Composite Texture Layer
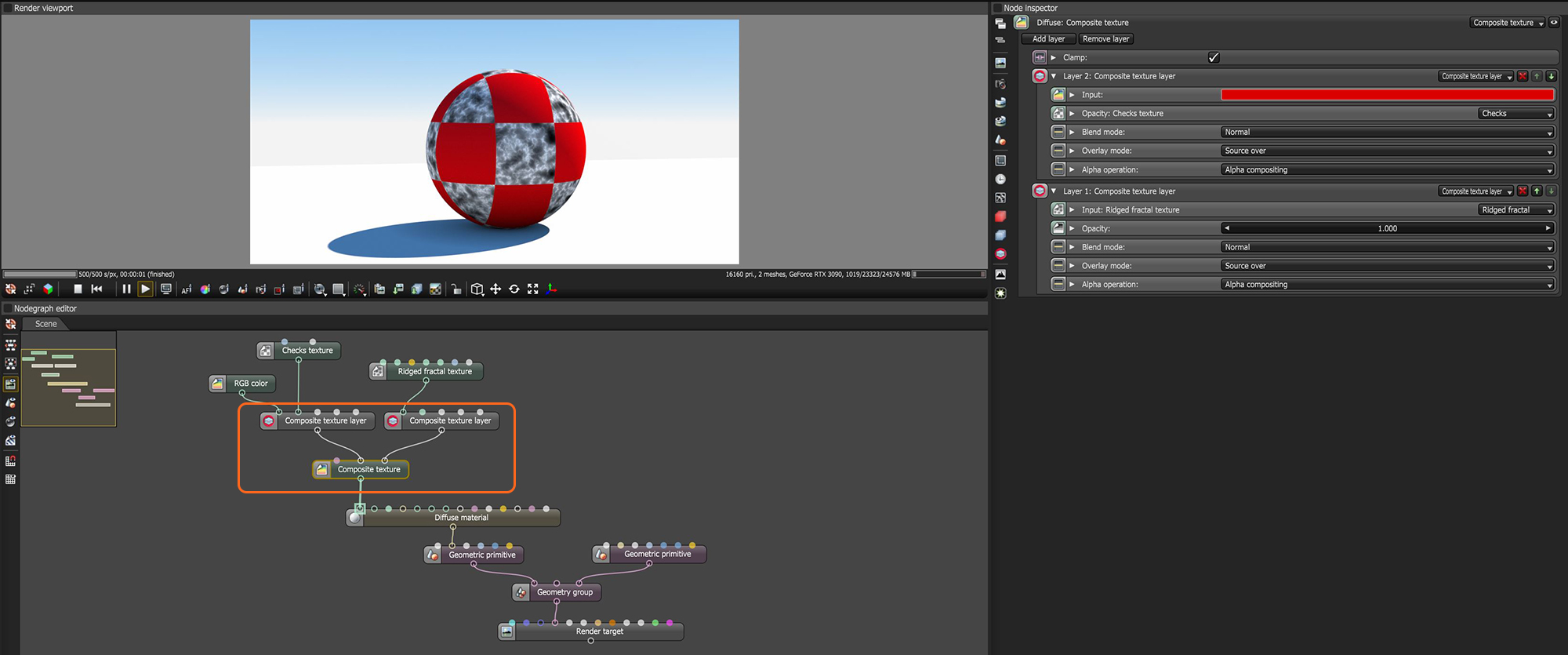
The Composite Texture Layer node is used in conjunction with the Composite Texture node to blend multiple texture or color nodes together (figure 1)
|
|
Composite Texture Layer
|
Figure 1: The Composite Texture Layer node is used to mix a RGB Color node using a Checks Texture node for opacity with a Ridged Fractal Texture node.
Composite Texture Layer Parameters
Input - The input texture for the texture layer. This can be an image texture or any Octane procedural texture or color node.
Opacity - The texture or color used to control the transparency of the layer.
Blend Mode - The blending mode used to mix the texture from this layer to the layers below. These options are similar to the blending modes found in other programs such as Photoshop. All blend modes are computed on non-premultiplied colours. They operate on each colour channel independently unless component access operators or the luminance function are used in the algorithm.
Overlay Mode - Determines how the specific Composite Texture Layer input will be treated within the composite stack.
- Source - The source is placed against black in the result.
- Source Over -The source is placed over the destination in the result.
- Source Conjoint Over -If the Source input partially obscures the Destination, only the source will appear in the result.
- Source Disjoint Over -This mode assumes that these components do not overlap, even if they actually do.
- Source In -Only the portions of the source that overlap the destination will remain in the result.
- Source Out- The source will be visible only in the portions not obscured by the destination in the result.
- Source atop- The source that overlaps the destination will be visible along with the remainder of the destination in the result.
- Destination- Only the destination will remain in the result.
- Destination Over- The destination is placed over the source in the result.
- Destination In -Only the portions of the destination that overlap the source will remain in the result.
- Destination Out -The destination will be visible only in the portions not obscured by the source in the result
- Destination atop -The destination that overlaps the source will be visible along with the remainder of the source in the result.
- Clear- Neither the source nor the destination will appear; the result is black or empty.
- XOR- The regions of the source and destination which do not overlap will remain in the result.
- Dissolve- Dissolve uses the alpha of the source layer as the threshold to a noise (random number) pattern that selects (per channel) between the source color and the background color as output for this sample. The source alpha is not used for transparency, but acts similarly in the sense that more samples from the source layer are selected as its alpha value increases.
- Plus -The sum of the pre-multiplied colors of the two layers (and likewise for the alpha values), clamped to [0,1].
- Matte- Matte calculates Source Alpha * Source Color + Background Color * (1 - Source Alpha). It is similar to "source over", but ignores the background alpha. The layer's output alpha is 1.0 for alpha operation "Alpha compositing".
Alpha Operation - Determines the behavior of the alpha for the Layer
- Blend Mode -If active, applies the selected blend operation to the alpha channels of the source (upper) and background (lower) layers and outputs the result of that as the layer's alpha.
- Alpha Composting -If an alpha channel is present, sets the layer's alpha output to the value returned by the compositing operation (overlay mode) - this is the most common use.
- Foreground- Sets the layer's alpha output to the source alpha.
- Background- Sets the layer's alpha output to the background alpha.
- One -Sets the layer's alpha to one.
- Zero- Sets the layer's alpha to zero.