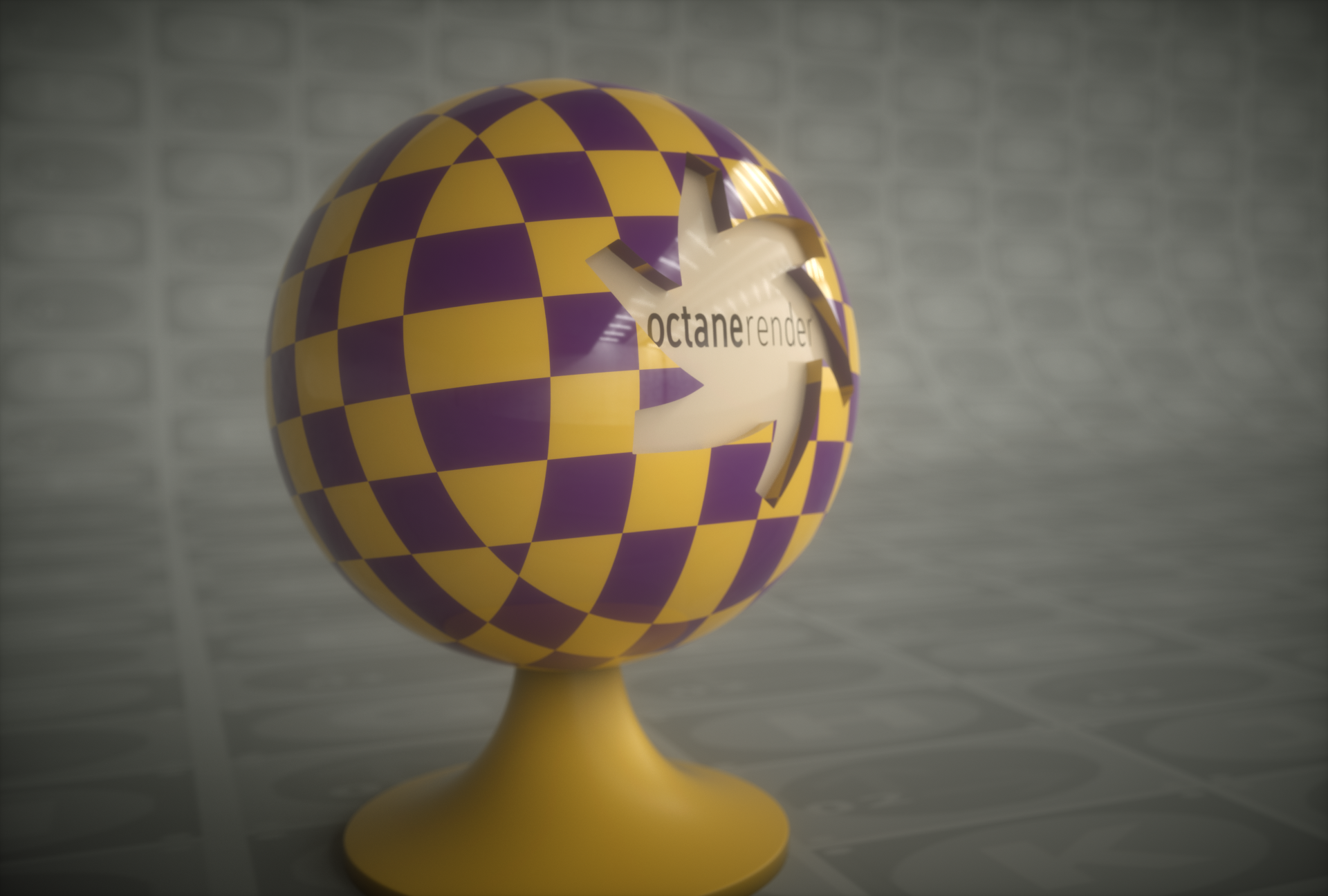
Projection
The Projection node is used for adjusting the UV mapping coordinates of a texture, and is often used with the Transform node.
|
NOTE When Octane projections other than MeshUV are used the Cinema 4D projection will be ignored. |
|
|
projection
|
HOW TO USE
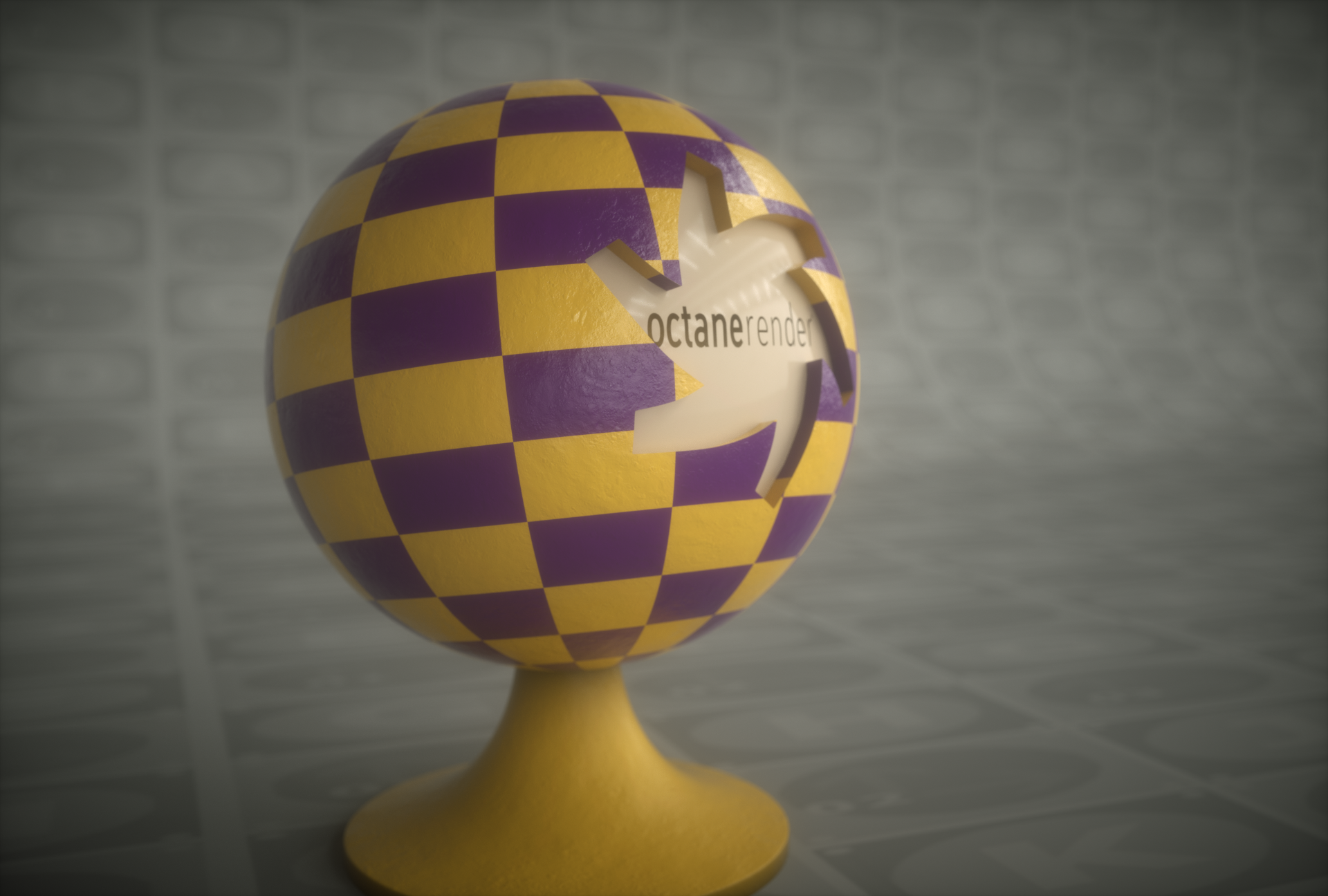
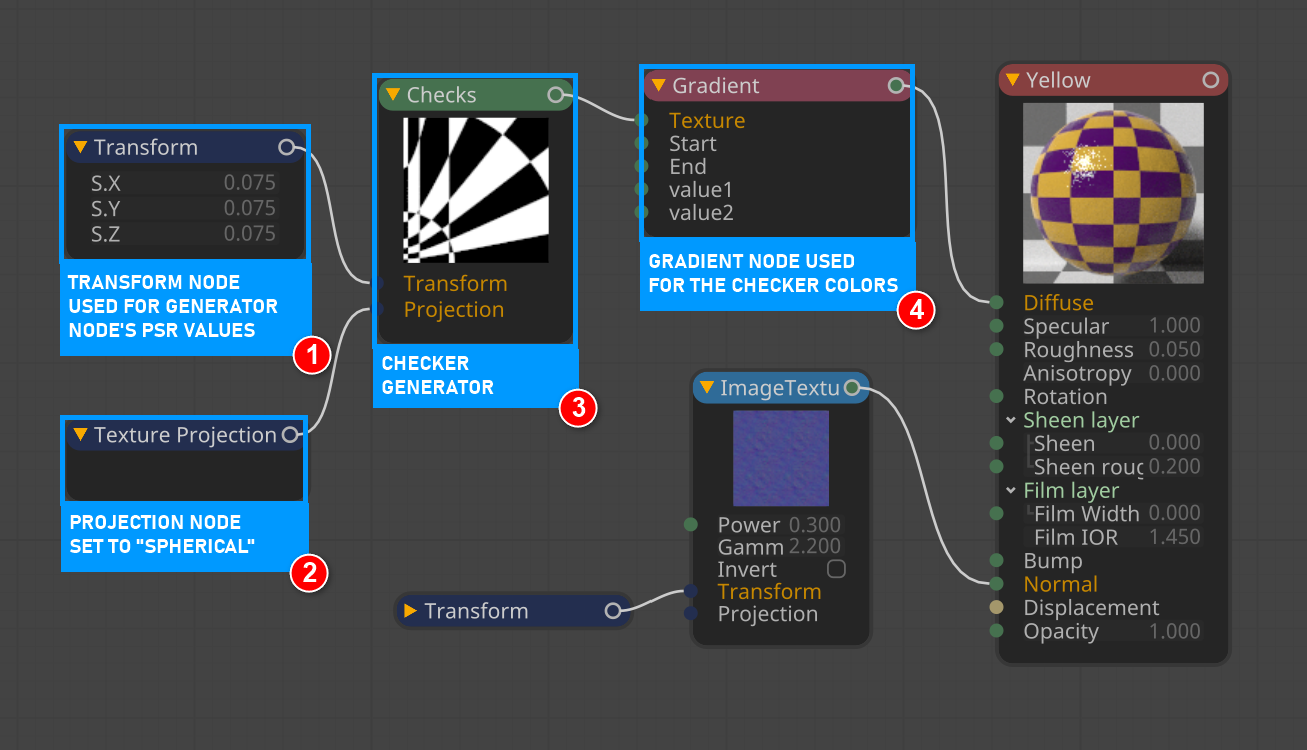
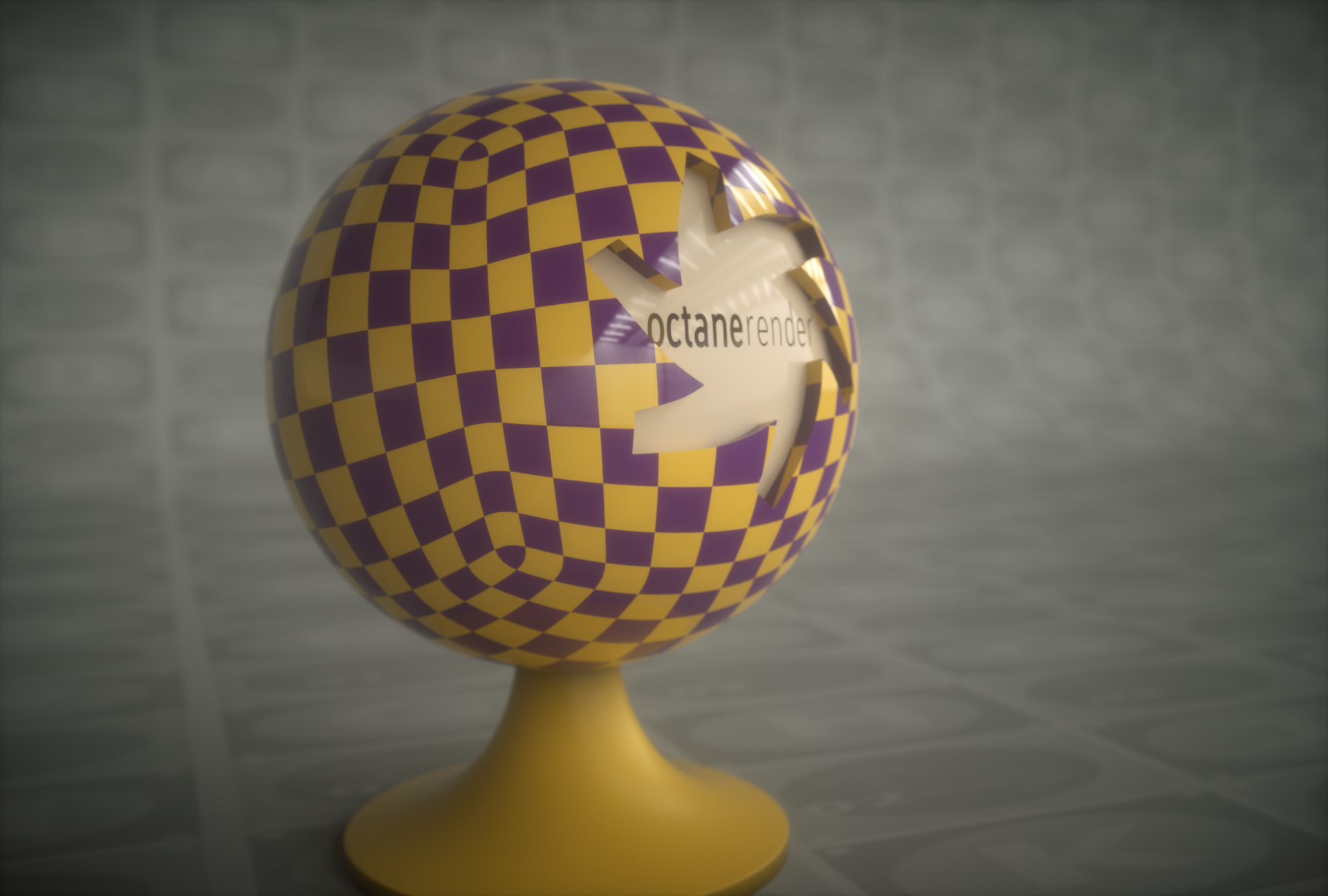
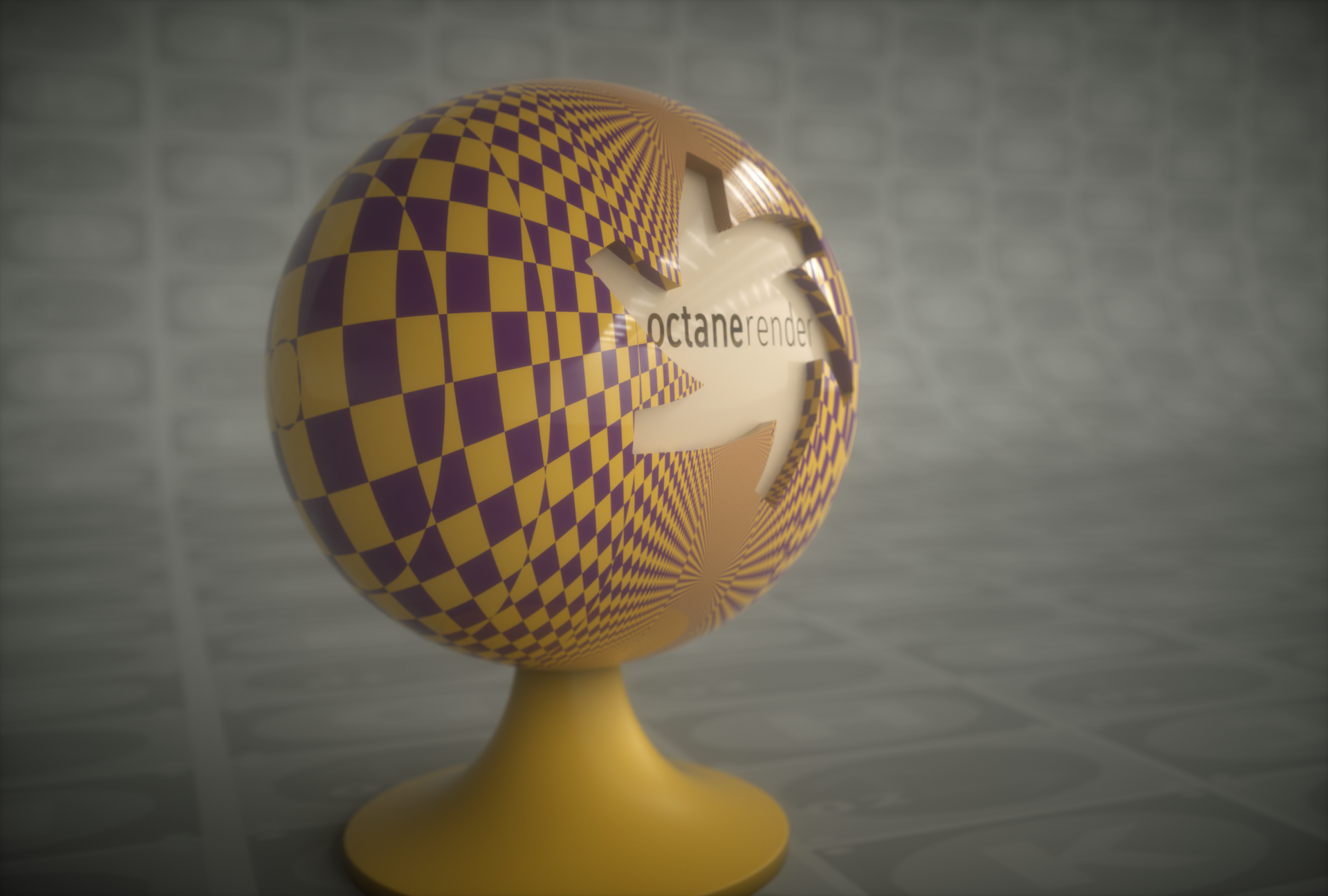
Open the Node Editor and prepare the setup as you see in the image below. As you can see, the Transform and Projection nodes are connected to the Checks node after the Checks texture. The node is assigned to the diffuse channel of the material. Spherical was used