OctaneRender® supports participating media inside objects (absorption, subsurface scattering, and volume). These settings are stored in Medium nodes, which are attached to the corresponding input pins of DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters., SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water., or Universal material nodes.
There are five primary types of Medium nodes:
To render with Medium nodes, the Path Tracing or PMC render kernels are the best choices. It is possible to render MediumsThe behavior of light inside a surface volume described by scatter, absorption, and transmission characteristics. using the Direct Light kernel, but the results are not as accurate.
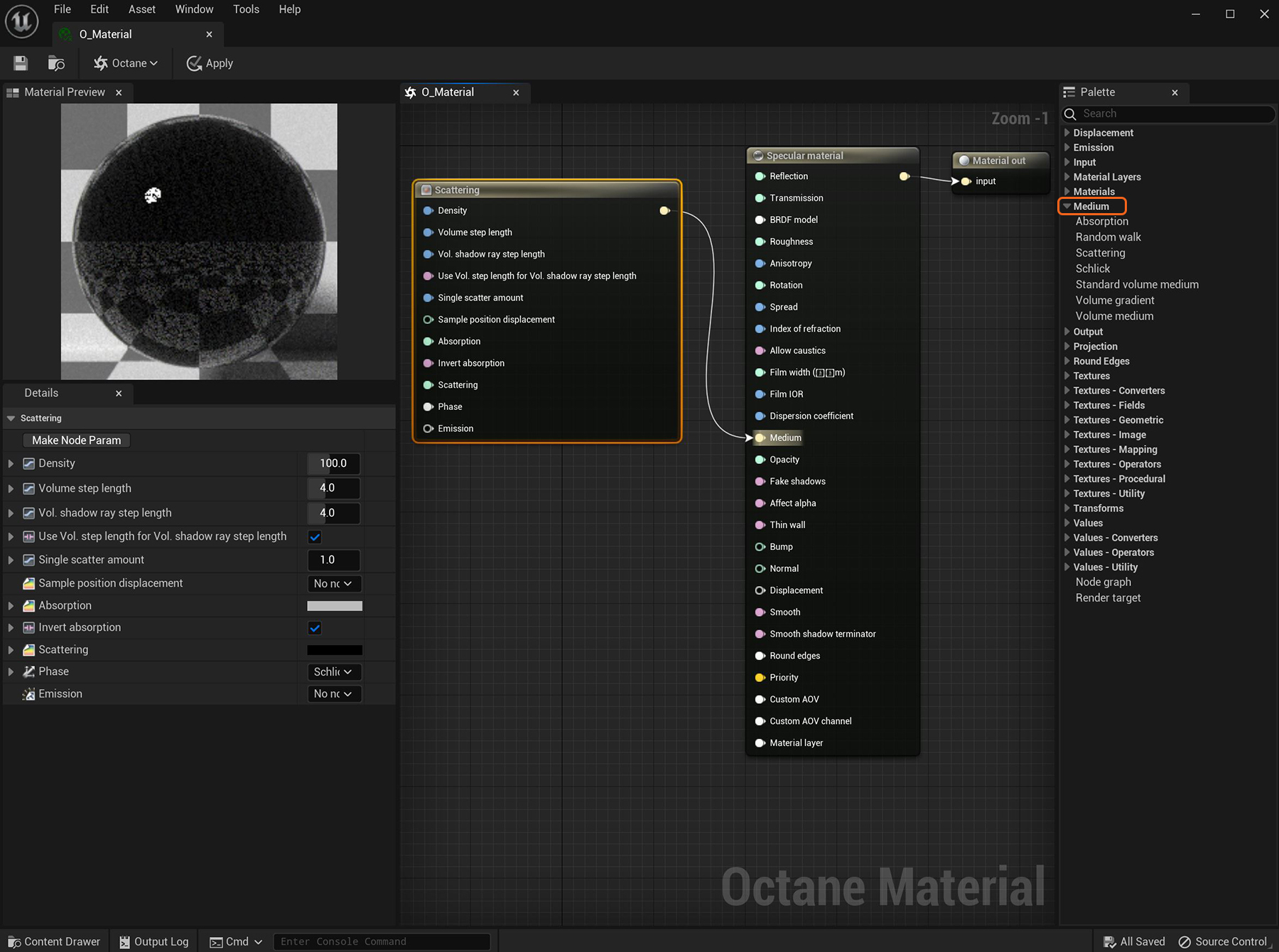
The Medium nodes are found in the Medium section of the Octane MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. window. These nodes connect to the Diffuse, Specular, and Universal materials using their respective Medium slots.

Figure 1: A Scattering medium node attached to the Medium pin on an Octane Specular materialUsed for transparent materials such as glass and water.
Add Medium nodes to MaterialsA set of attributes or parameters that describe surface characteristics. applied to Meshes that define a closed volume. A single-sided plane will not work. For example, a plane representing a leaf will not work if you apply a Medium to a Material. The one exception is a plane representing the ground. OctaneRender® treats the ground plane as an infinite, deep surface.
