Using Octane Post Processing
The Octane Post Processing provide various tools to enhance render results after the rendering process has been completed. This feature is accessed as one of the rollouts under the Camera Object Data Properties tab (Figure 1). You can also access it in the viewport by opening the Sidebar. Post-processing effects added via the Octane Post Processing rollout will not cause the engine to re-render.
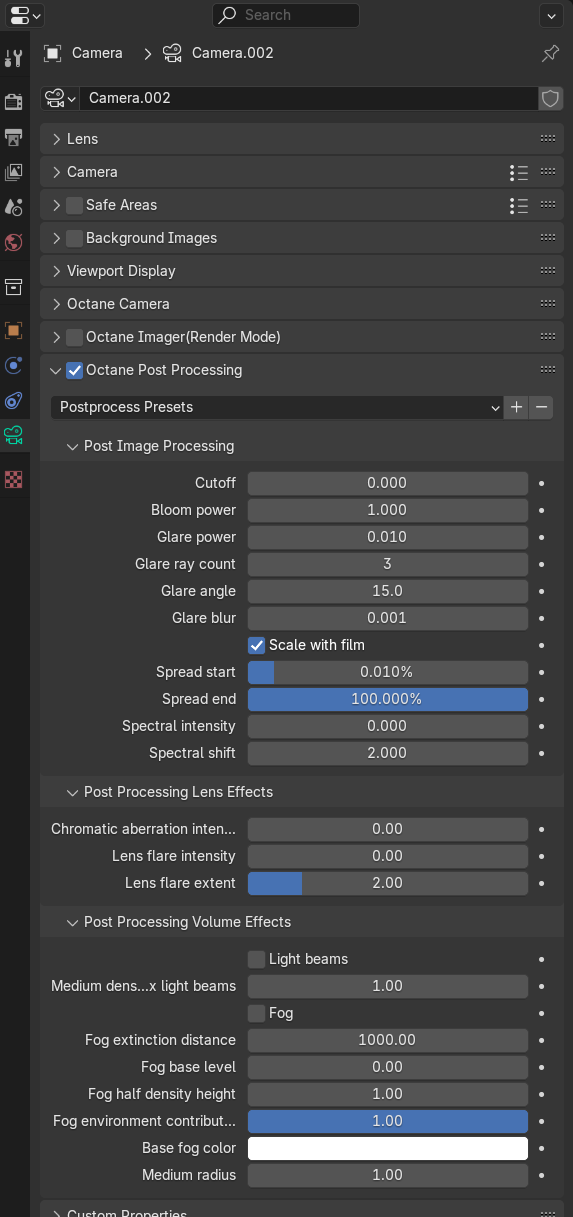
Figure 1: Octane Post Processing Parameters
Parameters
Post Image Processing
- Cutoff - Applies bloom/glare to pixel values above the Cutoff value.
- Bloom Power - Controls the size of the glow originating from an emitter, the size of the halo of light originating from the sun and/or concentrated light on reflective glossy materials to add a bloom effect to the rendered image.
- Glare Power - Controls the size of the visible rays originating from an emitter, the size of the glare originating from reflective glossy materials at a point where concentration of light is at the highest to add a glare effect to the rendered image.
- Glare Ray Count - Controls the number of visible rays radiated or reflected.
- Glare Angle - This is used to adjust the rotation of the glare relative to the object. A glare angle of -90 and 90 results to one main horizontal glare, and a glare angle of 0 results to one main vertical glare.
- Glare Blur - Controls the sharpness of the glare. Smaller values will result to a crisp linear glare and this is softened as the value is adjusted and set higher.
- Scale with film - If enabled, bloom and glare will scale with film size. If disabled, the size of bloom and glare features will be the same number of pixels regardless of film size. This should only be disabled to matchthe behavior of previous versions of Octane. To maintain the same result when enabling this, find the image length in pixels (which is film width or film height, whichever is larger), and set thefollowing values:
Spread start = 0.6 * sqrt(2) / image length
Spread end = 614.4 * sqrt(2) / imagelength
Spectral shift = old spectral shift + log2(image length).