because the example object is a sphere. Colors were created using the Gradient Texture node, since Checks generator does not have a color parameter. Detailed descriptions of the other nodes used in this example in the relevant sections following.
|
|
projection node setup
|
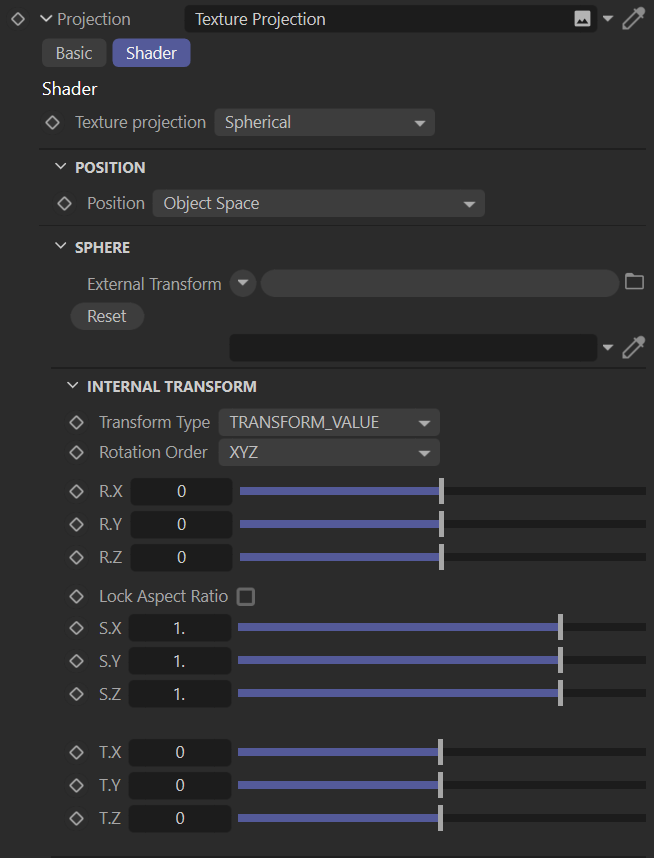
Projection Settings
Texture Projection
This option contains the various texture projection types available in OctaneRender. Pick the projection type that best matches the topology of the mesh:
Box
Box projection provides a quick way to map a texture on any object without too much distortion, however the seams between the projection planes of the box may be visible in the render depending on the shape of the surface.
