Devices Tab
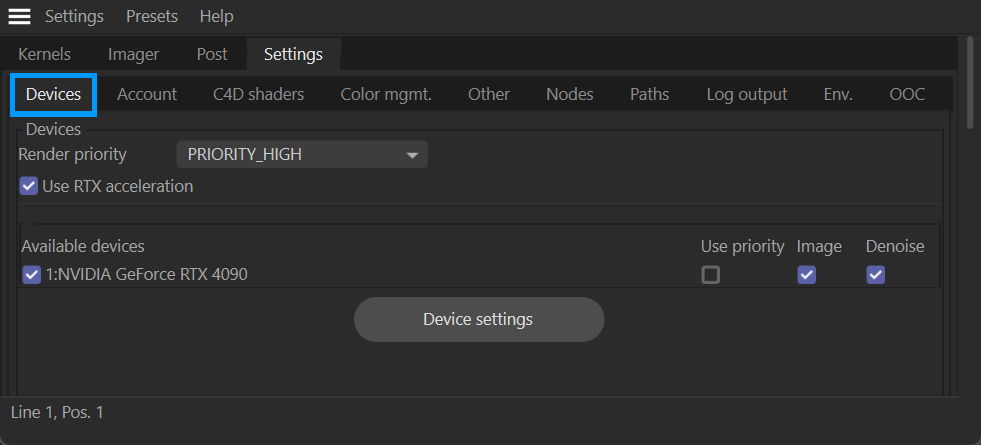
The Devices tab presents a review the of the GPUs installed in your system and allows you to determine how Octane will use the GPUs, set render priority, and so on. The illustration below shows the Devices tab:
|
|
live viewer — devices tab
|
Render Priority
The ‘Render Priority’ option is for adjusting the GPU usage. It is similar to the task manager ‘CPU Priority’. This setting depends on the scene structure you have and may vary performance from scene to scene.
Use for Denoising
Check this box if you want to enable the "AI Denoiser" in Octane. Details are explained in the "Camera Imager" section.
Available GPUs
This list shows all the GPU cards in your system. There are several check boxes in this list that enable/disable the following options:
- Using the GPU for Rendering
- Using the GPU Priority setting
- Using the GPU for Tone mapping
- Using the GPU for Denoising
If the check box next to the feature is disabled, that GPU will not be available for that function.
Device Settings
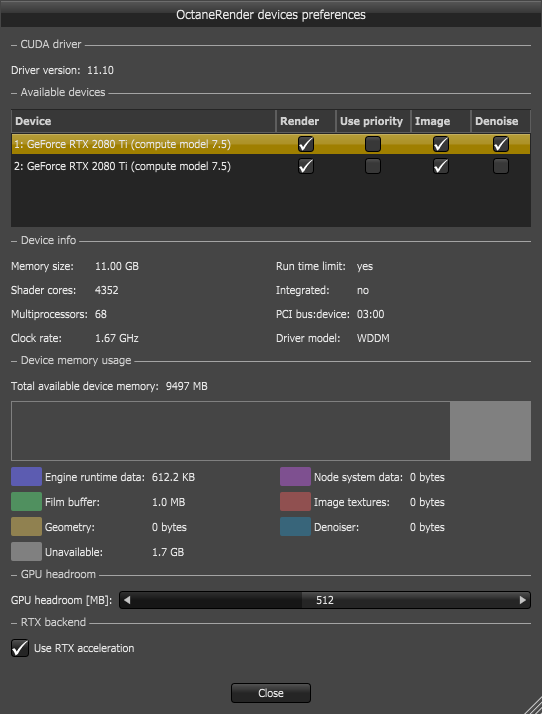
The Device Settings button will activate the OctaneRender devices preferences dialog. This dialog contains some of the information found in the Octane Settings tab, with the addition of the Use RTX acceleration option (defaults to enabled.) There are also information readouts regarding the device selected in the Device list.
