Dirt Texture
The Dirt texture creates different effects based on ambient occlusion calculations. This texture always returns a random value and can simulate dirt, dust, or wear and tear. This texture is often plugged into the Diffuse, Bump, or Transmission parameters.
|
|
dirt texture
|
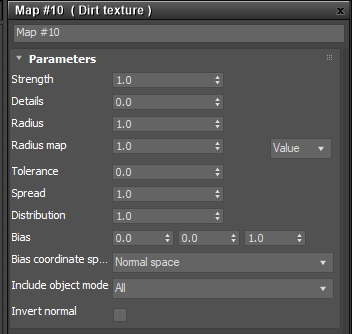
Figure 1: Dirt parameters
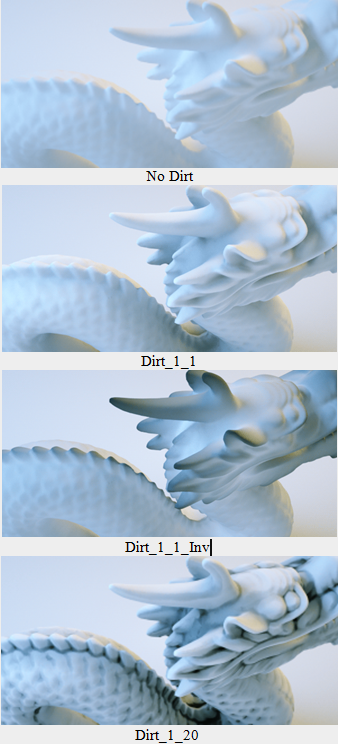
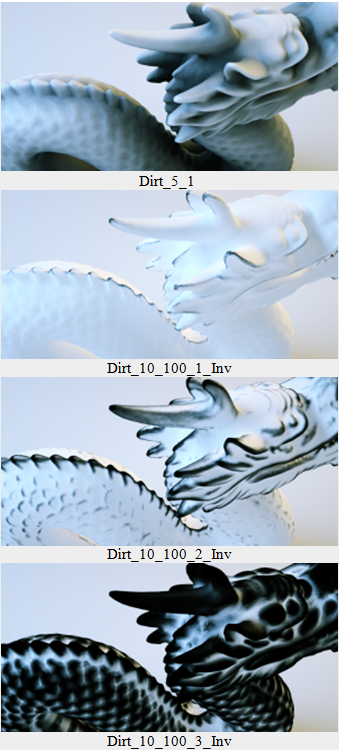
Figure 2 illustrates the Dirt texture with differing Strength, Details, Radius, and Invert settings.
|
|
dirt texture
|
|
|
dirt texture
|
Figure 2
Dirt Texture Parameters
Strength - Controls the Dirt intensity across the geometry surface.
Details - Controls the Details intensity.
Radius - Controls the dirt spread across the model's surface from the recessed parts towards the exposed parts.
Radius Map - Determines the proportion of the maximum area affected by the dirt texture.
Tolerance - Reduces black edges on rough tessellated meshes.
Spread - Controls the ray direction with respect to the normal of the surface. A value of 0 means the dirt direction is shot in the direction of the surface normal and a value of 1 shoots the dirt rays in all directions.
Distribution - Forces the rays to gather closer to the surface normal. A value of 1 is the equivalent to ambient occlusion on a diffuse surface. A value of 0 gathers the rays in the normal direction.
Bias - Any non-zero bias will be used as the shading normal to sample the dirt rays.
Bias Coordinate Space - Determines the coordinate space for the bias vector.
Include Object Mode - By default the mode is set to All, which considers all object intersections in the dirt calculation. If Self is selected, then only the ray-intersection with other objects is used for the dirt calculation.
Invert Normal - Reverses the Dirt texture effect based on the normal surface direction.