|
|
box projection
|
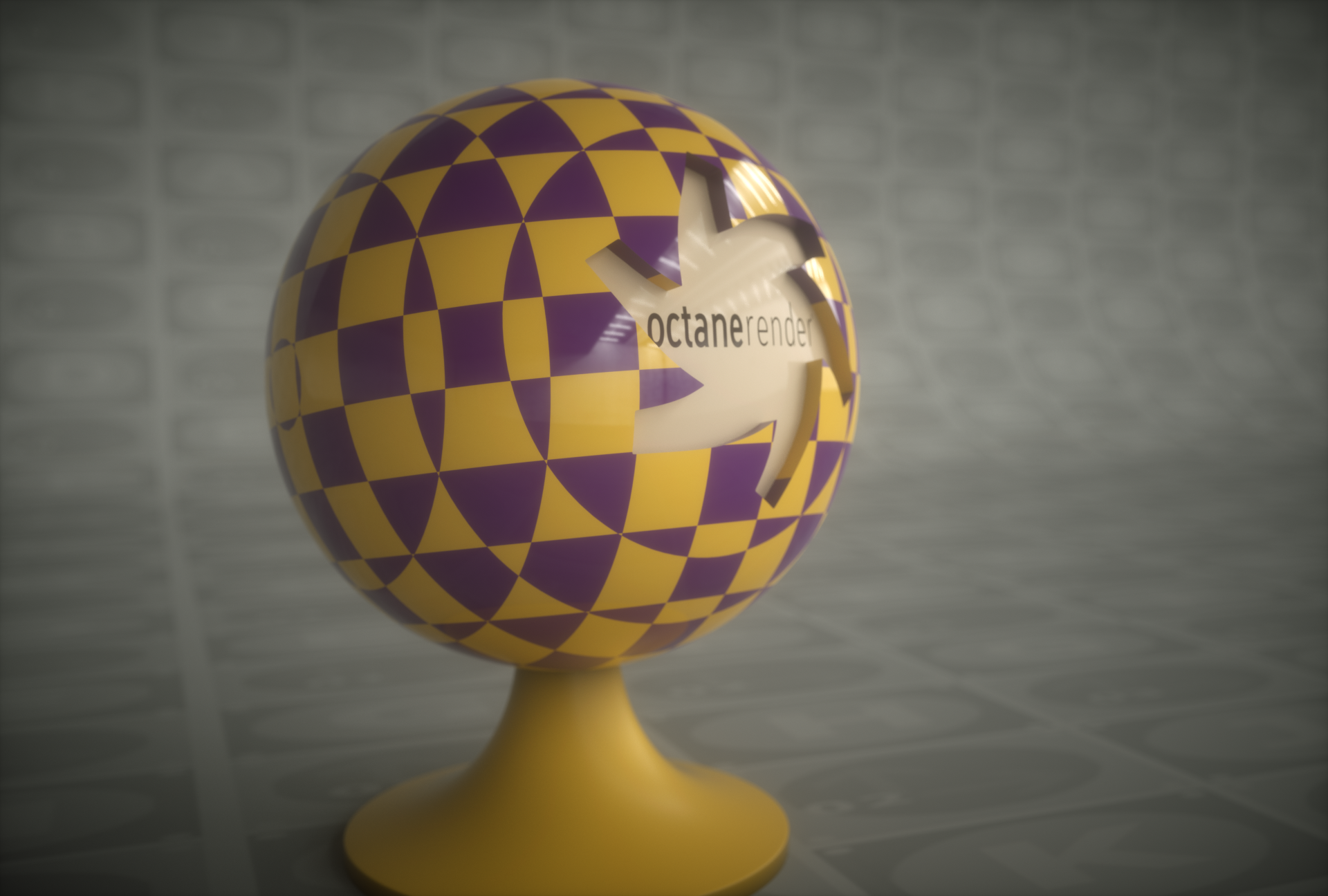
Cylindrical
Cylindrical projection wraps texture maps on a surface with a cylindrical shape. Cylindrical projection provides a quick way to map a texture on roughly cylindrical shaped surfaces without too much distortion, however the seams of the texture may be visible in the render depending on the shape of the surface.
|
|
cylindrical projection
|
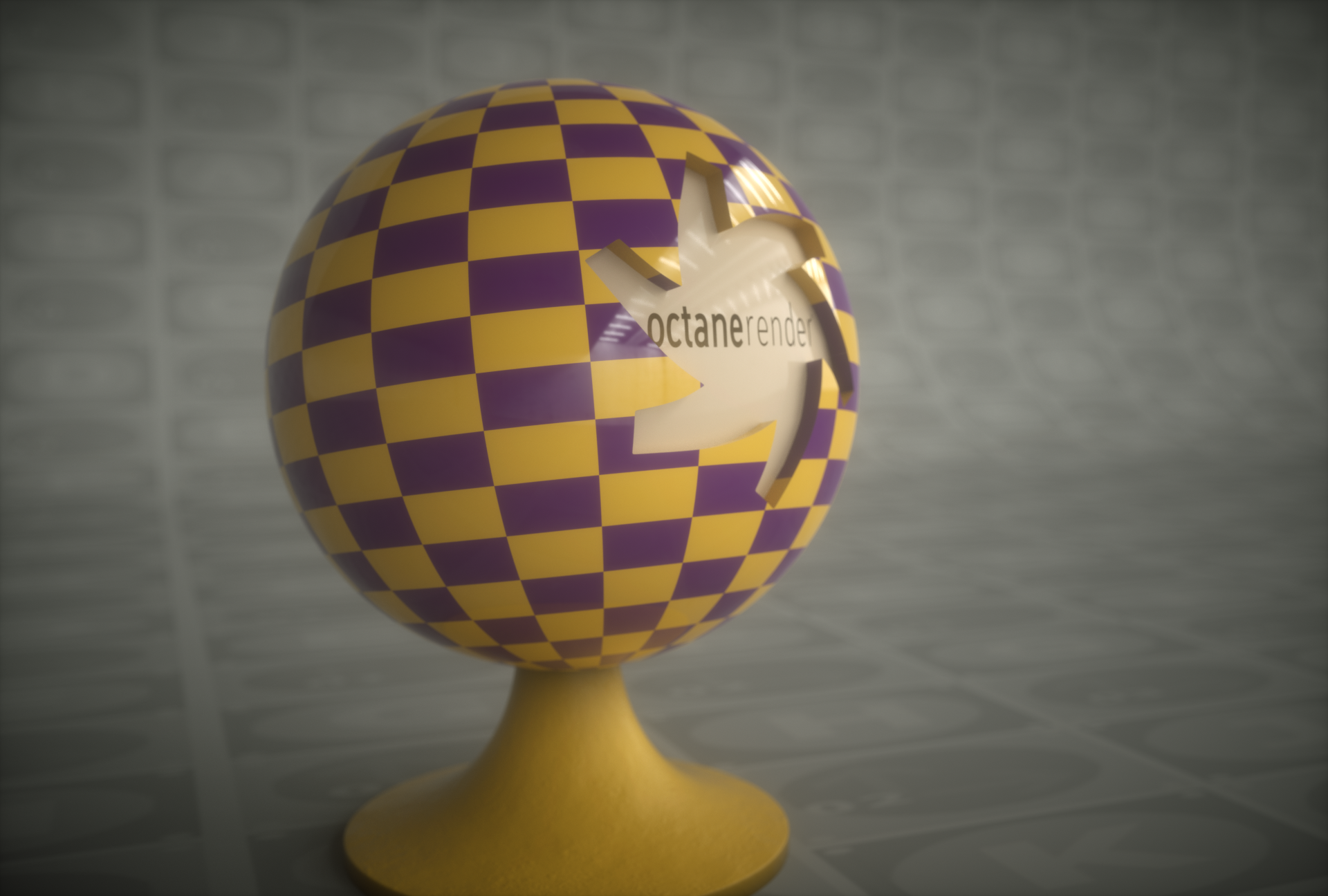
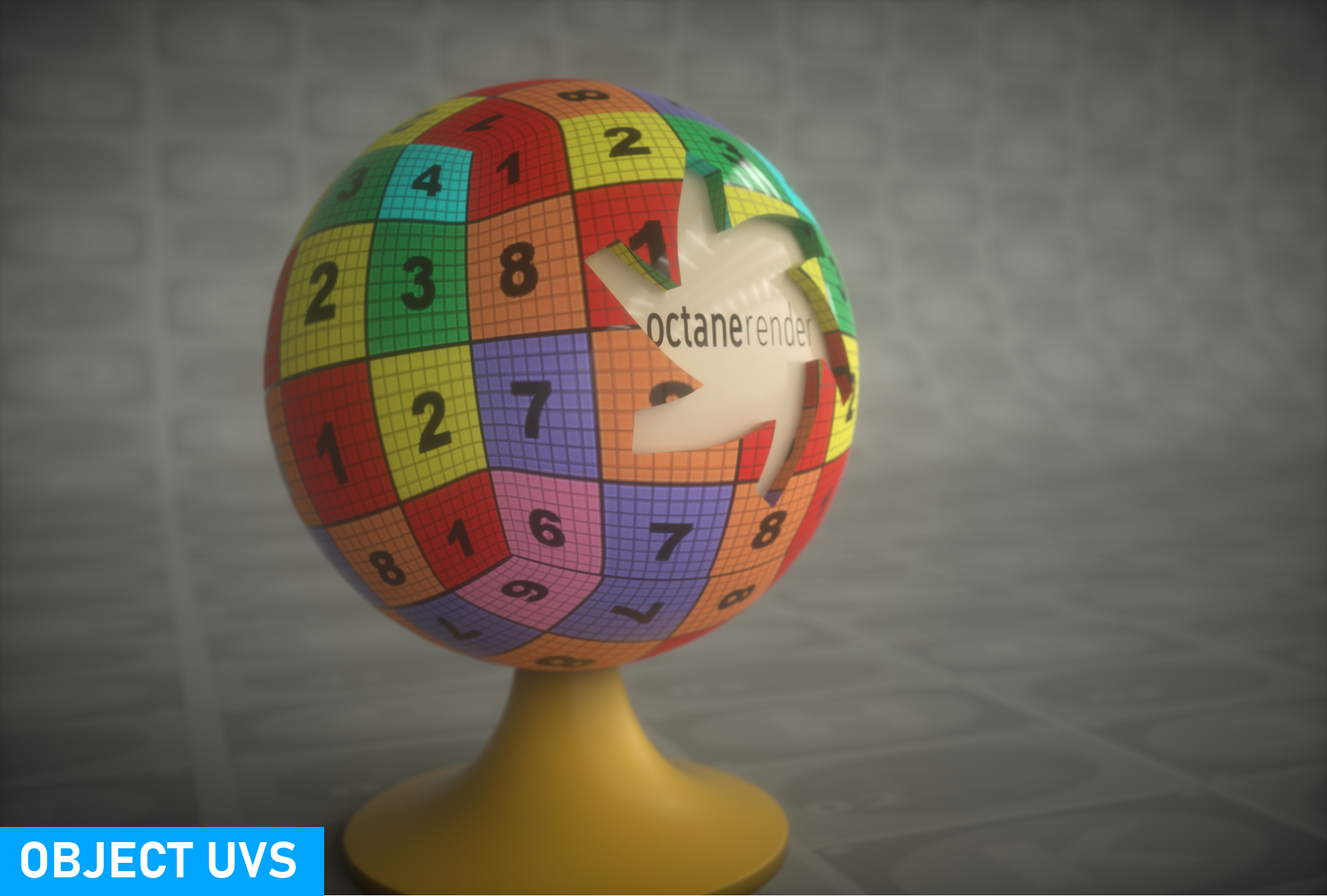
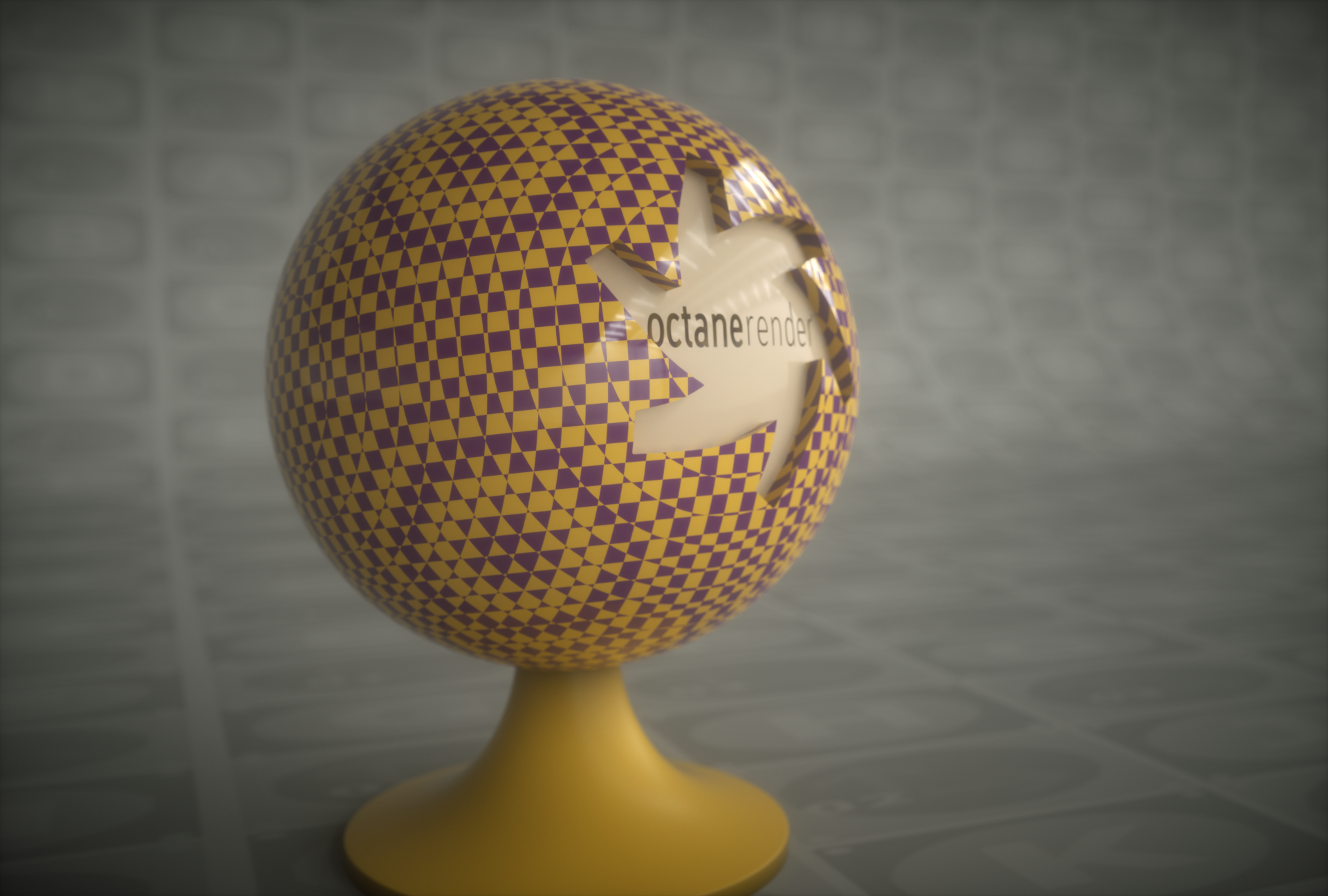
Mesh UV
The Mesh UV projection node uses the mesh's UV coordinates to map the texture to the surface, if present. This is the default behavior for all textures, so in many cases its unnecessary to use a projection node when mapping a texture based on the mesh's UVs. The UV set is reserved for future updates.
|
|
mesh uv projection
|
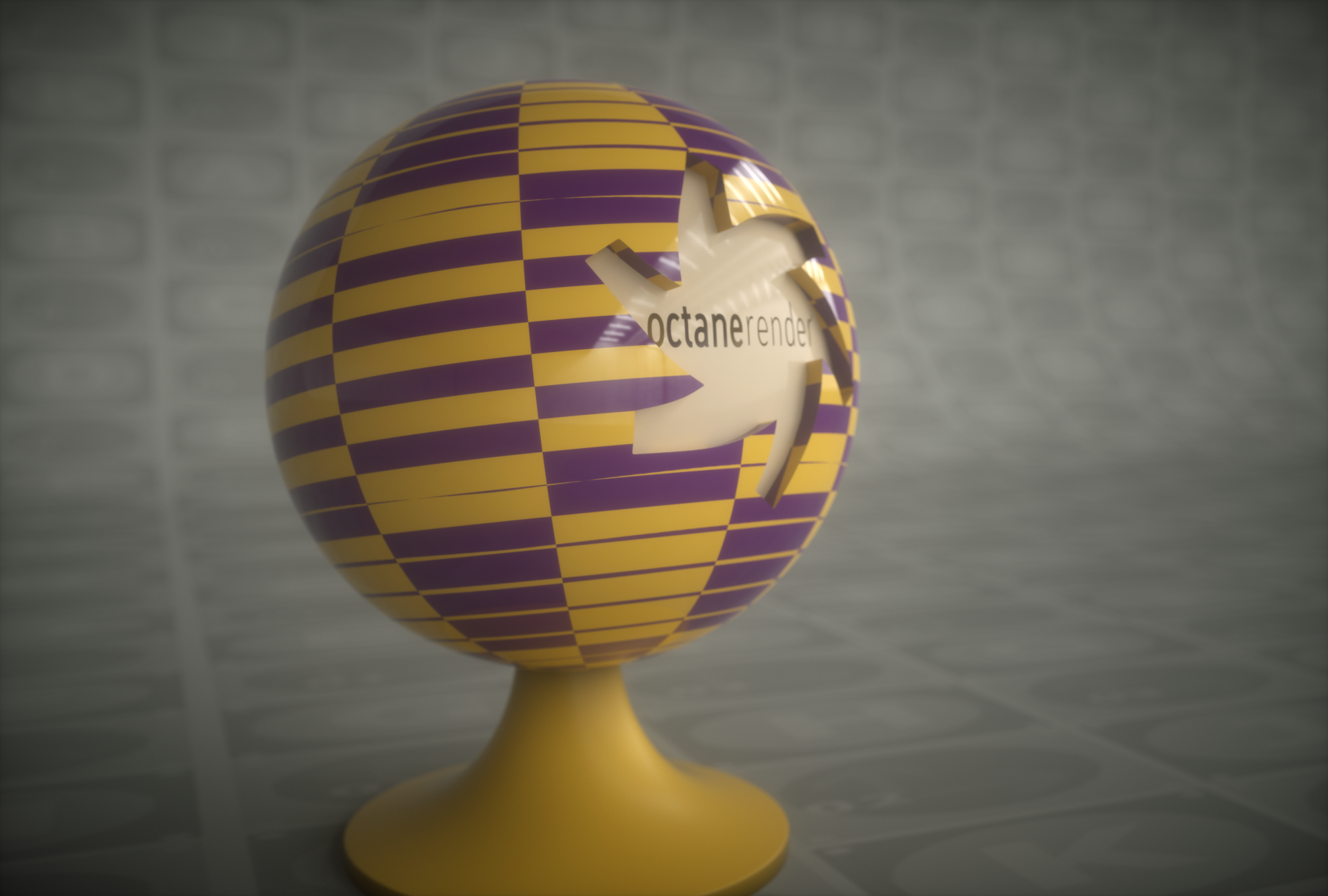
Perspective
Perspective mapping takes the world space coordinates and divides the X and Y coordinates by the Z coordinate. This can be a useful way to model a projector (using a texture with this projection as the distribution, with black border mode). It can also be used for camera mapping. Explained in the Usage Samples section of this topic.
|
|
perspective projection
|
Spherical
The Spherical projection performs latitude-longitude mapping for the U and V coordinates. This projection is used for environment textures and IES Light distributions. Explained in the Usage Samples section of this topic.
|
|
spherical projection
|
Triplanar
The Triplanar Projection is used in conjunction with a Triplanar Texture Node. It will project images in the direction of the main X, Y or Z axes, allowing you to feather the blend between each projection axis. A single image or separate images for each axis, positive and negative, can be used. More here.