GPU Scenarios
The following scenarios describe several common GPU hardware scenarios, and recommended options:
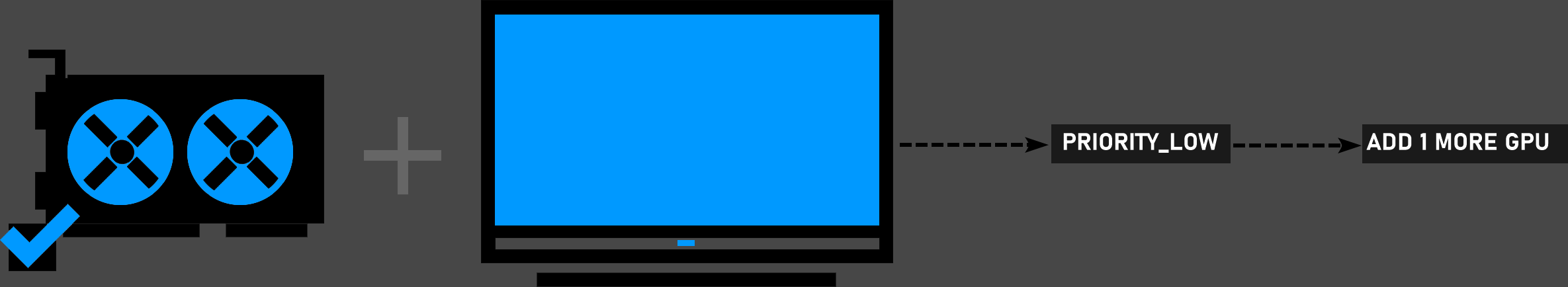
Single GPU card and one Monitor
You may add one more GPU. User interface and Viewport feedback will be faster this way. It is recommended to leave Render priority at "LOW" with a single GPU card.
|
|
1 GPU + 1 MONITOR
|
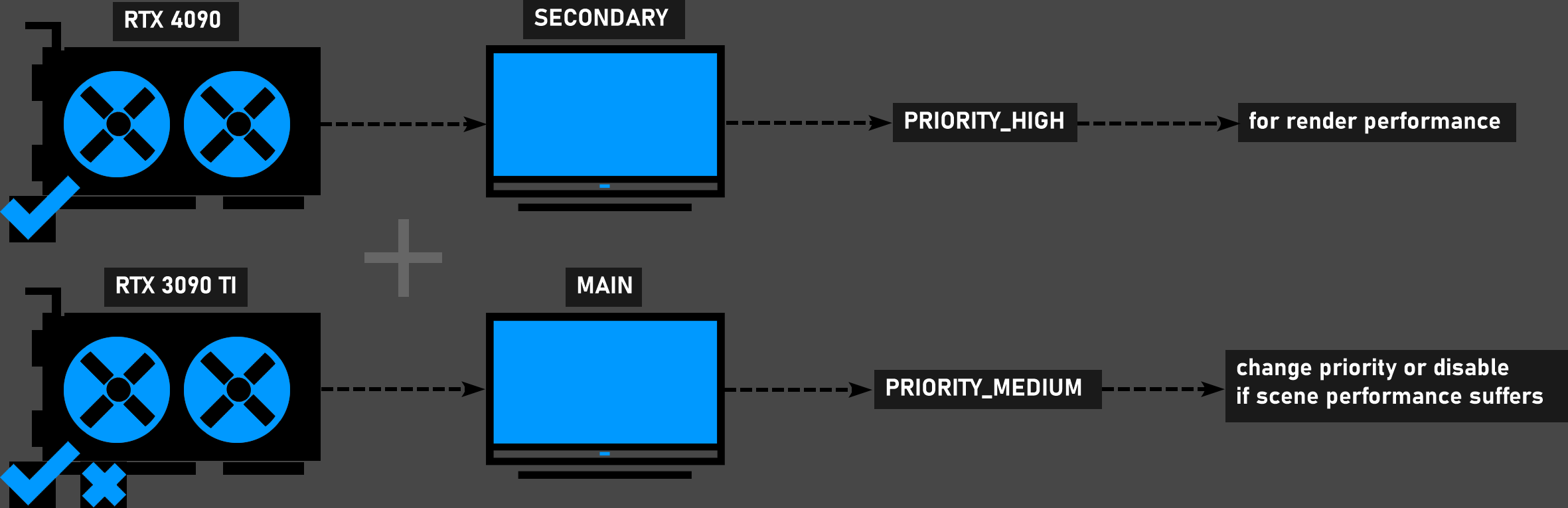
Two different models of GPU cards and two Monitors
You can connect one of the GPUs (preferably the weaker one) to the main monitor you are working with. Activate "High Priority" for the more powerful GPU. If your scene is heavy and complex, try setting a lower priority for the weaker GPU or disable it altogether.