- Spread Start - The minimum blur radius for bloom/glare, as a proportion of image width or height (whichever is larger). Ideally this should be set to correspond to about half a pixel (i.e. 0.5 / max(width, height) * 100%) at the maximum resolution you will be using. Too large a value will produce an overly blurry result without fine details. Too small a value will reduce the maximum possible strength of the bloom/glare.
- Spread End - The maximum blur radius for bloom/glare, as a proportion of image width or height (whichever is larger).
- Spectral Intensity - Used to adjust the intensity distribution of the rays across a source. This affects the strength or weakness (brightness) of the radiant energy.
- Spectral Shift - Used to adjust the displacement of the spectrum as the frequency of light emitted from a source changes affecting the visible spectrum relative to the source on the scene. The shift is evident by a color change, similar to the Doppler Effect, as the distance travelled by the ray from its source increases or decreases.

Figure 2: Example of added post processing effects:
- Bloom Power: 50
- Glare Power: 20
- Glare Ray Amount: 2
- Glare Rotation Angle: -90
- Glare Blur: 0.0010
Post Processing Lens Effects
- Chromatic Aberration Intensity - Adds color fringing or color distortion to the edges of the image.
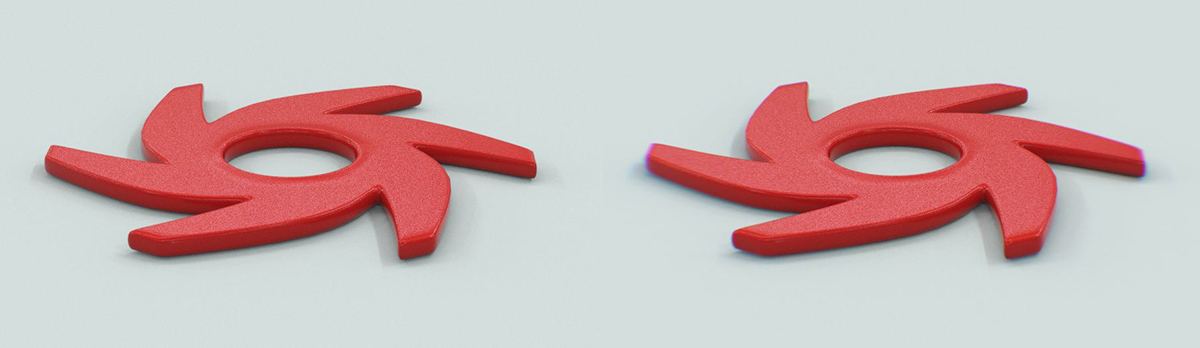
Figure 3: Chromatic Aberration is applied to the object on the right
- Lens Flare Intensity - Produces a lens flare effect on shiny surfaces and light sources.
- Lens Flare Extent - Changes the lens distance which affects the sahpe of the lens flare.
Post Process Volume Effects
- Light Beams - Enables post FX light beams for all configured light sources in the scene. This effect is only available with the Analytic light type.
- Medium Density for Postfx Light Beams - Thickness of the Light Beams
- Fog - Enables post FX fog.
- Fog Extinction Distance - The distance where the primary ray's transmittance becomes 0 due to fog's density accumulation.
- Fog Base Level - Base height in world space for post fog effects.
- Fog Half Density Height - The height from the base level where post fog density halves.
- Fog Environment Contribution - Controls how strong fog color is affected by the environment.
- Base Fog Color - The base color for the fog contribution.
- Medium Radius - Radius of the post volume. The post volume acts as a sphere around the camera position with the specified radius.

Figure 4: Renders using post-process effects
The follow example utilizes the Post Processing Lens Effects and the Post Processing Volume Effects (figure 5).
