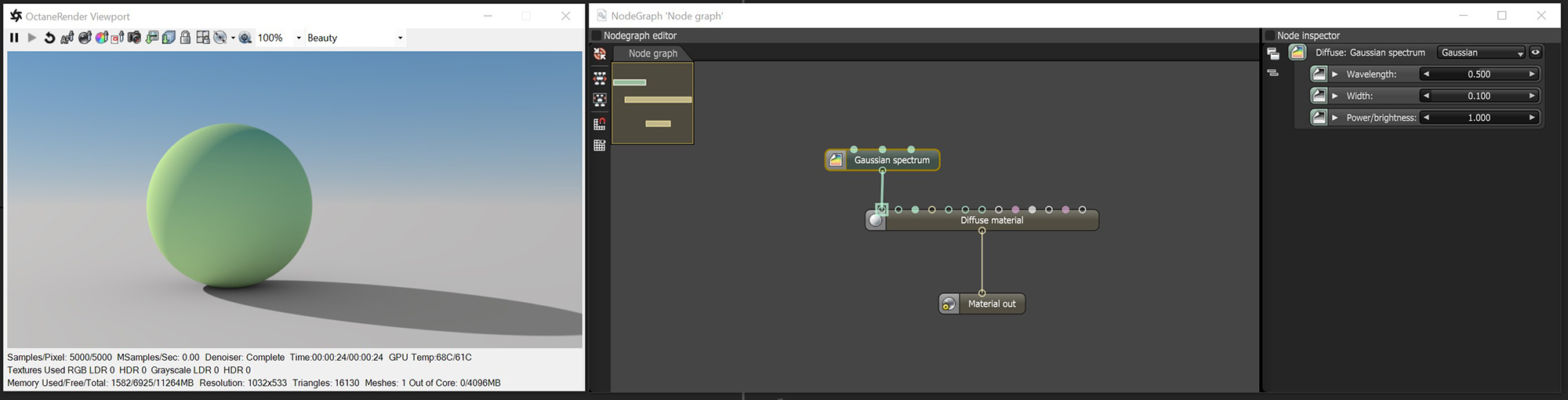
The Gaussian Spectrum texture is based on a Gaussian distribution spectrum. Wavelength sets the center of the spectrum, and Width sets the width of the curve. The narrower the width, the more pure and saturated the color (figure 1). The narrower the width, the more pure and saturated the color. In the following illustration, the NodeGraph Editor window is used to clearly illustrate the association of the various texture nodes.

Figure 1: Gaussian Spectrum texture
Wavelength
This represents the mean wavelength approximation between 380nm - 720nm. The lower wavelength values appear bluish, while higher wavelengths (around 700nm) appear reddish.
Width
Almost no color is visible when using a width of 0.000. On the other hand, a width of 1.000 means the color is spread thin over a large space, and the texture appears faint.
Power
The brightness of the texture.