|
|
tri-planar projection
|
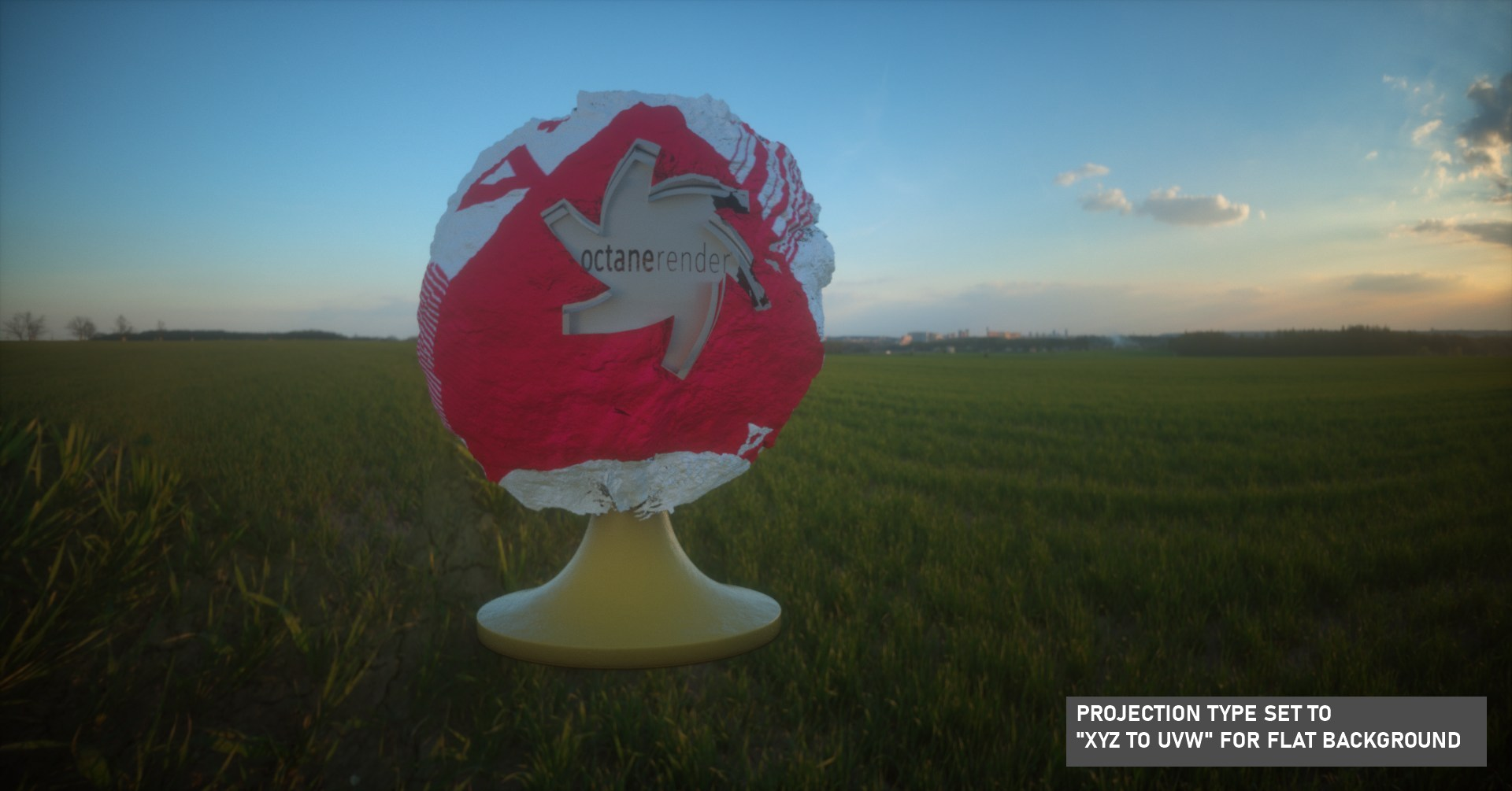
XYZ to UVW
XYZ to UVW is also known as Planar or Flat mapping. This mapping type takes the coordinates in world or object space and use them as UVW coordinates.
|
|
xyz to uvw projection
|
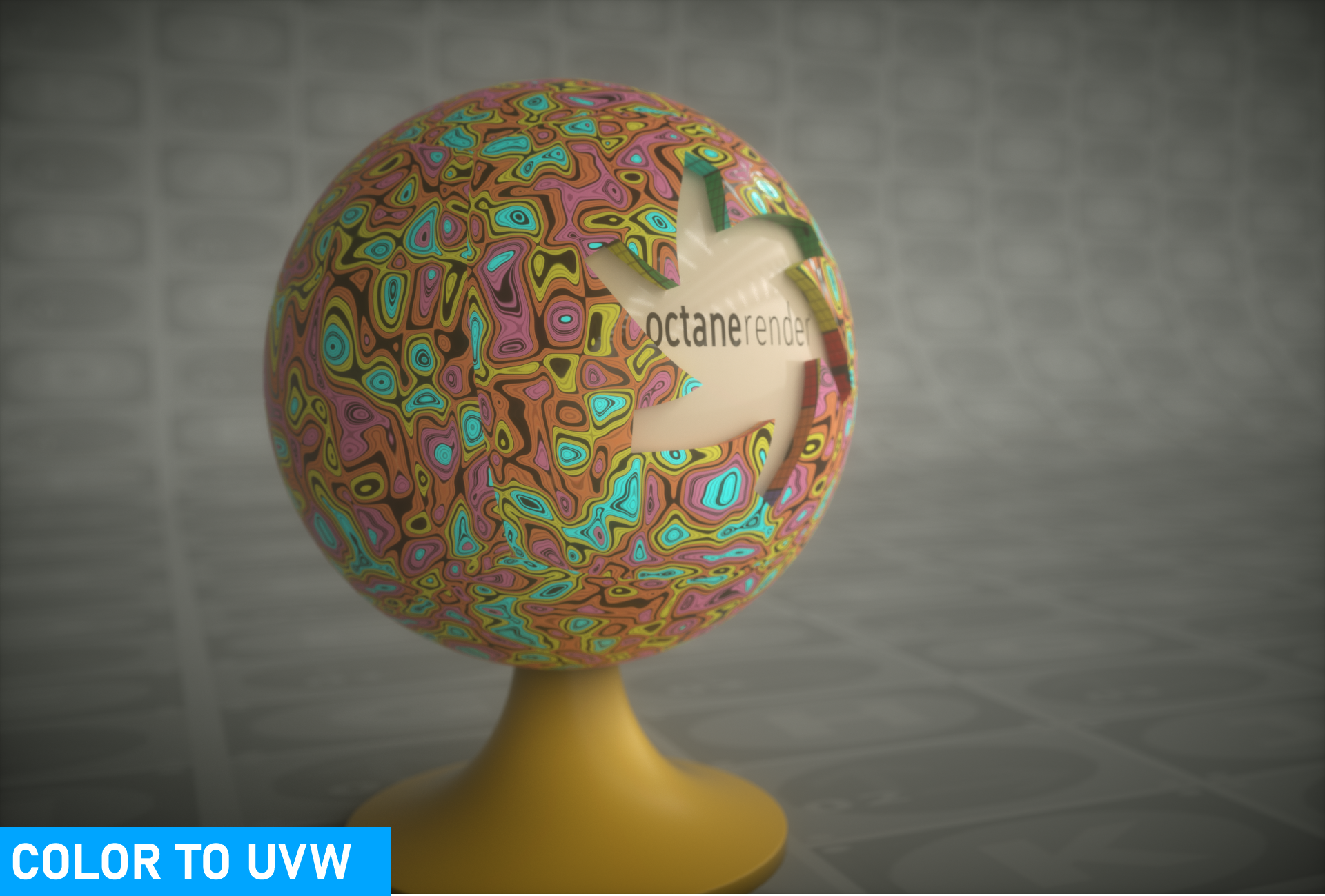
Color to UVW
Color to UVW is used to transform the coordinates from one of the other projection nodes using texture operators. That is, a projection is converted into a texture using UV coordinate, then transformed using texture operations, and converted back to a projection using Color to UVW.
|
|
Color to uvw projection
|
A simple example would be displacing textures in UV space using another procedural texture, such as the image above, where the main texture is an image map and an Octane Noise is displacing the UVW space when the material is applied to the mesh object.
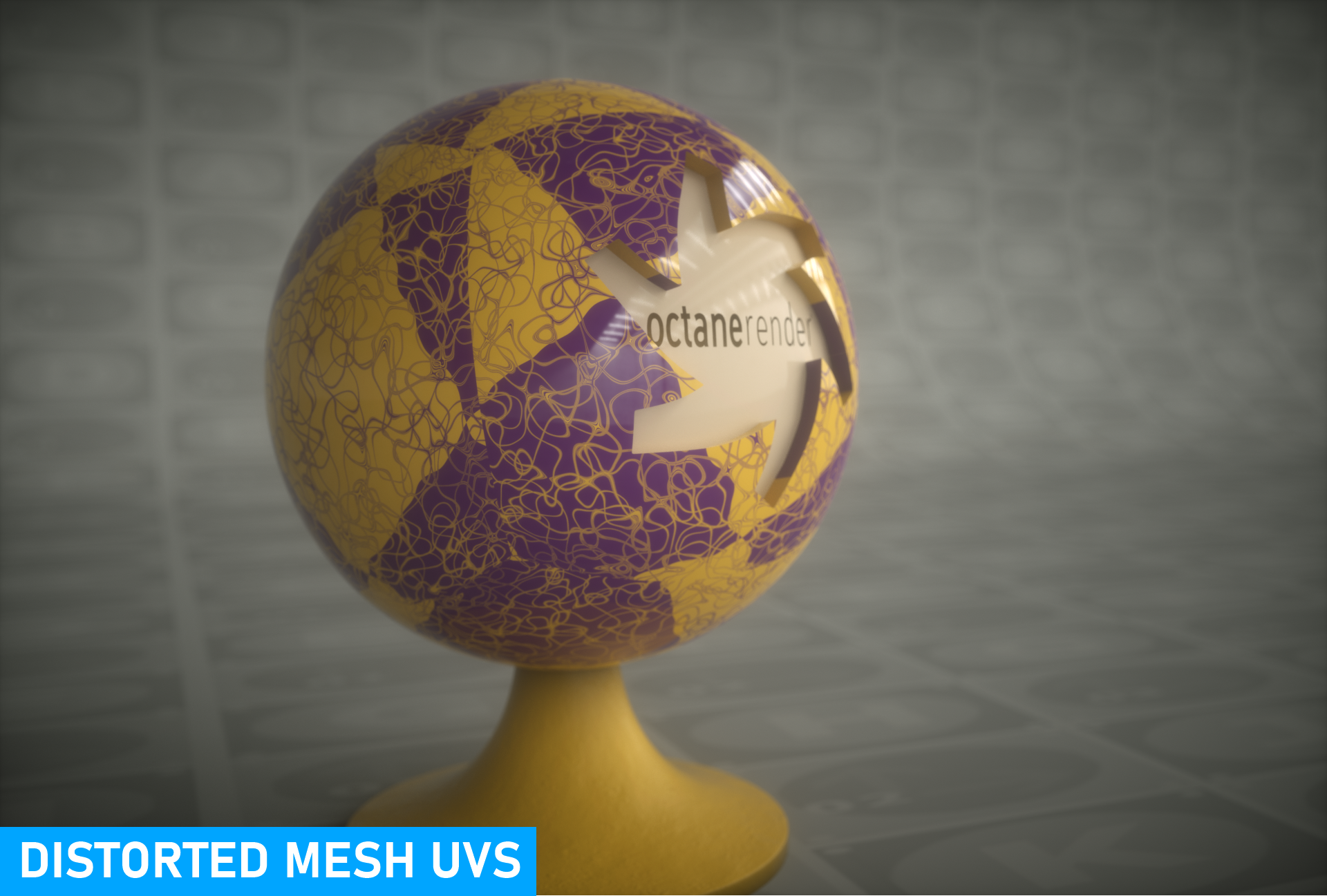
Distorted Mesh UV
This projection type will distort the UVs of the mesh by the input textures connected to the input pins described below:
- Translation — Input texture modifies the UV translation, given the values in the texture. Results are attenuated via the Translation range.x and Translation range.y values
- Scale — Input texture modifies the UV scale, given the values in the texture. Results are attenuated via the Scale range.x and Scale range.y values
- Rotation — Input texture modifies the UV rotation, given the values in the texture. Results are attenuated via the Rotation range.x and Rotation range.y values
|
|
distorted mesh uv projection
|
A value slider is used if an input texture is not provided. The value slider will offer basic results, whereas input textures, such as noise, will produce more sophisticated distortions, as seen above.
