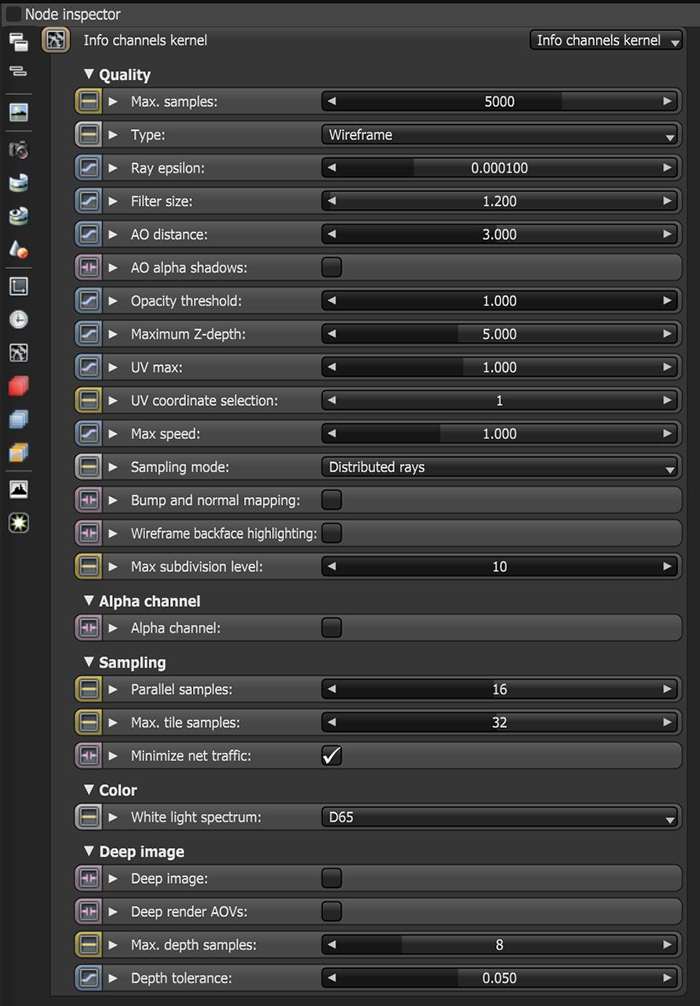
The Info Channel kernel creates false-color images of the scene containing various types of information about the scene. In scenes where the environment is visible, you should enable the Alpha ChannelA greyscale image used to determine which areas of a texture map are opaque and which areas are transparent..

Figure 1: The Info Channel parameters
Quality
Max Samples - This sets the maximum number of samples per pixel before the rendering process stops. Higher values result in cleaner renders. There is no rule as to how many samples per pixel are required for a good render - it depends on the content and complexity of the scene being rendered.
Type - This parameter specifies the various passes that the compositing process can render and use.
Ray Epsilon - The distance between the geometry and the light ray when calculating ray intersections for lighting and shadowing. Larger values push rays away from the geometry surface. Lower values are more accurate, but can cause artifacts on large or distant objects. Ray Epsilon is similar to ray tracing bias in other rendering engines. Adjust Ray Epsilon to reduce artifacts in large-scale scenes.
Filter Size - Sets the filter size in terms of pixels. This can improve aliasing artifacts in the render. However, if the filter is set too high, the image becomes blurry.
AO distance - Sets the maximum distance of the ambient occlusion shading's spread.
AO Alpha Shadows - Takes the surface opacity as determined by its shader into account when rendering with the Ambient Occlusion info channel.
Opacity Threshold - While checking Opacity channels, the geometry with an Opacity value greater than or equal to this parameter's value is treated as opaque.
Maximum Z-DepthA measure of object distances from the camera typically represented as a grayscale image. - Determines the maximum depth as shown in the shading of the Z-Depth info channel pass.
UV Max - Sets the maximum value shown for the texture coordinates.
UV Coordinate Selection - Specifies the set of UV coordinates to use.
Max Speed - Speed mapped to the maximum intensity in the motion vector channel. A value of 1 specifies a maximum movement of 1 screen width in the shutter interval.
Sampling Mode - Enables motion blur and depth of fieldThe distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions. source: wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field), and sets the pixel filtering modes.
Bump And Normal Mapping - Enables Bump and Normal map rendering in images created with Info Channel renders.
Wireframe Backface Highlighting - Enables backface highlighting in the Wireframe channel.
Max Subdivision Level - The maximum subdivision level applied on the scene's geometry. A value of 0 disables subdivision.
Alpha Channel
Alpha Channel - Enables direct lighting through Opacity maps. If disabled, ray tracing is faster, but it renders incorrect shadows for alpha-mapped geometry or Specular materials with Fake Shadows enabled.
Sampling
Parallel Samples - Controls how many samples are calculated in parallel. Small values require less memory to store the sample's state, but increases render time. High values require more memory, but reduce render time. The change in performance depends on the scene, the GPUThe GPU is responsible for displaying graphical elements on a computer display. The GPU plays a key role in the Octane rendering process as the CUDA cores are utilized during the rendering process. architecture, and the number of shader processors contained on the GPU.
Maximum Tile Samples - This controls the number of samples per pixel that OctaneRender® will render until it takes the result and stores it in the frame buffer. A higher value means that results arrive less often in the frame buffer, but reduces the CPU overhead during rendering.
Minimize Net Traffic - If enabled, OctaneRender® distributes the same tile to the net render slaves until it reaches the max samples/pixel, and then it distributes the next tile to slaves. This option doesn't affect work done by local GPUs. A Render Node can merge all of its results into the same cached tile until the Primary Render Node switches to a different tile. You should set the maximum samples per pixel to a reasonable value, or else the network rendering focuses on the first tile for a long time.
Color
White Light Spectrum - Controls the appearance of colors produced by spectral emitters (daylight, environment, black body).This determines the spectrum that will produce white (before white balance) in the final image.
Deep Image - Enables deep pixel image rendering for deep image compositing. It is covered in more detail in the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.
Deep Render PassesRender passes allow a rendered frame to be further broken down beyond the capabilities of Render Layers. Render Passes vary among render engines but typically they allow an image to be separated into its fundamental visual components such as diffuse, ambient, specular, etc.. - Includes render passes for deep image pixels.
Maximum Depth Samples - This is used when Deep Image Rendering is enabled. It sets the maximum number of depth samples per pixel, and is covered in more detail in the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.
Depth Tolerance - This is used when Deep Image Rendering is enabled. The depth samples with a relative depth difference below this value are merged together. This is covered in more detail in the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.