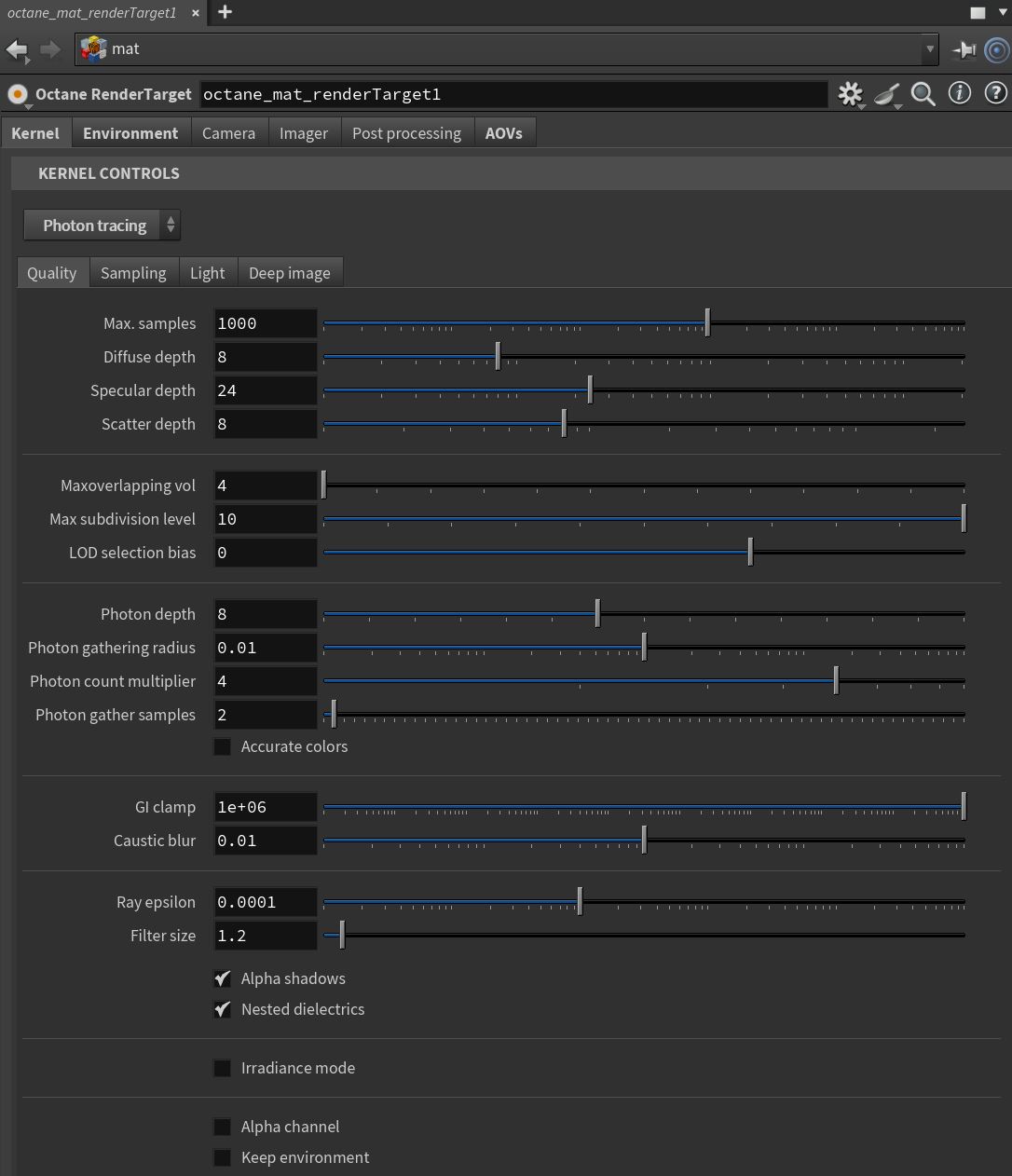
Figure 1: The Photon Tracing kernel parameters
Photon Tracing Parameters
Quality Tab
Max. Samples - Sets the maximum number of samples per pixel before the rendering process stops. Higher values result in cleaner renders.
Diffuse Depth - The maximum number of times a ray can bounce off of a diffuse or very rough surface. Higher values mean higher render times, but more realistic results. For outdoor renders, a good setting is around 4. For lighting interiors with natural light from the sun and sky, you need settings of 8 or higher. In the real world, the maximum diffuse bounces would not exceed 16. It is possible to use a value higher than 16, but this is not necessary.
Specular Depth - Controls the number of times a ray refracts before dying. Higher values lead to higher render times, but more color bleeding and more details in transparent materials. Low values introduce artifacts or turn some refractions into pure black.
Scatter Depth - The maximum path depth that allows scattering.
Max Overlapping Volumes - Determines how much space to allocate for overlapping volumes. Ray marching is faster with lo values but it can cause artifacts where many volumes intersect.
Max Subdivision Level - The maximum subdivision level applied on the scene's geometry. A value of 0 disables subdivision.
LOD Selection Bias - Used in conjunction with Meshlets. This setting influences the LOD data selection. Decreasing this value will make the loaded LOD data cruder and increasing this value will make the loaded LOD data finer.
Photon Depth - Determines the maximum depth for the photons.
Photon Gathering Radius - The maximum radius where photons can contribute.
Photon Count Multiplier - Approximate ratio between photons and camera rays.
Photon Gather Samples - Determines the maximum amount of photon gather samples per pixel between photon tracing passes. This is similar to the Max. Tile Samples but it also affects the quality of the caustics rendered. Higher values give more samples per second at the expense of caustic quality.
Accurate Colors - If enabled, the colors will be more accurate but noise will converge more slowly.