Matcap
This projection type will correctly apply Matcap textures onto surfaces. Just connect the Matcap texture to the desired channel, and choose Matcap for the projection type.
|
|
matcap projection
|
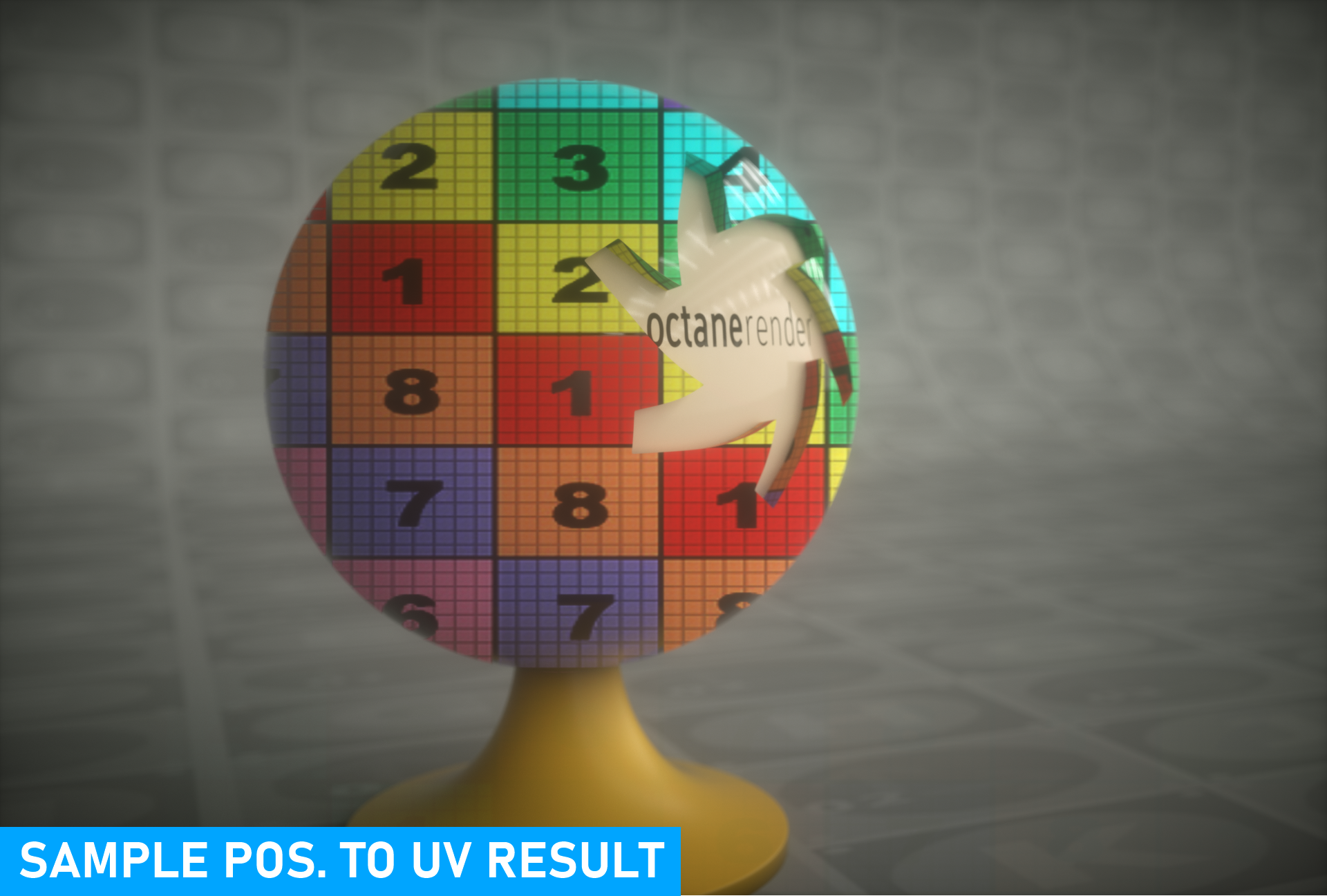
Sample POS. to UV
This projection is primarily meant to be used with Global Texture AOVs — it converts the sample position of the current image space to a UVW coordinate — this is not the same as screen space projection, which maps the sample pixel position in world space into screen space. This projection is only useful on the "first bounce" in image space — subsequent bounces are not usable. Therefore, it is possible that errors may occur when sample sources are secondary, such as Emitter bounces.
|
|
Sample pos. to uv projection
|
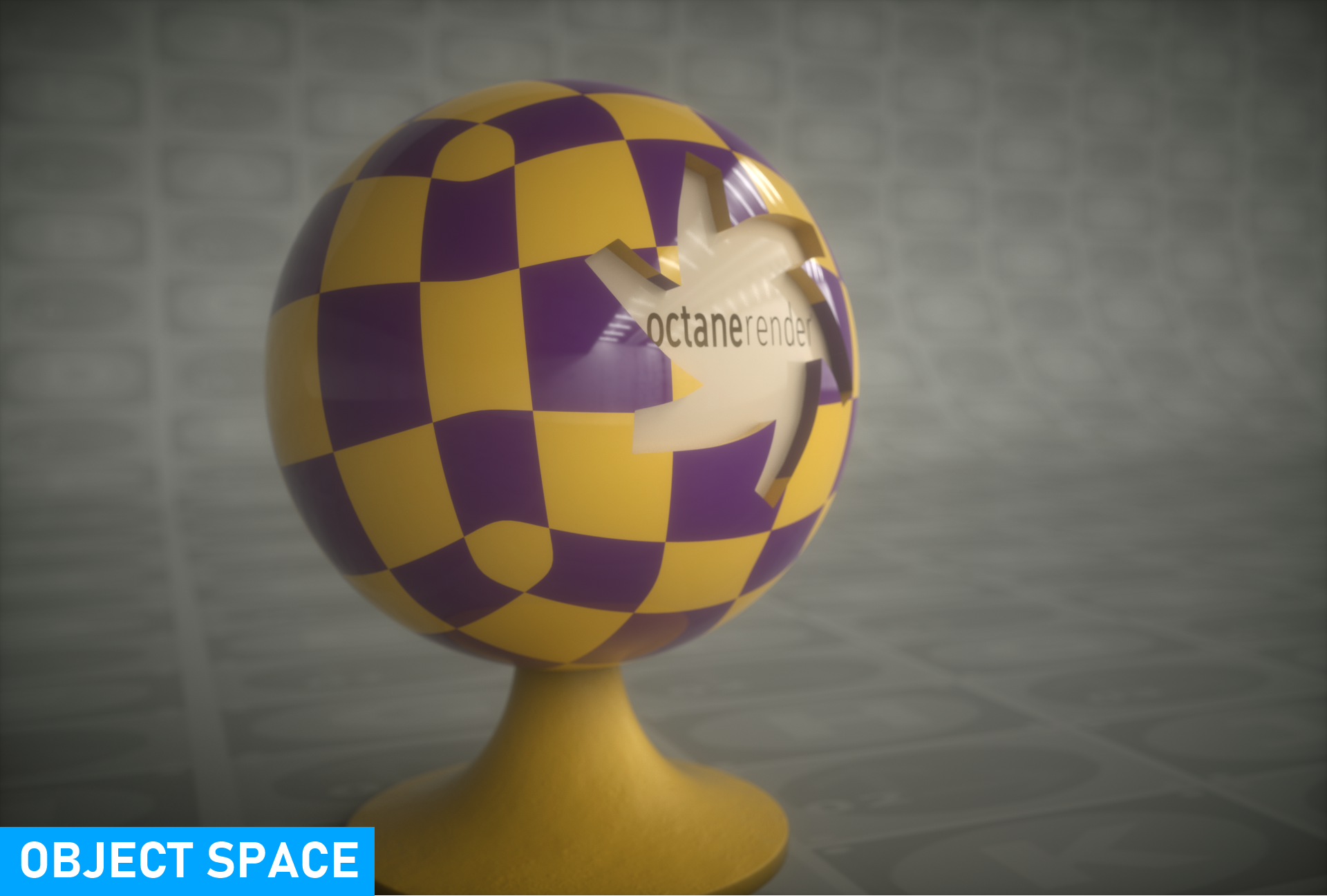
Position
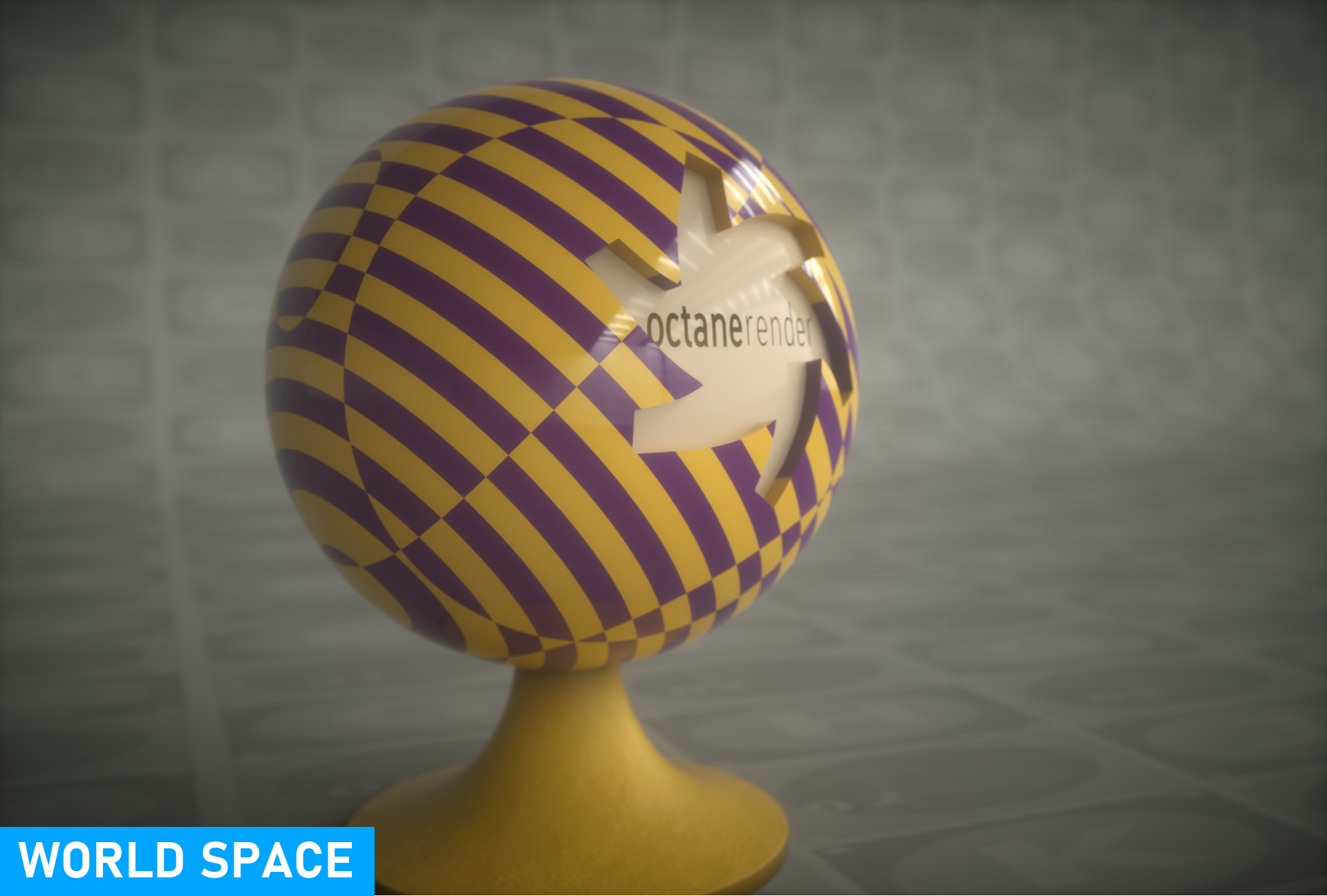
From here you can set which projection coordinate system the texture will use — Object Space and World Space. Object Space is based on the local coordinates of the object in the scene. World Space is based on scene coordinates. In texture creation, both are often used according to purpose.
