Spectron is a procedural lighting system that lets you create procedurally-driven volumetric lighting - like spotlights - with blockers, barn doors, gels (in the Distribution pin) and more. Spectron is exposed as a Procedural light node type, which you can use for quick volumetric effects and spotlight generation (Figure 2).
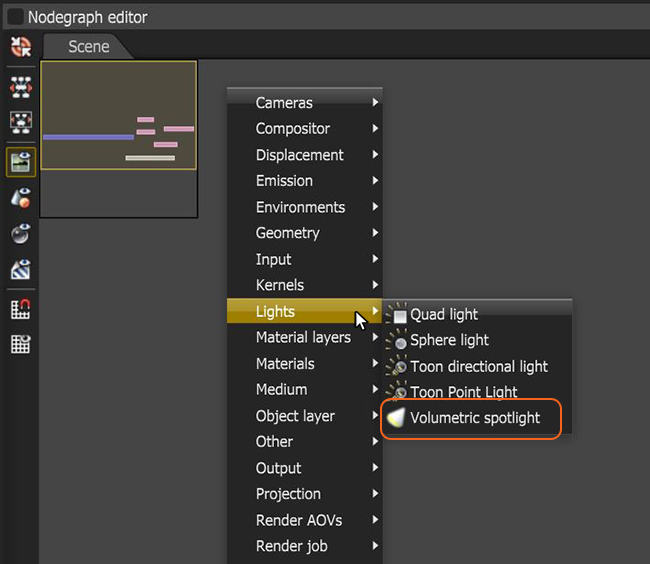
To start using Spectron procedural lighting, right-click anywhere in the Nodegraph Editor, then click on Lights, followed by Volumetric Spotlight (Figure 1).

Figure 1: Creating a Volumetric Spotlight in the Nodegraph Editor
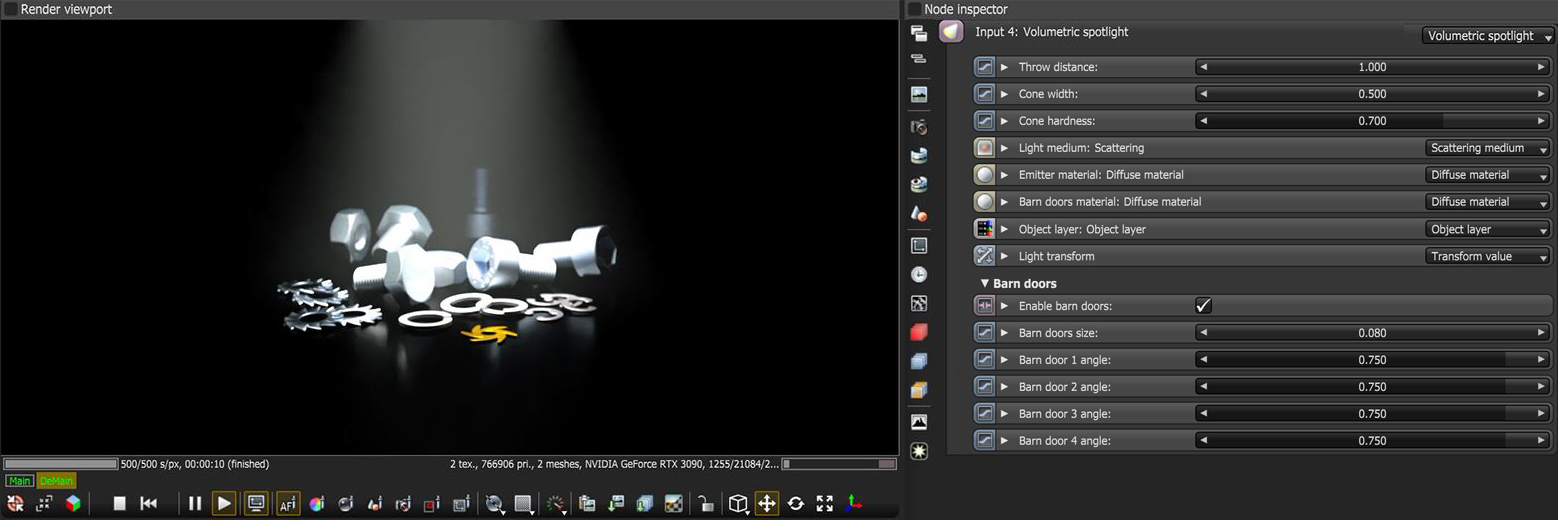
Figure 2: Example of a Volumetric Spotlight with its associated parameters
Throw Distance - The distance from the origin of the light source that the volumetric light will reach.
Cone Width - The width of the volumetric light's cone.
Cone Hardness - Determines the softness/hardness of the light cone's edge.
Light Medium ScatteringDefines how fast light gets scattered when traveling through the medium.