|
|
2 gpus + 2 monitors
|
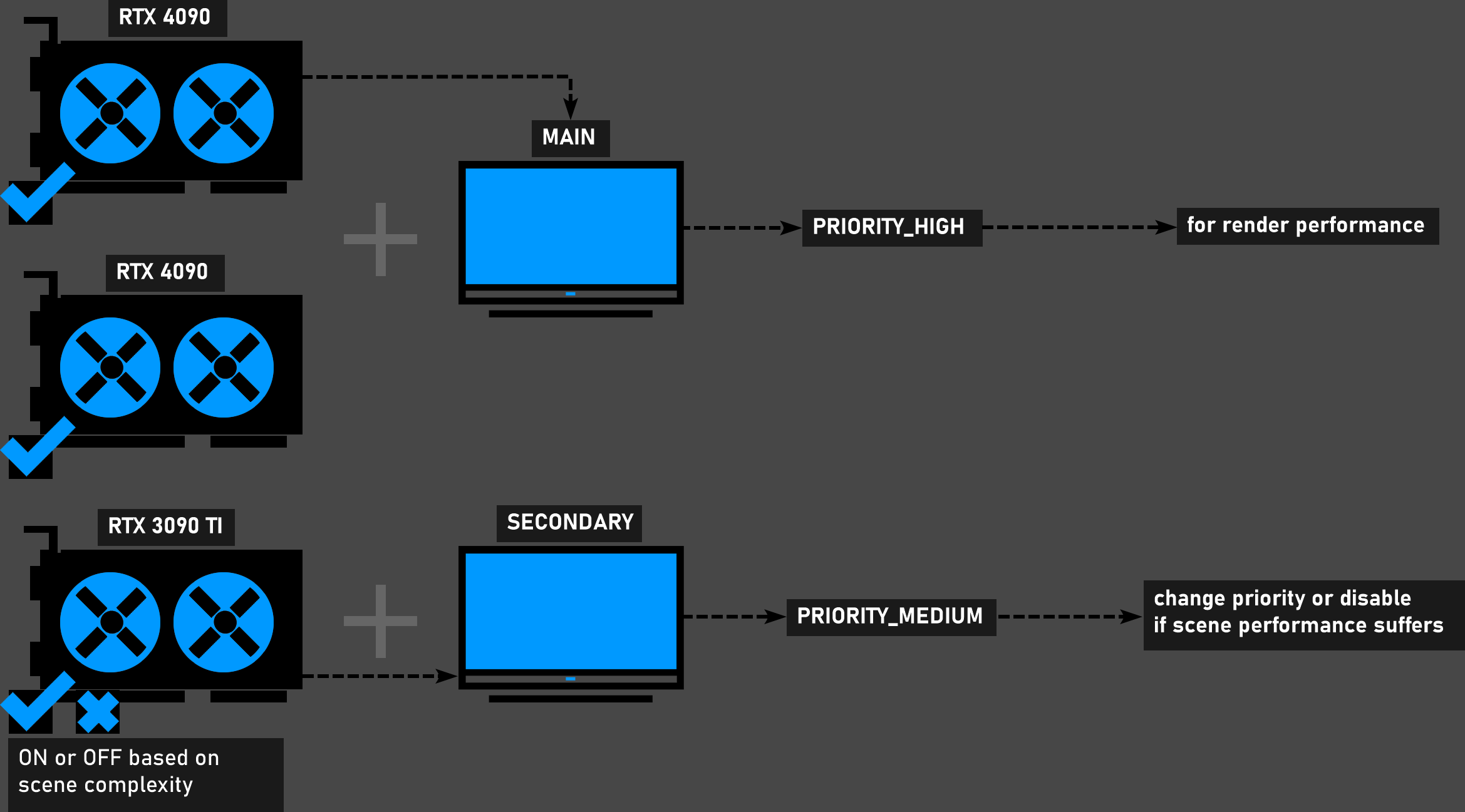
Two identical powerful GPUs and one weaker GPU
In this scenario, you can connect the GPU with the highest VRAM to the monitor you are working with. You can set the other powerful GPUs to "HIGH PRIORITY". If your scene is heavy and complex, try setting a lower priority for the weaker GPU or disable it altogether.