|
|
position
|
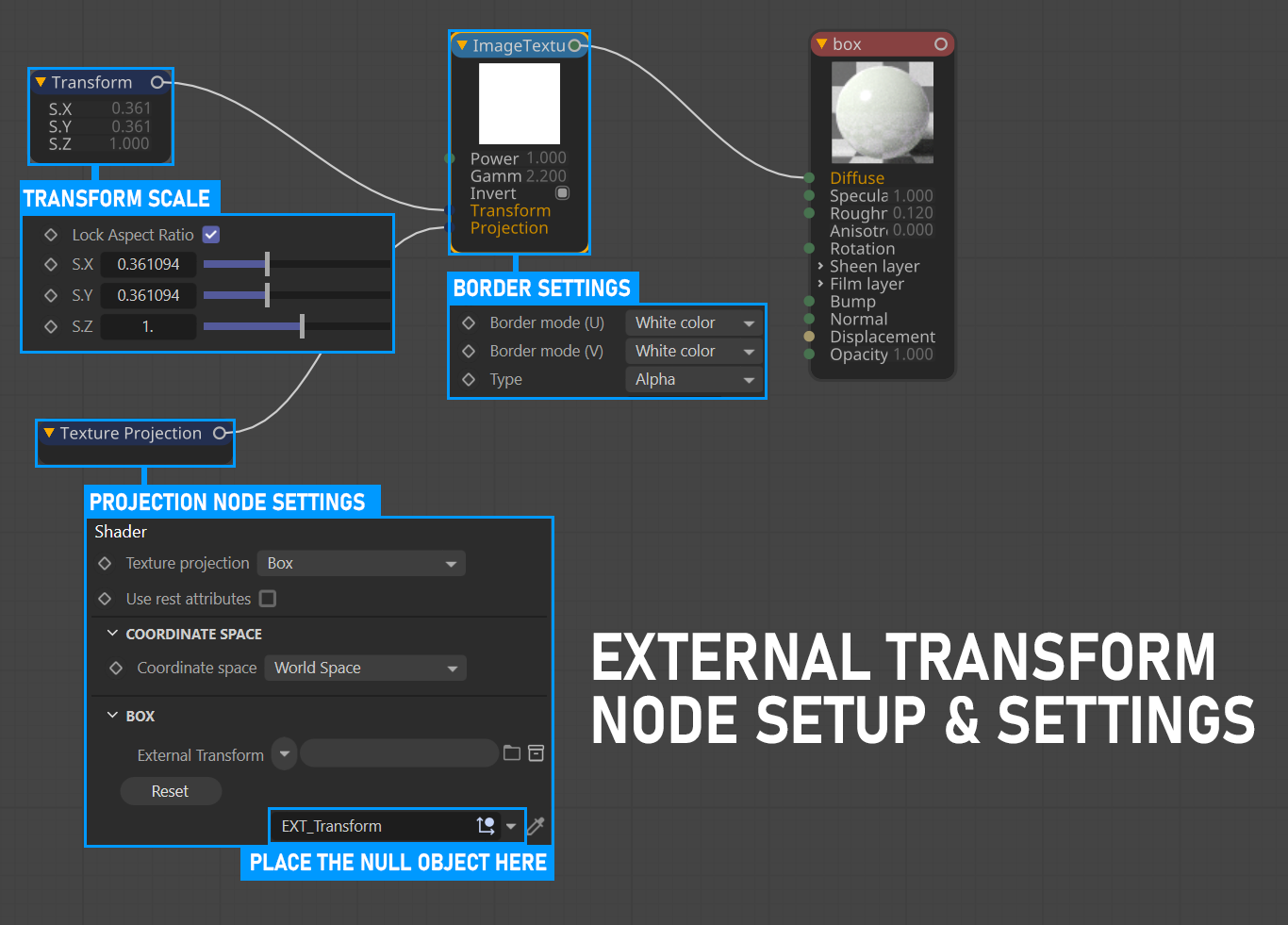
External Transform
This option enables the use of a separate object in the scene as a texture transform. The best result will appear when World Space is selected in the Position option.
Internal Transform
Depending on the type of projection chosen, texture transforms can be performed here. It has the same function as the Transform node explained earlier.
Usage Examples
The following examples can help to illustrate the different ways to use projections when applying textures to objects in a scene. There are three different methods:
- Textures applied to objects with helper objects to position the texture.
- Textures projected onto objects from cameras with perspective.
- Textures applied to environments.
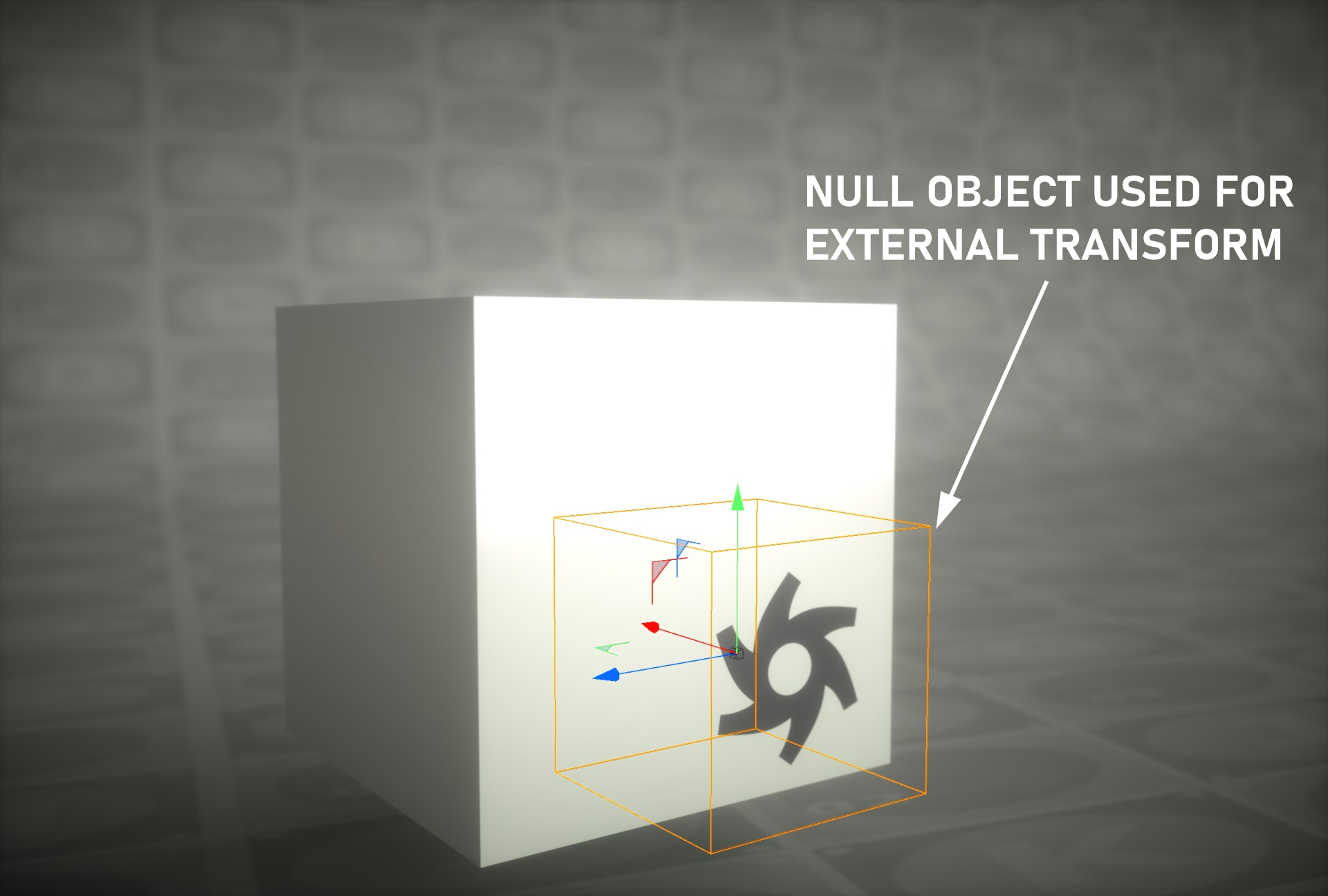
Texture Projection with External Transform
Previously we mentioned that you can use any object in the scene as an external texture transform. In the following example, the Null object is used as external transform or helper object. Any transform operation with the exception of scale can be used in this case.. You can download the scene from this link.
