
The Camera Imager setting provide useful parameters for post-rendering adjustments. To adjust the Imager select the Imager Node in the Graph Editor or select the Current Imager icon in the Node Inspector (Figure 1).

Figure 1: The Camera Imager button on the Node Inspector toolbar
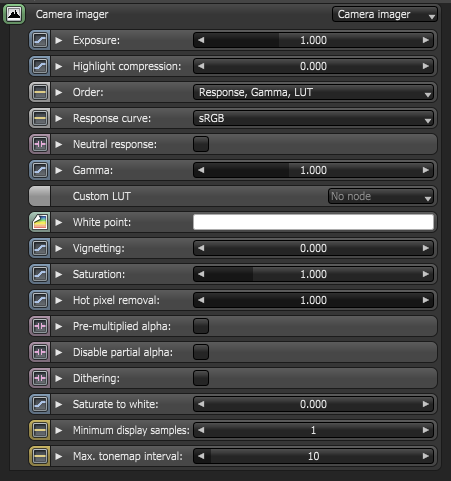
Figure 2: The Camera Imager parameters
Exposure
Controls the exposure of the scene. Smaller values will create a dark scene while higher values will brighten the scene. Note also that exposure has no effect on any of the render layer passes.
Highlight Compression
This reduces burned out highlights by compressing them and reducing their contrast.
Order
This defines the order in which the Response curve, the GammaThe function or attribute used to code or decode luminance for common displays. The computer graphics industry has set a standard gamma setting of 2.2 making it the most common default for 3D modelling and rendering applications. and the Custom LUT is applied on the scene. Typically, 3D LUTs are defined for sRGB input values, i.e. you usually want to apply the custom LUT last, but there might also be 3D look-up tables for linear input data in which case you might want to apply the custom LUT first.
Response Curve
The use of measured camera response curves can be selected. Octane also has response curves that reproduces the rendering neutrally on a normal display. The “sRGB", "Gamma 2.2" and "Gamma 1.8" are applicable for most displays that either use sRGB or simply apply a gamma of 2.2 or 1.8.
Note: The most common response curve is "sRGB", hence this is also the default setting in the Camera Imager Node. Since this option did not exist in earlier versions of Octane, any scene with a response curve "sRGB" in the imager settings will fall back to "linear/off" in older versions.
For examples of all the camera responses, see the Appendix topic on Camera Response Curve.
Neutral response
If enabled, the camera response curve doesn't tint the render result anymore. In the following example (figure 3), the left image is the material ball rendered with no response curve and gamma set to 2.2. The center image uses the Agfacolor HDC 200 curve and a gamma of 1. The right image shows the same curve with "neutral response" enabled.

Figure 3: Adjusting the Neutral Response curve
Gamma
This adjusts the gamma of the render and controls the overall brightness of an image. Images which are not properly corrected can look either bleached out, or too dark. Varying the amount of gamma correction changes not only the brightness, but also the ratios of red to green to blue.
Custom LUT
This allows you to specify any standard or user-defined 3D Lookup Table (.cube file) for Octane to map one color space to another. If this attribute is set, the custom LUT is applied in the order specified through the Order attribute.
White Point
Specifies the color used to adjust the tint to produce and simulate the relative temperature cast throughout the image by different light sources. The white point is white by default, acting as a white balance which helps achieve the most accurate colors possible.
Vignetting
Adjusting this parameter increases the amount of darkening in the corners of the render. Used sparingly, it can greatly increase the realism of the render. Note also that vignet is not applied to any of the beauty passes except the main pass.
Saturation
Adjusts the amount of color saturation of the render.
Hot Pixel Removal
The Hot Pixel Removal slider is used to remove the bright pixels (fireflies) during the rendering process. While many of the pixels can disappear if the render is allowed to progress, the Hot Pixel Removal feature allows the bright pixels to be removed at a much lower Sample per Pixel.
Pre-Multiplied Alpha
Checking the Pre-multiplied Alpha button multiplies any transparency value of the output pixel by the pixels color.
sRGB Color Picker Space
To invoke the sRGB Color Picker Space, click on the colored square found in the diffuse sliders in the Node Inspector to show a panel of colors that allows easier color picking.
Disable Partial Alpha
Option to make pixels that are partially transparent (alpha > 0) fully opaque.
Dithering
Adds random noise which removes banding in very clean images.
Saturate To White
When the sun is too bright , it can create multicolored reflections. Increasing this value will change the colors to white. This is also applicable to all sources of light. Fully saturated parts of the render can be pushed towards pure white with this option. This helps avoid large patches of fully saturated colors caused by over-bright light sources such as very bright colored emitters or reflected sunlight off colored surfaces.
Minimum Display Samples
This is minimum amount of samples that is calculated before the image is displayed. This feature can significantly reduce the noise when navigating and is useful for real-time walkthroughs. When using multiple GPUs, it’s recommended to set this value as a multiple of the number of available GPUs for rendering, e.g. if you’re rendering with 4 GPUs, set this value at 4 or 8.
Maximum Tonemap Interval
Maximum interval between tonemaps in seconds.
The Camera Imager also allows control of the Spectral AI Denoiser. With the Denoiser’s tiling and multi-GPUThe GPU is responsible for displaying graphical elements on a computer display. The GPU plays a key role in the Octane rendering process as the CUDA cores are utilized during the rendering process. support, the Octane engine can denoise any resolution up to Octane’s maximum while only consuming approximately 450MB per device. Refer to the section on Spectral AI Denoiser.