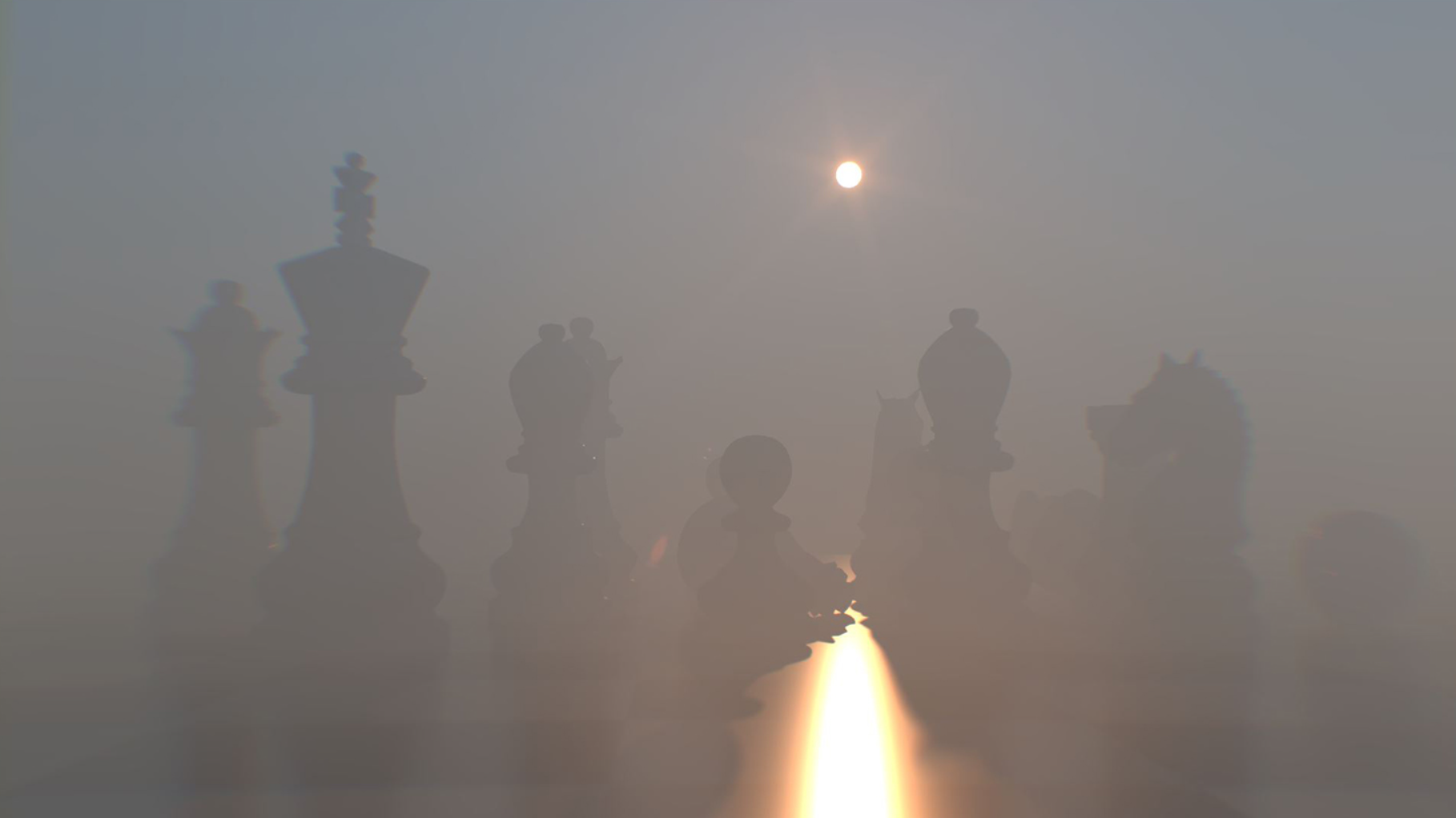

Figure 5: The Post Processing Lens Effects and Post Processing Volume Effects Fog enabled