|
|
external transform
|
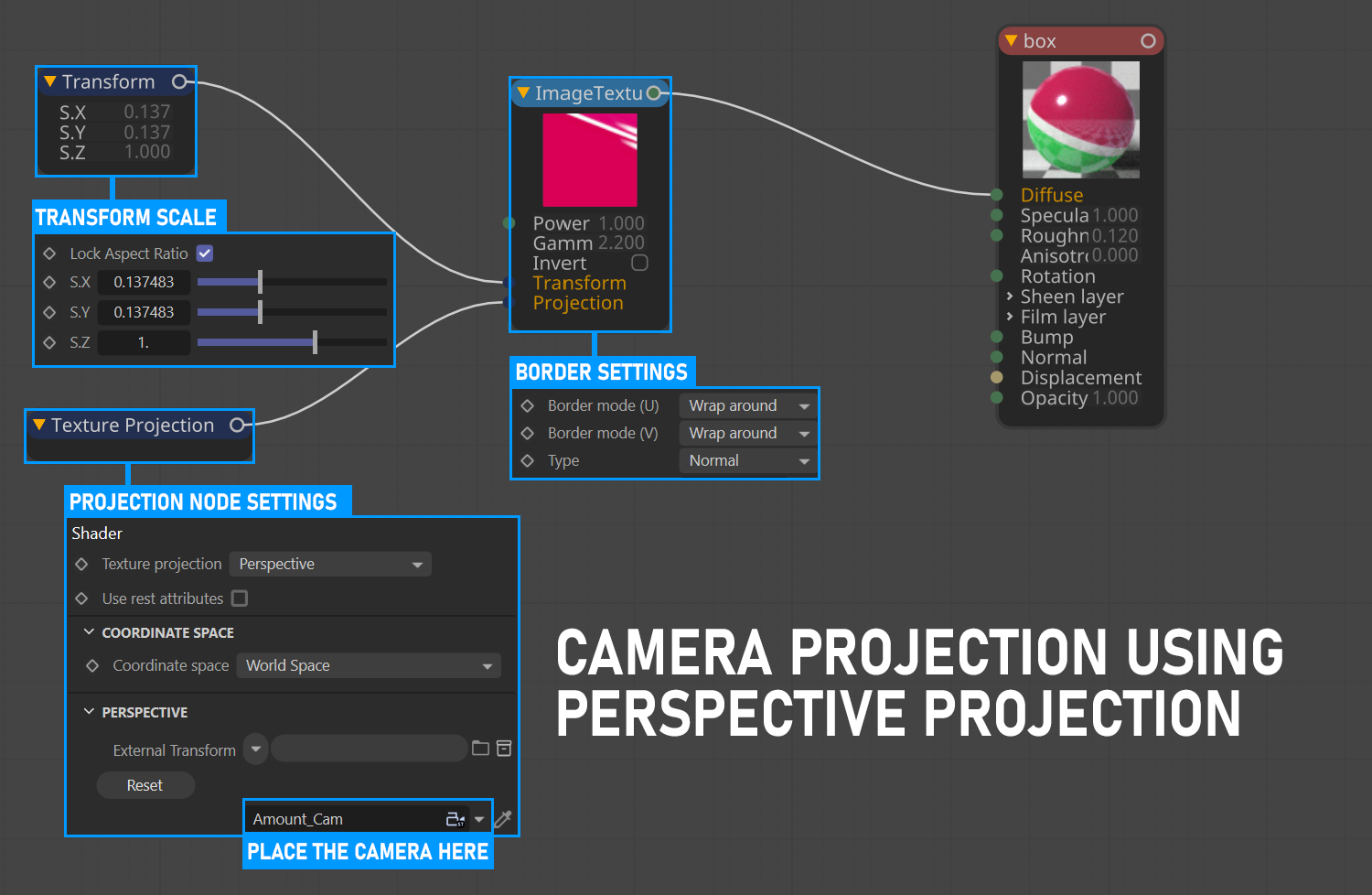
Camera Projection with Perspective Projection
This option allows the use of a camera or screen projection. You can download the scene from this link.
|
|
camera projection with perspective projection
|
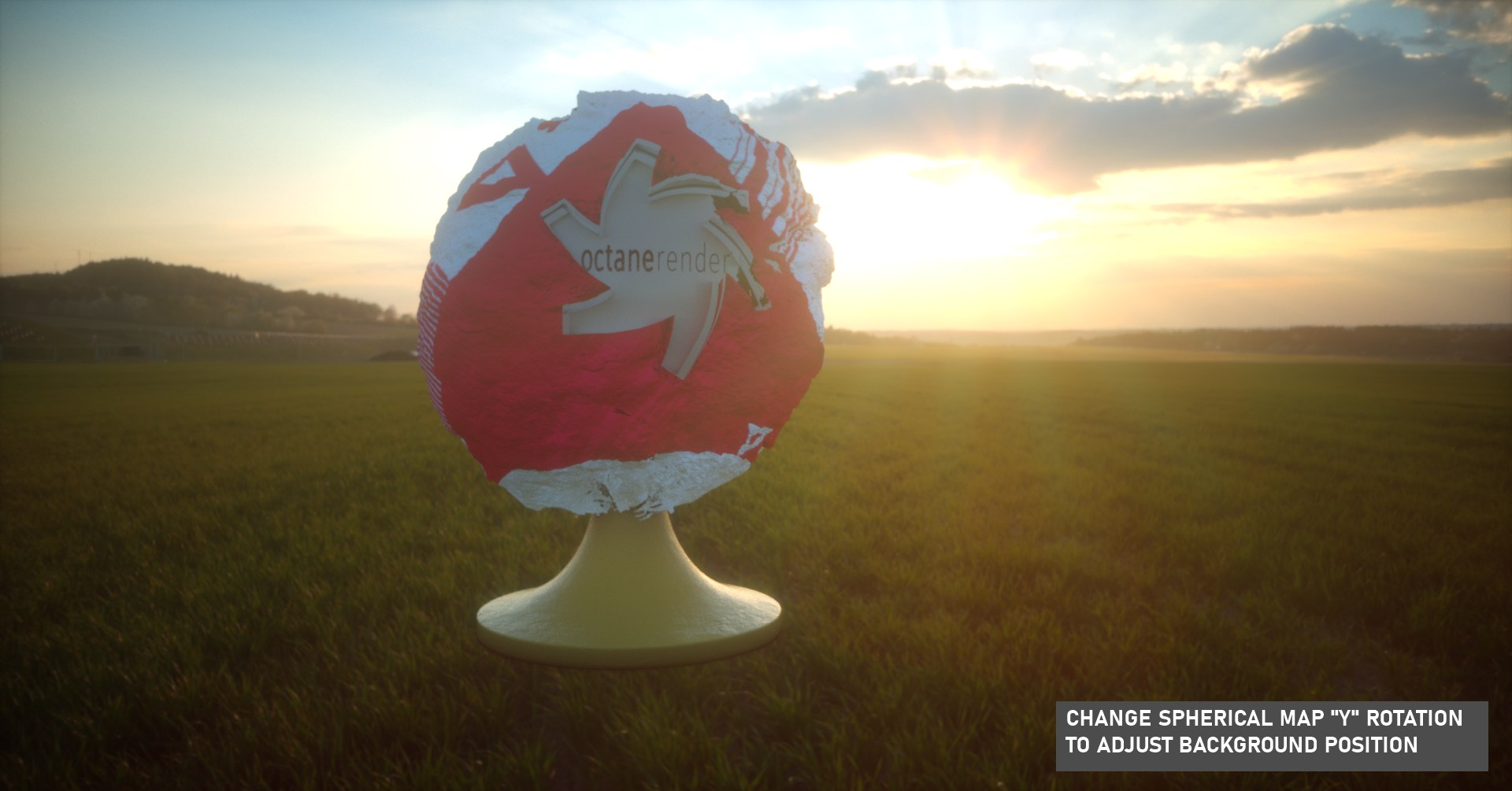
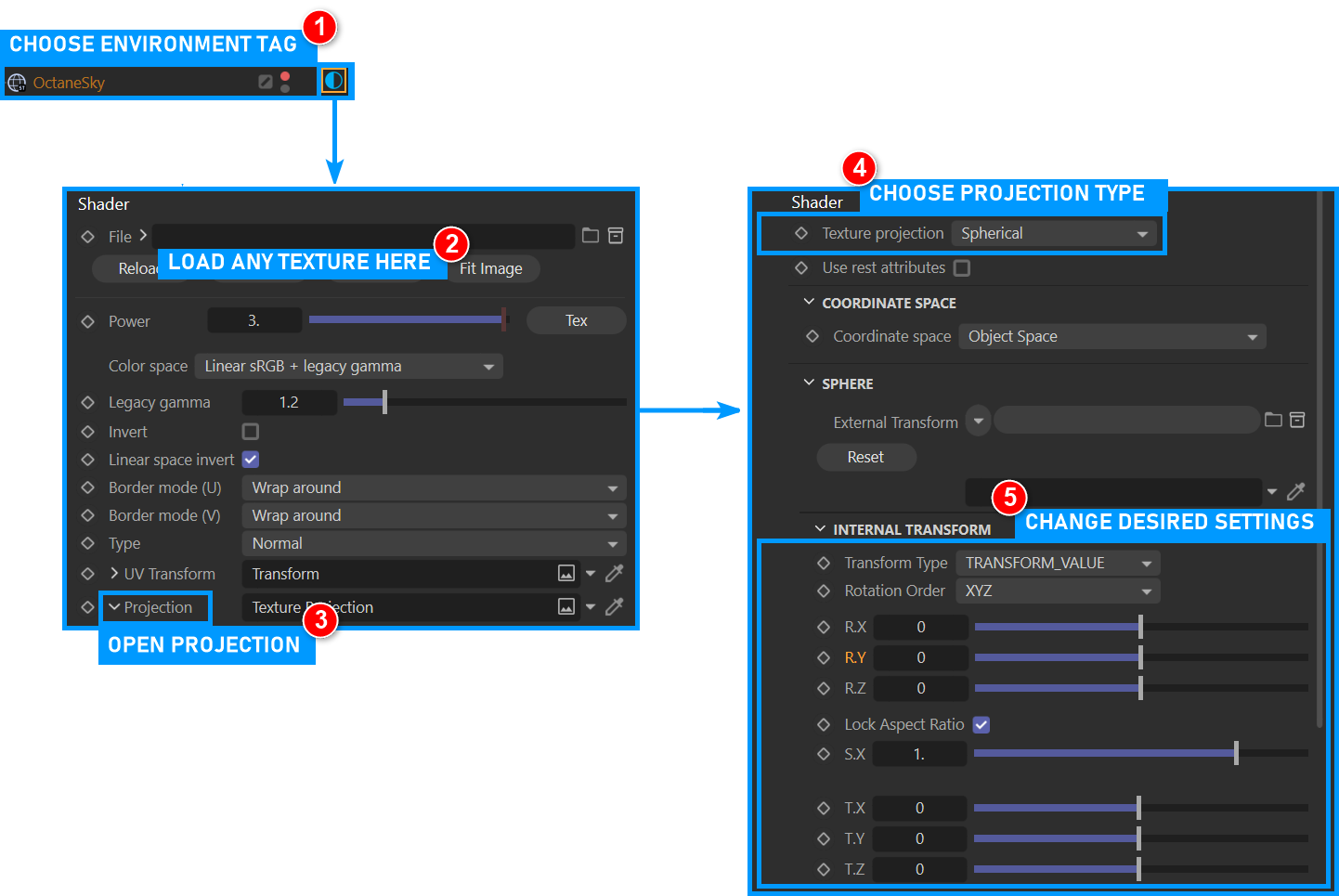
Using Projection in Environment Textures
When you use Octane sky object, any image source you upload, whether HDR or texture, is automatically assigned a spherical map projection. This behavior can be changed by adding a Projection node to the Environment Tag. The following images show this process.
|
|
environment tag projection
|
|
|
environment tag projection
|
|
|
environment tag projection
|