GI Clamp - Clamps the contribution for each path to the specified value. By reducing the GI Clamp value, you can reduce the amount of fireflies caused by sparse but very strong contributing paths. Reducing this value reduces noise by removing energy.
Caustic Blur - Reduces noise in caustic light patterns. High values result in soft caustic patterns.
Ray Epsilon - The distance between the geometry and the light ray when calculating ray intersections for lighting and shadowing. Larger values push rays away from the geometry surface. Smaller values are more accurate, but cause artifacts on large or distant objects. Ray Epsilon is similar to ray tracing bias in other rendering engines. Adjust Ray Epsilon to reduce artifacts in large-scale scenes.
Filter Size - Sets the filter size in terms of pixels. This can improve aliasing artifacts in the render. However, if the filter is set too high, the image becomes blurry.
Alpha Shadows - Allows any object with transparency (Specular materials, materials with Opacity settings and Alpha Channels) to cast a shadow instead of behaving as a solid object.
Nested Dielectrics - If disabled, the surface IORs are not tracked and surface priorities are ignored.
Irradiance Mode - This renders the first surface as a white Diffuse material. Irradiance Mode works similar to Clay Mode, but it applies to the first bounce. It disables the Bump channel and makes samples that are blocked by back faces transparent.
Alpha Channel - This option removes the background and renders it as transparent (zero alpha). This can be useful if you want to composite the render over another image and don't want the background to be present.
Keep Environment - This option works in conjunction with the Alpha Channel setting. It allows the background to render with zero alpha, but is still visible in the final render. This allows even further flexibility in compositing images.
Sampling Tab
Adaptive Sampling - When enabled, the kernel stops rendering clean areas of the image and focuses on noisy areas.
If Adaptive Sampling is activated, the follow parameters are available:
- Noise Threshold - Specifies the smallest relative noise level. When the noise estimate of a pixel is less than this value, sampling switches off for this pixel. Good values are in the range of 0.01 - 0.03. The default is 0.02, which is pretty clean.
- Min. Adaptive Samples - Specifies the minimum number of samples to calculate before adaptive sampling kicks in. A pixel's noise estimate has a large initial error. The higher you set the noise threshold, the higher you should also set this parameter to avoid artifacts.
- Expected Exposure - This value should be close to the same value as the image's exposure, or 0 (the default value) to ignore these settings. Adaptive sampling uses this parameter to determine what pixels are bright and dark, which depends on the Octane Imager's exposure setting. If the value is not 0, adaptive sampling adjusts the noise estimate of the image's very dark areas. It also increases the Min. Adaptive Samples limit for very dark areas, because very dark areas tend to find irregular paths to light sources, resulting in over-optimistic noise estimates.
- Pixel Grouping - Specifies the number of pixels handled together. When all of the pixels in a group reach the noise level, sampling stops for all of these pixels.
Exploration Strength - The higher this value, the more the photon sampling is influenced by which photons are actually gathered.
Path Termination Power - High values increase render speed, but also increase noise in dark areas.
Direct Light Rays - Specifies the number of direct light rays traced for every sample. This amount is used after camera rays and after smooth specular reflections or transmission.
Coherent Ratio - Increasing this value increases the render speed, but it also introduces low-frequency noise (aka blotches), which requires a few hundred or a few thousand samples per pixel to go away, depending on the scene.
Static Noise - When enabled, the noise is static, so it doesn’t change between frames.
Parallel Samples - This controls how many samples are calculated in parallel. If this is set to a small value, OctaneRender® requires less memory to store the sample's state, but rendering is slower. If this is set to a high value, then OctaneRender requires more graphics memory, and rendering becomes faster. The change in performance depends on the scene and the GPU architecture.
Max Tile Samples - This controls the number of samples per pixel that OctaneRender will render until it takes the result and stores it in the film buffer. Higher values mean that results arrive less often in the film buffer.
Minimize Net Traffic - If enabled, OctaneRender distributes the same tile to the net Render Nodes until the tile reaches the max samples/pixel, and then OctaneRender distributes the next tile to Render Nodes. This option doesn't affect work done by local GPUs. A Render Node can merge all of its results into the same cached tile until the Primary Render Node switches to a different tile.
Light Tab
AI Light - Enables AI Lights. AI Light functionality learns from the scene, and the rendering becomes more efficient as more samples are rendered. When used with Adaptive Sampling, AI Light becomes even more effective, as it learns pixel and light importance in a scene and no longer samples some pixels.
AI Light Update - Available when AI Light is activated, enables dynamic light update.
Light IDs Action - This parameter determines whether the Light ID's action enables or disables lights with matching Light Pass ID numbers.
Light IDs - This is the ID of the light pass that captures the emitter's contribution. For more information about the Light IDs and their attributes, see the Light Passes topic in this manual.
Light Linking Invert - This option inverts the light linking behavior for selected light IDs.
White Light Spectrum - Controls the appearance of colors produced by spectral emitters (daylight, environment, black body).This determines the spectrum that will produce white (before white balance) in the final image.
- D65 - Adapts to a reasonable daylight "white" color.
- Legacy/Flat - Preserves the appearance of old projects (spectral emitters will appear more blue)
Toon Shadow Ambient - This is the ambient modifier of Toon Shadowing.
Deep Image Rollout
Deep Image - Enables rendering deep pixel images used for deep image compositing.
Deep Render AOVs - Includes render passes for deep image pixels.
Maximum Depth Samples - Used when Deep Image Rendering is enabled. It sets the maximum number of depth samples per pixel. For more details, read the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.
Depth Tolerance - Used when Deep Image Rendering is enabled. OctaneRender merges depth samples whose relative depth difference falls below this tolerance value. For more information, see the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.