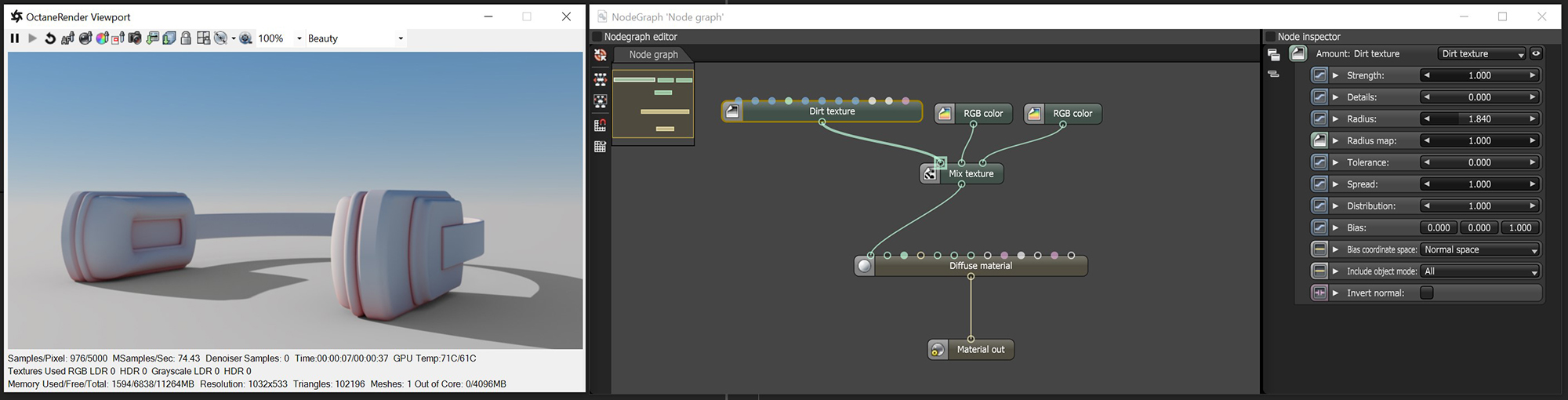
The Dirt texture can create different shading effects based on ambient occlusion calculations (figure 1). This texture is useful for simulating dirt, dust, or wear and tear, as well as blending textures based on a surface's recesses.
Dirt textures are often connected to the DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters., Bump, or TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. inputs of OctaneRender® materials.
In the following illustration, the NodeGraph Editor window is used to clearly illustrate the association of the various texture nodes.

Figure 1: A Dirt texture node determining the Mix amount for two RGB Color nodes
Strength
Controls the Dirt intensity across the geometry surface.
Details
Controls the Details intensity.
Radius
Controls the dirt spread across the model's surface from the recessed parts towards the exposed parts.
Tolerance
Reduces black edges on rough tessellated meshes.
Invert Normal
Reverses the Dirt texture effect based on the normal surface direction.