Clipping material
The Clipping material allows for real-time Boolean operations using a shader-based clipping process. The clipping material can be applied to a mesh, volume, or Vectron object. The new surface(s) can be automatically filled with the parent object's material and textures using the clipping material's UV set (figure 1).
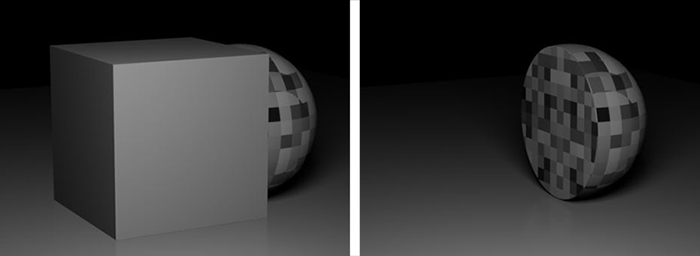
Figure 1: The Clipping Material applied to a cube primitive and used to clip away part of a sphere primitive
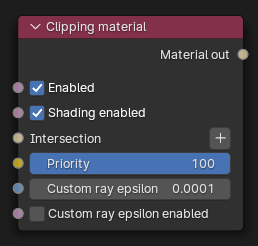
Figure 2: Clipping material Node
Parameters
- Enabled - Activates or deactivates the Boolean system.
- Shading enabled - If true, the clipping material will try to shade the gap with the material it has clipped or the intersection material, otherwise the clipping material will just leave the gap unfilled.
- Intersection - An intersection material can be specified here and will be applied to the clipped area, otherwise, the clipped area will be shaded with the parent material.
- Priority - The material priority for this surface material.
- Custom Ray Epsilon - The clipping material offset distance.
- Custom Ray Epsilon Enabled - If activated, the clipping material will use the specified custom ray epsilon instead of the global ray epsilon found in the Kernel node.
NoteThere are a couple of requirements for using the clipping material:
|