|
|
2 POWERFUL GPUS + 1 WEAKER GPU + 2 MONITORS
|
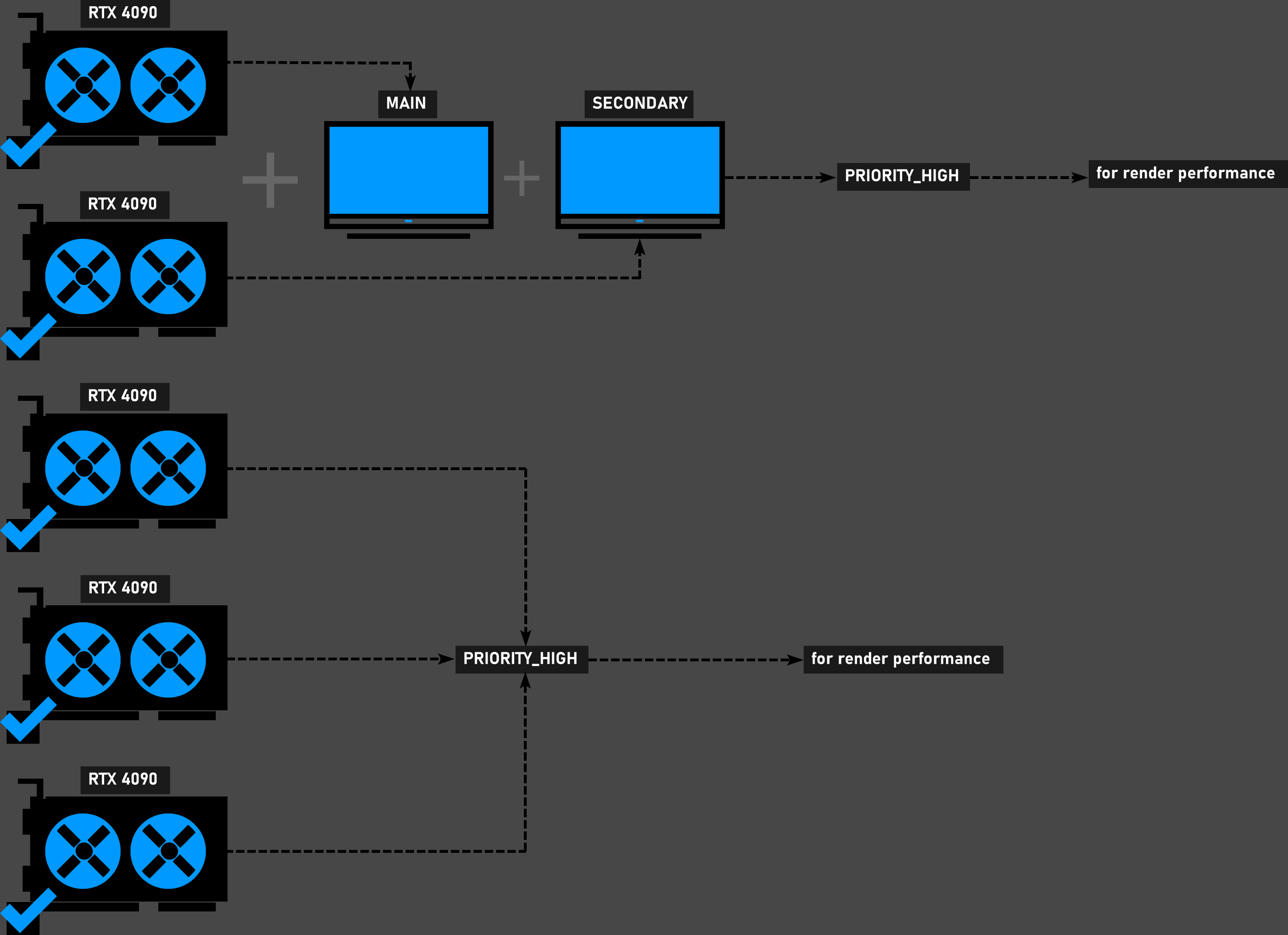
Multiple identical GPUs and 2-3 Monitors
In this scenario, all GPUs will provide high performance so you can leave them all open and set to "High Priority". It is also not advisable to add a weak GPU in these configurations.
|
|
5 identical powerful gpus
|
|
VRAM conundrum Adding multiple GPU cards into the same rig will result in a linear increase in render performance; however, the same thing is not true for VRAM — memory is not compounded in the same manner on GPUs. All the scene assets used in rendering must fit into a functional swap space – that is, each GPU must have a copy of all scene elements it needs to process — and therefore this swap space will be limited to the memory on the card with the least amount of VRAM present in your machine or in the network where all GPUs used for GPU rendering resides. This is a general GPU technology limitation. |