Density - This parameter multiplies against Scattering.
Volume Step Length - Only applicable when rendering Volume mediums. This attribute may need to be adjusted depending on the surface. The default value for the step length is 4 meters. Should the volume be smaller than this, the step length will need to be decreased. Please note that decreasing this will reduce the render speed. Increasing this value will cause the ray marching algorithm to take longer steps. Should the step length far exceed the volume’s dimensions, then the ray marching algorithm will take a single step through the whole volume. Most accurate results are obtained when the step length is as small as possible.
Volume Shadow Ray Step Length - Step length that is used by the shadow ray for marching through volumes.
Use Volume Step Length for Volume Shadow Ray Step Length - Check box for using the Volume Step Length for the Volume Shadow Ray Step Length as well.
Single Scatter Amount - Determines how often the direct light is calculated in the volume.
Sample Position DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface. - Allows a texture to control a volume's sample positions displacement.
AbsorptionDefines how fast light is absorbed while passing through a medium. - Determines the absorption value of the material by assigning a texture. This can be either a grayscale or color texture. When using greyscale values, 0 (black) means that there is no absorption. Values greater than zero determine how quickly the medium absorbs white light (figure 3).
Invert Absorption - Inverts the absorption value allowing the specified absorbed color to be the actual color that is visible.
Scattering - The Scattering value determines how quickly light is scattered as it moves through the surface. A high value means that light is scattered sooner as it enters the surface, a low value means that light passes deeper into the surface before it is scattered. A value of 0 disables scattering entirely. This can be either a grayscale or color texture. When using a float or grayscale texture, values greater than zero determine how quickly the light scatters (figure 5).
Phase - The Phase function controls the direction of the light as it is scattered in the surface. A value of 0 results in light being scattered equally in all directions, positive values result in forward scattering, where the photons continue in roughly the same direction they were going when they entered the surface. Negative values result in backwards scattering where the light moves through the surface in the direction roughly opposite to the angle at which the light entered the surface. Additionally, the Schlick node can be used to control which direction the scattering occurs.
Emission - This parameter is not applicable to the Spectron Light type.
Emitter MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object.: DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. Material
The Diffuse materialUsed for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters.'s Emission parameters are the only options applicable to the Spectron light.
Texture - Sets the light source's efficiency. You can set this to a value, color, or texture. Keep in mind that real-world lights aren't 100% efficient at delivering power at their specified wattage - a 100-watt light bulb doesn't deliver 100 watts of light. This parameter enters the real-world values.
Power - The light source's wattage. You should set each light to their real-world wattage - for example, set a desk lamp to 25 watts, a ceiling lamp to 100 watts, and an LED light to 0.25 watts.
Surface Brightness - Causes emitters to keep a constant Surface Brightness, independent of the emitter surface area.
Keep Instance Power - Enabling this option with Surface Brightness disabled and Uniform Scaling applied to the object causes Power to remain constant.
Double Sided - Allows emitters to emit light from the front and back sides.
Distribution - Controls the light pattern. You can set this to a Greyscale or RGB image so that you can load an Image texture or IESAn IES light is the lighting information representing the real-world lighting values for specific light fixtures. For more information, visit http://www.ies.org/lighting/. file. the Image texture's Projection nodes adjust the light's orientation and direction.
Sampling Rate - Choose what light sources receive more samples.
Light Pass ID - The Light Pass ID captures the respective emitter's contribution.
Visible On Diffuse - Enables light source visibility on diffuse surfaces. It enables Black BodyAn opaque object that emits thermal radiation. In Octane, this is used to designate illumination properties for mesh emitters. or Texture emission light sources to cast illumination or shadows on diffuse objects. Disabling this option disables emission - it's invisible in diffuse reflections, but is still visible on specular reflections. It's also excluded from the direct light calculation. This option is enabled by default.
Visible On SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. - Enables the light source's visibility on specular surfaces, and hides emitters on specular reflections/refractions. This is enabled by default.
Visible on Scattering Volumes - If enabled, the illumination is visible on scattering volumes.
Transparent Emission - Allows light sources to cast illumination on diffuse objects, even if the light source is on transparent material.
Cast Shadows - Enables light sources to cast light and shadows on diffuse surfaces, letting you disable direct light shadows for Mesh emitters. To make this option work, the Direct light calculation must include the emitter (the sampling rate must be greater than 0). This option is enabled by default.
Barn Doors Material: Diffuse Material- A Diffuse material is connected by default to control the surface characteristics of the barn door geometry.
Object Layer - Provides standard Object Layer parameters to control render visibility and light pass options.
Transformation - Provides standard transformation controls for placement and orientation of the light source.
Barn Doors
Enable Barn Doors - Enables or disables the barn door feature.
Barn Door Size - Determines the size of the barn doors.
Barn Door 1-4 Angle - Determines the angle for each of the four barn doors.