Material Portal
The OctaneRender® Portal material is used to optimize the rendering of light sources in interiors by helping the render kernel find important light sources in the scene. For example, interior scenes illuminated by an outside light source that comes through windows can be difficult for the path tracer to optimize the light as it enters the interior environment. To help the path and photon tracers find these light sources, polygonal planes can be placed outside the window, with a Portal material assigned to that plane.
Portal materials work best when every window or opening in the environment is covered by a portal plane. It will not work if only one window has a portal over it when all other windows do not have a portal over them. The normal direction of the portal plane should be facing inwards towards the interior, or the scene will not render properly. Don't block portal planes with other geometry like glass surfaces. Objects with the Portal material are invisible in the rendering.
Portal planes should have very few polygons. A few simple rectangular planes are best, as complex geometry used for portal planes can slow down rendering. It is possible to use a single piece of portal geometry to cover several openings such as multiple windows on a single wall. However, if the geometry is too large, that can reduce rendering efficiency. It's important to strike a balance between an opening's coverage and the size of the geometry that uses the Portal material.
The Portal Material has no tabs; there is only one control, the Enabled toggle (figure 1). This toggle needs to be on, otherwise, the portal will be ignored.
|
|
Material Portal
|
Figure 1: The Octane Portal material
|
IMPORTANT Use the Portal material with the Pathtracing and PMC kernels, not Direct Lighting. |
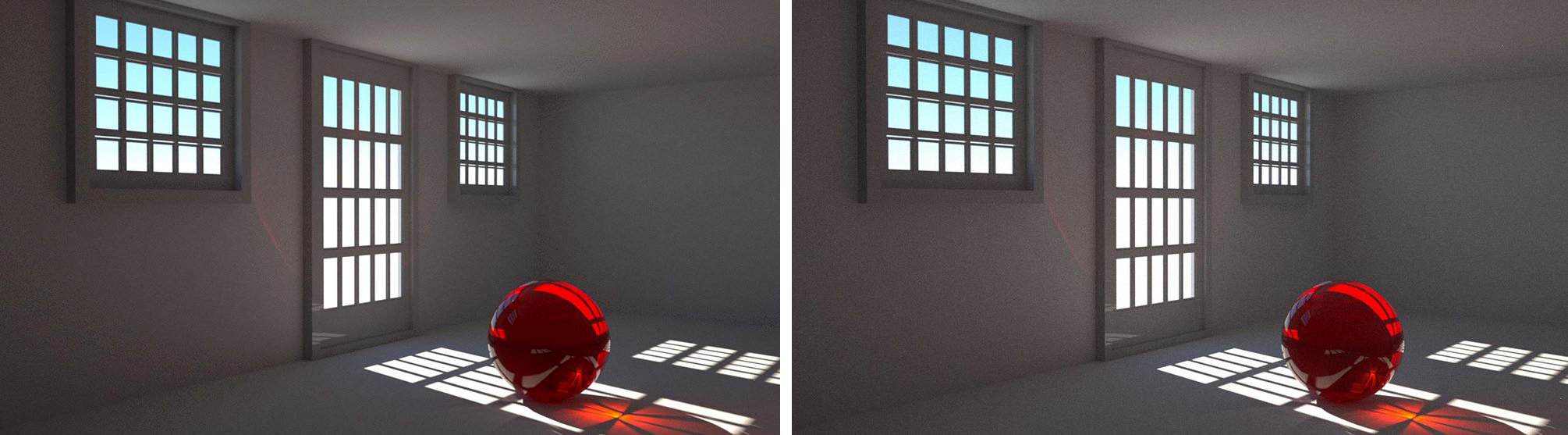
The left image in Figure 2 shows a scene with a portal over a small window lighting a room with glass sphere. The right image is the same scene without a portal material applied. There is a bit more noise in the image on the right. Also note that the wall in the Portal image is also darker than in the non-portal image. This is because the portal is helping to contain/guide the light rays in the scene, which mimimizes the amount of light getting to the wall. Without the portal, the light is scattering in all directions, brightening up the image and also adding more noise. Portal results are usually very subtle and the advantage of using portals becomes more apparent the smaller the opening or window size .
|
|
MAterial Portal
|
Figure 2: A comparison rendering of a scene with and without a Portal material