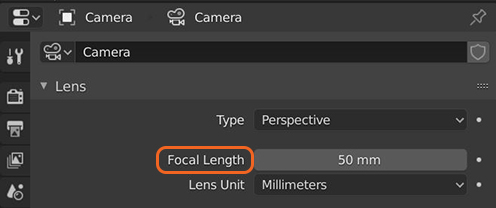
The Thin Lens Camera is the standard photographic camera used to render Blender® scenes. There are two types to choose from: Perspective or Orthographic. The OctaneRender® Camera uses Blender's Lens and Camera settings in addition to the active OctaneRender® Camera's attributes. If you choose the Perspective camera type, OctaneRender® considers the lens's Focal Length (Figure 1). If you choose the Orthographic camera type, OctaneRender® considers the lens's Orthographic Scale (Figure 2).

Figure 1: The default Perspective setting
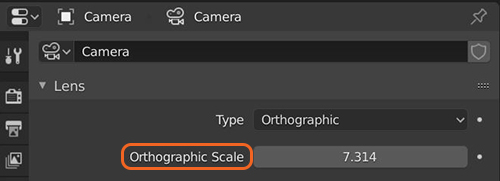
Figure 2: The default Orthographic setting
Type - These options change based on the Camera type selected.
Focal Length - The lens's focal length.
Field Of ViewThe area that is visible to a camera lens usually measured in millimeters. A wide angle lens provides a larger field of view and a telephoto lens provides a narrow field of view. - This sets the horizontal field-of-view for the camera in the scene, measured in degrees. Large values make more of the scene visible, and smaller values reduce the amount the amount of visible scenery.
Lens Unit - Switch between Focal Length or Field of View
Lens Shift (X, Y) - Renders images of tall buildings or structures from a similar height as the human eye, but keeps the vertical lines parallel.
Clipping Start (Near Clip Depth) - The distance from the Camera to the near clipping plane, measured in meters. This parameter helps you get good shots of entire rooms for interior scenes but cannot do so without a very large field-of-view and keep the camera inside the room. You can position the camera outside the room - lower the FOVThe area that is visible to a camera lens usually measured in millimeters. A wide angle lens provides a larger field of view and a telephoto lens provides a narrow field of view. and increase the clipping plane distance in front of you until the closest walls are clipped out. OctaneRender® doesn't alter the geometry, but it alters the Camera's clipping, which means that shadows, reflections, and refractions are still affected by the clipped geometry.
Clipping End (Far Clip Depth) - The distance from the Camera to the far clipping plane, measured in meters. This clips off Objects in the background starting at this specified distance.
Sensor Fit - Adjust sensor based on Auto, Horizontal, or Vertical.
Sensor Width (Width, Height, or Size) - The size of the sensor or film in millimeters.
Adapt to Camera View Resolution - Uses the camera resolution for previews.
Used as Universal Camera - The option provides additional parameters associated with the Octane Universal Camera. See the Universal Camera article for more information.
Distortion - Adjusts the spherical and cylindrical distortion. The rendered image displays the entire sphere and uses equidistant cylindrical projection, also known as lat-lon projection.
Pixel Aspect - Squash or stretch the depth-of-field disc and render it to a non-square pixel format like NTSC or PAL.
Perspective Correction - If the up-vector is vertical, enabling this option keeps vertical lines parallel.
Use F-Stop - Adjusts the aperture-to-focal-length ratio to control the field-of-view and depth-of-field like a camera.
Depth of FieldThe distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions. source: wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field): Autofocus - Keeps focus on the closest visible surface at the center of the image, regardless of the ApertureDetermines how much light enters a camera lens. A large aperture produces a narrow depth of field and a small aperture produces a wide depth of field., Aperture Edge, and Focal Depth values. If Autofocus is disabled, you need to define the depth-of-field focus point relative to an Object in the scene, and you need to define the Camera's distance from the focus point.
Distance - If Autofocus is disabled, this specifies the Camera's distance to the focus point. Make sure the Distance attribute encompasses the scene (or the Object in focus), because like the real world, you cannot see any Objects if Distance is 0, and some Objects won't be visible if the Distance is too short.
Aperture - Represents the radius of the Camera's lens opening, measured in centimeters. Low values have a wide depth-of-field where everything is in focus.High values create a shallow depth-of-field where objects in the foreground and background are out of focus.
Aperture Aspect - Squashes or stretches the depth-of-field disc.
Aperture Edge - Controls aperture edge detection at all points within the aperture, and modifies the bokeh effect. Lower values give more pronounced edges to out-of-focus Objects affected by the shallow depth-of-field, like Objects in the foreground and background. High values increase the contrast towards the edge.
Bokeh Side Count - The number of edges making up the bokeh shape.
Bokeh Rotation - The bokeh shape's orientation.
Bokeh Roundedness - The roundedness of the bokeh shape's sides.
Stereo Mode - Enables stereo mode, and gives you options to use off-axis or parallel stereo camera projections.
Stereo Output - This specifies the output rendered in stereo mode.
Stereo Distance - The distance between the left and right eye in stereo mode, measured in meters. This is also refers to the inter pupillary distance (IPD), stereo interocular distance, or stereo distance. When working with scenes for virtual reality, the IPD scale unit used by OctaneRender® is not affected by the scene scale unit. This is intentional, as when the IPD is set, this must remain consistent even when scenes change in scale or proximity. However, the units used by the IPD in OctaneRender® are also interpreted in meters, so when checking the Camera attribute, Eye Distance is effectively 0.02, which is its default value equal to 2 cm or 20 mm. For a distance of 65 mm, set the Camera node's Stereo Distance value to 0.065. For realistic depth, use values between 0.055 and 0.075.
Swap Eyes - Swaps the left and right eye positions when stereo mode shows both.
Stereo Distance Falloff - Used by the Panoramic camera to control how fast the eye distance reduces towards the poles. This reduces eye strain at the poles when the panorama is viewed through a head-mounted display. A value of 1 reduces the eye distance from equator to the poles, which creates a relaxed viewing experience, but this also causes flat surfaces to appear curved. Values smaller than 1 keeps the eye distance constant for a larger latitude range above and below the horizon, but reduces the eye distance near the poles. This keeps flat surface flat, but cause more eye strain near the poles. You can reduce the eye distance more by setting the Pano Blackout Latitude to less than 90 degrees.
Pano Blackout Latitude - Used by the Panoramic camera. This is the minimum latitude that blacks out areas with higher latitude values the panorama when Stereo Rendering is enabled.
Left Stereo Filter/Right Stereo Filter - The left and right filter colors adjust the colors that create the anaglyphic stereo affect in the render.