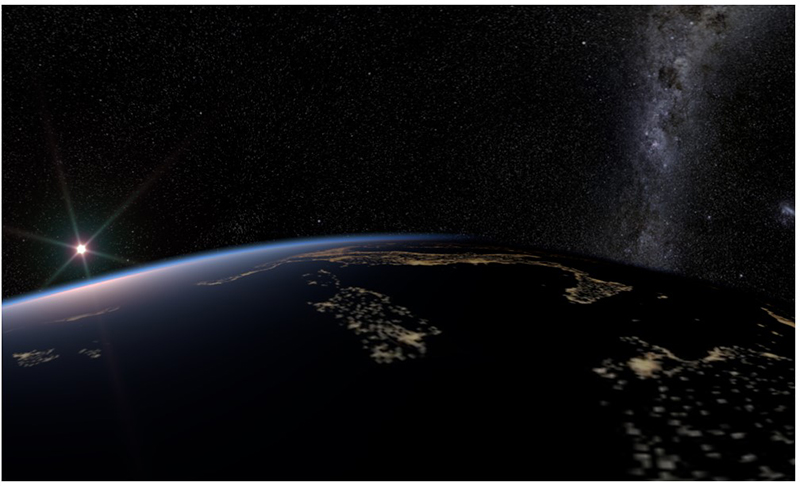

This environment type is a flexible Nishita Sky model. It is most useful when rendering scenes as they are seen from outer space (figure 1). For its effects to be visible, the camera has to have a very high altitude as it moves out into outer space to view the expansive horizon of the planetary body.

Figure 1: Using the Planetary Environment to create a space scene.
It takes into account the conditions within and beyond the atmosphere of a planetary body (e.g. planet earth) and its surroundings in space. Instead of a single ground color and a sky/sunset color, there is a planetary surface that reflects and emits light. Most importantly, this node serves to extend the environment's medium (volume rendering and subsurface scattering) with an atmospheric scattering through the planetary body's atmosphere. This atmospheric scattering is based on the Nishita Sky Model, a physically based model which displays the variations of color which are optical effects caused by the particles in the atmosphere.
This environment is not connected to the camera and this allows you to zoom the camera view of the objects in the scene in and out while not affecting the position of the environment in the scene. It is a physically based model so it gathers optical depth (transmittance) from the sun position, if the sun position is greater than 0.0f on y axis (upward direction), then it will be colored. If you put it below horizon (i.e. sun position less than 0.0f on the Y axis) then it won't gather transmittance so it will be invisible.
The Planetary Environment can be accessed in the OctaneRender panel under the Environment rollout (figure 2).
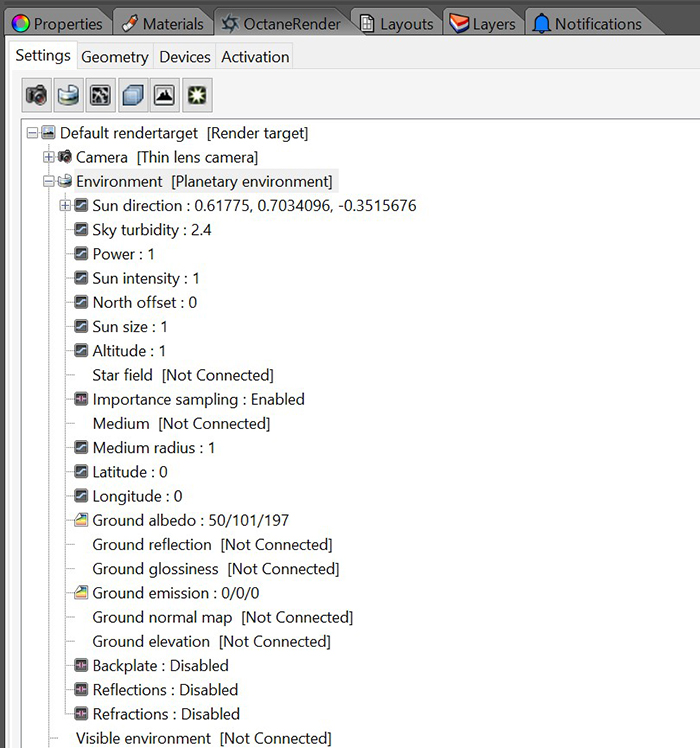
Figure 2: Accessing the Planetary Environment parameters in the OctaneRender panel.
Sun Direction
Determines the location of the sun in the sky.
Sky Turbidity
The Turbidity can be used to adjust the sharpness of the sun lights shadows. A low value creates sharp shadows (like on a sunny day) and a higher value diffuses the shadows similarly to a cloudy day.
Power
The Power slider can be used to adjust the strength of the light. This can affect overall contrast and exposure level of the image.
Sun Intensity
Scale Factor that is applied only to the sun. Used to adjust the relative power of the sun compared to the sky.
North Offset
The North offset slider can be used to adjust the actual North direction of the scene. This is useful for Architecture Visualization to ensure the direction of the sun is accurate to the scene.
Sun Size
This allows users to control the sun radius in the daylight environment.
Altitude
The camera's altitude. Set this to a very high value in order to view the expansive horizon of the planetary body.
Star Field
Texture that conveys star fields behind the planet.
This toggles the importance sampling of the sky texture – similar to the importance sampling in the texture environment.
Medium
This parameter can accept an AbsorptionDefines how fast light is absorbed while passing through a medium., ScatteringDefines how fast light gets scattered when traveling through the medium., or Volume medium node to create volume/fog effects across the scene.
Medium Radius
Adjusts the scale of the medium.
Latitude
The latitude coordinate of the camera's current position.
Longitude
The longitude coordinate of the camera's current position.
Ground Albedo
The surface texture map on the planet.
Ground Reflection
The specular texture map on the planet.
Ground Glossiness
The planetary glossiness.
Ground Emission
The planet's surface texture map at nighttime.
Ground Normal Map
Normal map on the planet.
Ground Elevation
Elevation map on the planet.
Backplate
This makes the Visible environment behave as a background plate.
Reflections
Makes the Visible environment visible in material reflections.
Refractions
Makes the Visible environment visible in the material refractions.