Specular materials are the best choice when using a Medium node. Set the TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. and Reflection parameters to a non-zero value, or a color other than black, or a Texture map.
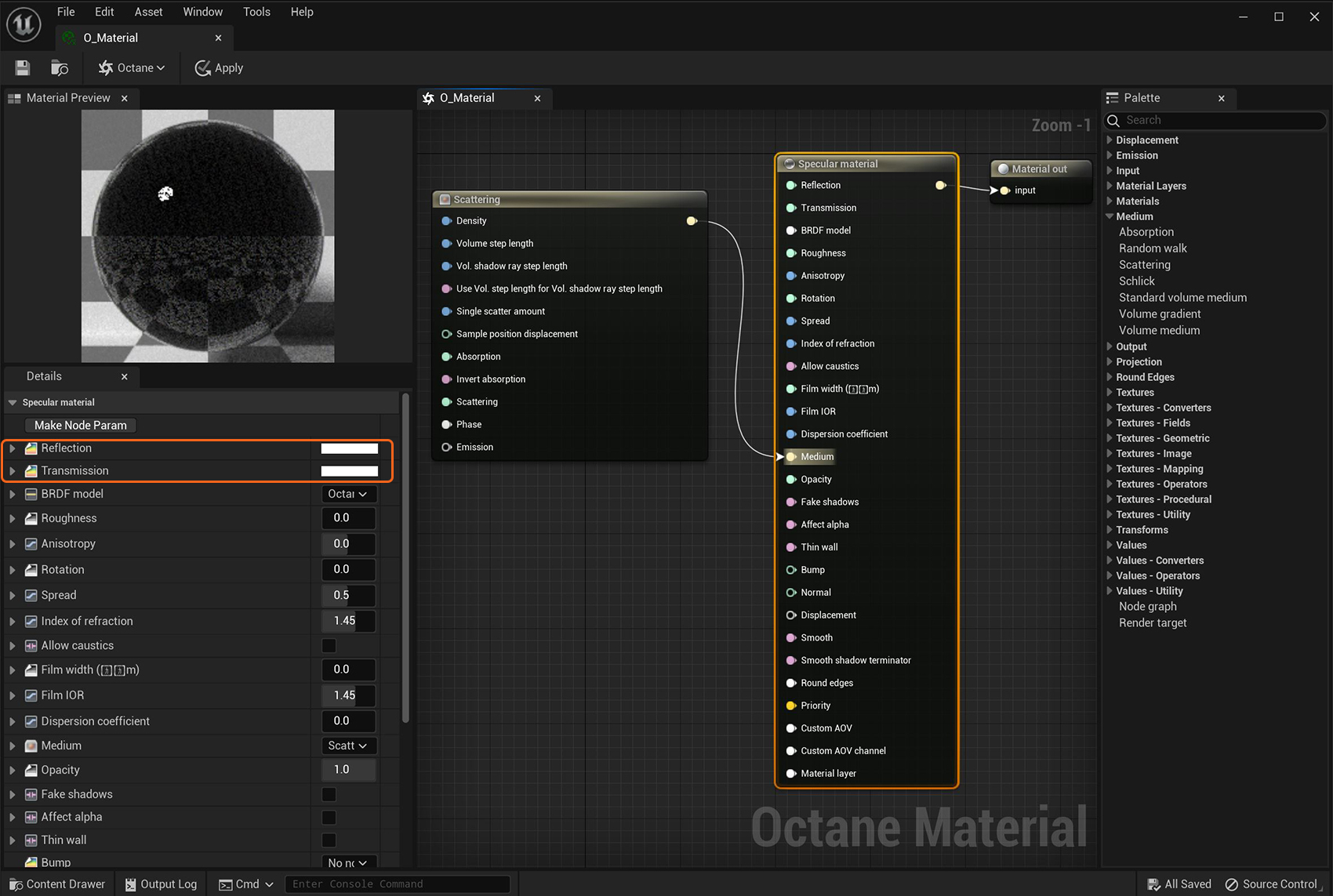
Figure 2: A Medium node connected to a Specular material
When using a Specular shader, you should set the Reflection to a low value because just the part of the spectrum that is not reflected can enter the object for scattering. If you set Reflection to 1.0, all light reflects regardless of the Transmission value. If you set Reflection to 0.0, all light transmits through the surface. However, the result is an unnatural appearance. Reflection values of 0.1 - 0.2 are good starting points.
If the Reflection attribute uses a color, the light transmitted through the surface is shaded as the complementary color. For example, if the reflection is set to yellow, the transmitted light is bluish.
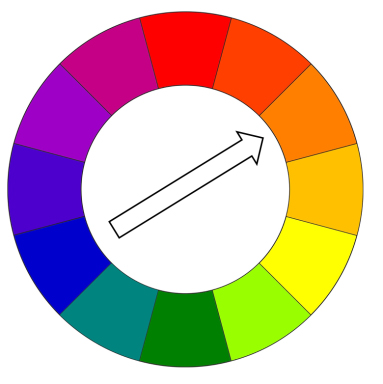
Figure 3 : A diagram shows that complementary colors are opposite each other on the color wheel