The Panoramic camera is used for rendering VRImmersively engaging and experiencing depth perception in a three dimensional scene through stereo vision goggles and head-mounted displays.-related images. There are three types of Panoramic cameras available: Spherical, Cylindrical, and various Cube Map types (+x, -x, +y, -y, +z, -z).

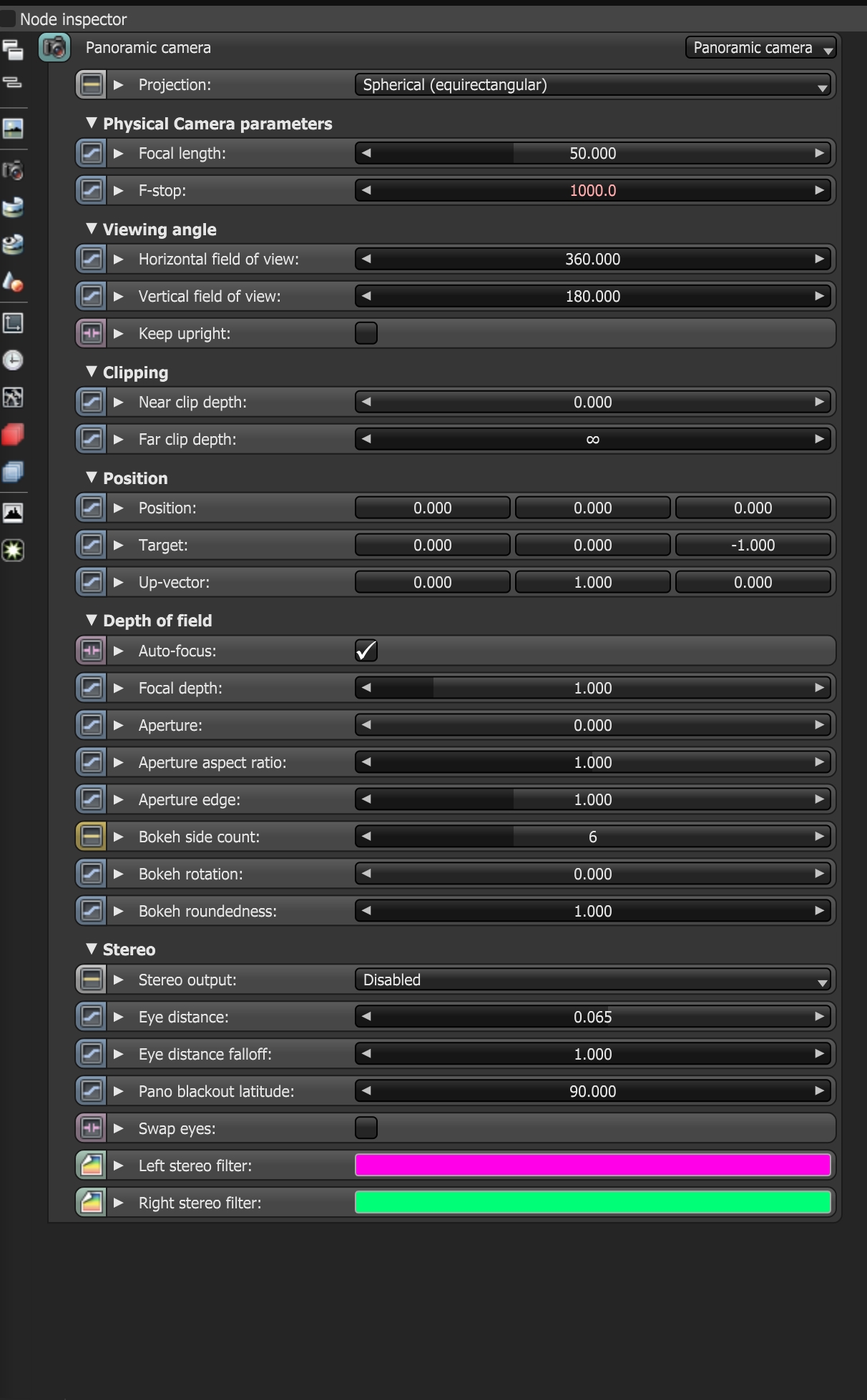
Figure 1: Panoramic camera parameters
Projection - Choose between a Spherical or a Cylindrical camera lens to use as the panoramic projection. Full-sized faced and single-face Cube Map projections are available to render all faces or one face of the cube. This is useful for animation overlays in stereo panorama renderings.
Focal Length - The lens focal length, in millimeters.
F-Stop - This is the aperture to focal length ratio.
Horizontal Field of ViewThe area that is visible to a camera lens usually measured in millimeters. A wide angle lens provides a larger field of view and a telephoto lens provides a narrow field of view. - The horizontal field of view, in degrees. This sets the X-coordinate for the camera's horizontal field of view in the scene. This is ignored when cube mapping is used.
Vertical Field of View - The vertical field of view, in degrees. This sets the Y-coordinate for the camera's vertical field of view in the scene. This is ignored when cube mapping is used.
Keep Upright - The panoramic camera always orients towards the horizon, and the up-vector stays in its default vertical direction (0, 1, 0).
Near Clip Depth - The distance from the camera to the nearest clipping plane, in meters.
Far Clip Depth - The distance from the camera to the farthest clipping plane, in meters.
Position - The camera's position in the scene in world space.
Target - The target position where the camera points to in the scene.
Up-Vector - This is the up direction of the camera in the scene. The default direction is in the Y-direction (0, 1, 0).
Auto-Focus - Focus is kept on the closest visible surface at the center of the image, regardless of the ApertureDetermines how much light enters a camera lens. A large aperture produces a narrow depth of field and a small aperture produces a wide depth of field., Aperture Edge, and Focal Depth values.
Focal Depth - The focal area's depth, measured in meters.
Aperture - The camera lens opening's radius, measured in centimeters. Low values create a wide depth-of-field, where everything is in focus. High values create a shallow depth-of- field, where objects in the foreground and background are out of focus.
Aperture Aspect Ratio - Squashes and stretches the depth-of-field disc.
Aperture Edge - Controls aperture edge detection at all points within the aperture, and modifies the bokeh effect. Lower values produce more pronounced edges to out-of-focus objects affected by a shallow depth-of-field, such as objects in the foreground and background. High values increase the contrast.
Bokeh Side Count - The number of edges making up the bokeh shape.
Bokeh Rotation - The bokeh shape's orientation.
Bokeh Roundedness - The roundness of the bokeh shape's sides.
Stereo Output - Enables stereo mode and specifies which of the following stereo outputs to render with.
Eye Distance - The distance between the left and the right eye in stereo mode, measured in meters.
Eye Distance Falloff - This controls how fast the eye distance reduces towards the poles. This reduces eye strain at the poles when the panorama is viewed through a head-mounted display.
Pano Blackout Latitude - This is the +/- latitude where the panorama cuts off when stereo rendering is enabled. This defines the minimum latitude (in spherical camera coordinates) where the rendering blacks out above this point.
Swap Eyes - This swaps the left and right eye positions when stereo mode shows both.
Left Stereo Filter/Right Stereo Filter - The left and right filter colors that create the anaglyphic stereo effect in the render.