Materials
There are several types of materials in OctaneRender® that can apply to surfaces to achieve a variety of appearances and rendering effects.
- Clipping Material - Allows one object to become a clipping volume for other objects in a scene.
- Composite - Mixes several materials using masks.
- Diffuse - Used for rough, non-reflecting materials, as well as light emitting meshes.
- Glossy - Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals.
- Hair - Designed for hair and fur objects.
- Layered - Constructs complex materials that consist of a base layer and several material layers.
- Metallic - Similar to the Glossy material, except by default it exhibits more metal-like characteristics.
- Mix - Mixes any two Material types.
- Null - Used for mesh objects that should be invisible but contain a medium.
- Portal - Designates openings in scenes to allow the render kernel to better sample light from those areas.
- Shadow Catcher - Captures shadows.
- Specular - Used for transparent materials such as glass and water.
- Standard Surface - A material that closely aligns with the Autodesk Standard Surface shader specification.
- Toon - Designs hand-drawn looking surfaces.
- Toon Ramp - Controls shading on the model. To use this material, you also need to use Toon lighting in the scene.
- Universal - Brings substance maps and PBR outputs into OctaneRender.
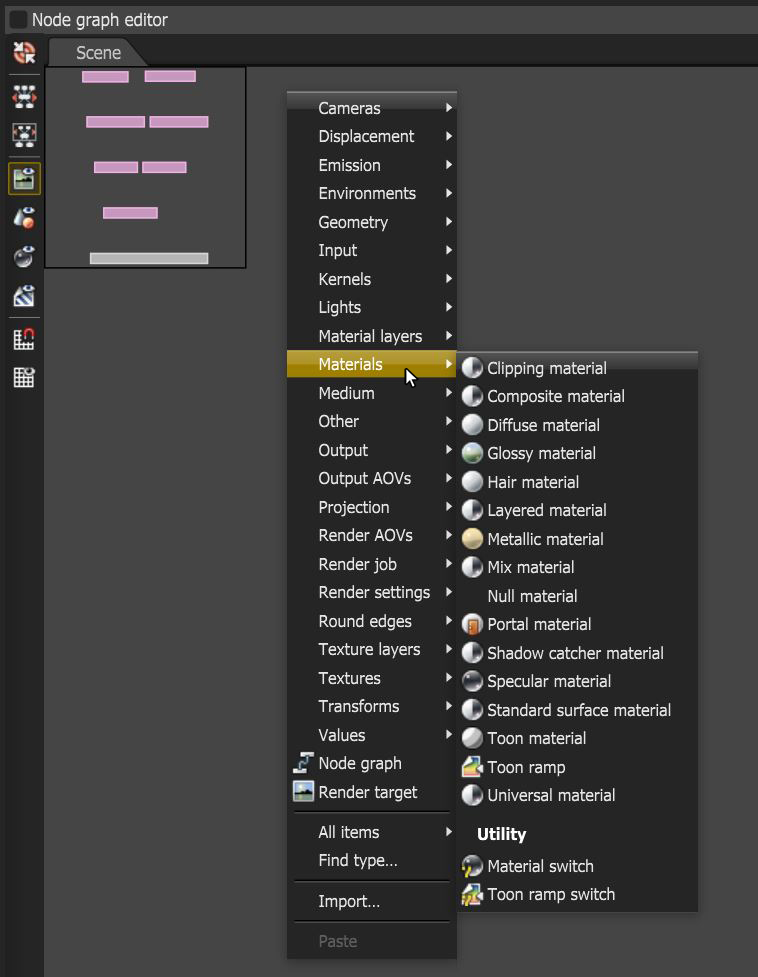
You can access OctaneRender materials by right-clicking in the Nodegraph Editor and navigating to the Materials category (Figure 1). Choose one of the materials and click in the graph to add the material to an OctaneRender scene. Once added, you can connect it to a Mesh node and edit it to simulate the desired surface quality. There are two switch types under the Utility section. These can be used to switch between different material types assigned to one object.
|
|
Materials
|
Figure 1: Adding Material nodes to the Nodegraph from the Materials section of the context menu
Select A Material In An OctaneRender Scene
There are several ways to select a material node in an OctaneRender scene. Once selected, you can edit the material parameters in the Node Inspector window.
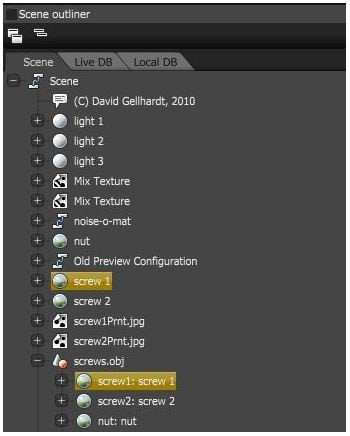
One way to select a material in the OctaneRender scene is by clicking on the Material node in the Scene Outliner as shown in Figure 2.
|
|
Material Node
|
Figure 2: Select Material nodes in the Outliner
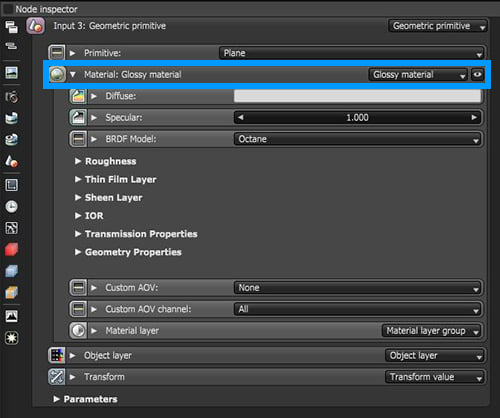
Another way to select a material node is to select the Mesh node in the Nodegraph Editor window, then locate the material in the Node Inspector (Figure 3).
|
|
Material Parameters
|
Figure 3: Access a material's parameters by selecting the associated Mesh and opening the Node Inspector
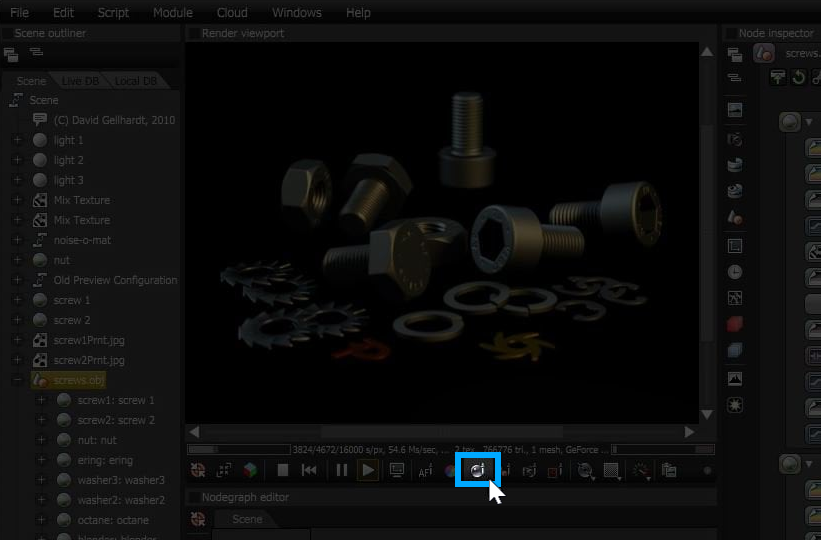
You can also select a material by choosing the Material Picker and selecting the associated Mesh in the Render Viewport (Figure 4).
|
|
Material Picker
|
Figure 4: Use the Material Picker to select materials in the Render Viewport