Falloff
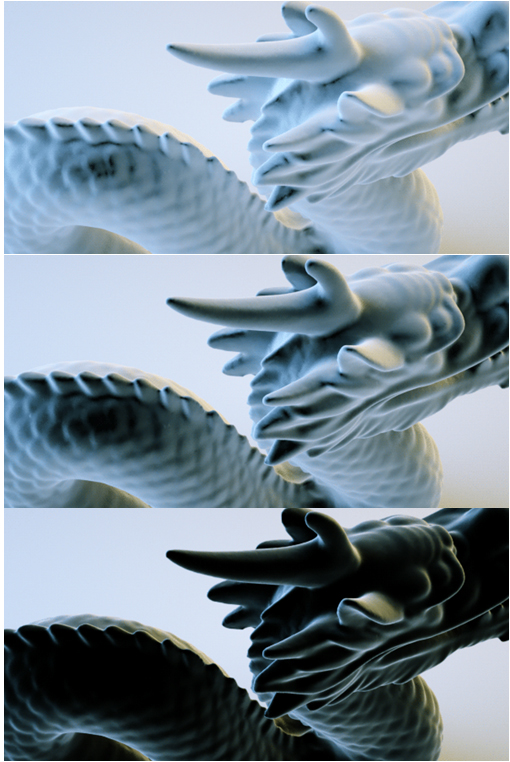
The Falloff node controls blending two materials, depending on the viewing angle of the material's geometry. This helps simulate coating effects visible in car shaders, or layered effects visible in velvet cloth or frosted glass (Figure 1).
This can also mimic architectural glass for Glossy and Specular materials by plugging the texture into the Opacity channel of the material node, allowing light to pass through based on the Falloff texture.
|
|
Falloff
|
Figure 1: Falloff texture node examples
|
|
Falloff
|
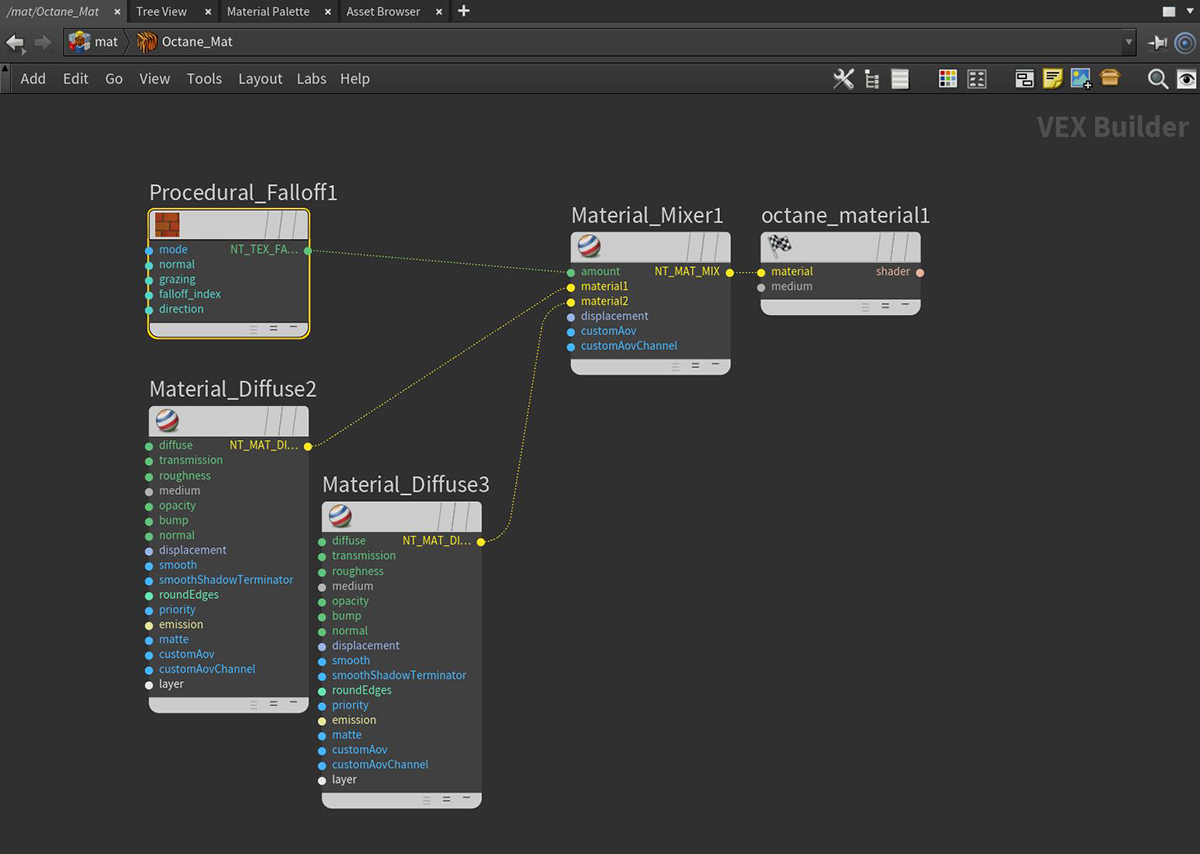
Figure 2: A typical network setup for using the Falloff texture node
Falloff Node Parameters
Mode - The falloff mode to be used for the material effect.
- Normal vs Eye Ray - Calculates the falloff from the angle between the surface normal and the eye ray.
- Normal vs Vector 90 Deg - Calculates the falloff from the angle between the surface normal and the specified direction, with a maximum vector angle of 90 degrees.
- Normal vs Vector 180 Deg - Calculates the falloff from the angle between the surface normal and the specified direction, with a maximum vector angle of 180 degrees.
Minimum Value - The value (from 0-1) of the map at straight-on viewing angles, sometimes referred to as the normal angle. When used as an input to a Mix material node, the normal is the spectral shade value between Material 1 and Material 2.
Maximum Value - The value (from 0-1) of the map at grazing angles. When used as an input to a Mix material node, the grazing is the spectral shade value between Material 1 and Material 2.
Falloff Skew Factor - The relative amount of the normal and grazing values that are at an angle to the straight on view. A value of 0.1 results in almost complete coverage by the grazing value, regardless of viewing angle, whereas a value of 15 results in complete coverage by the normal value.
Falloff Direction - The direction vector used by the various falloff modes.