
The GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals. MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. is used for shiny materials such as plastics. It may also be used for metals, but the Metallic Material is better suited for this purpose.

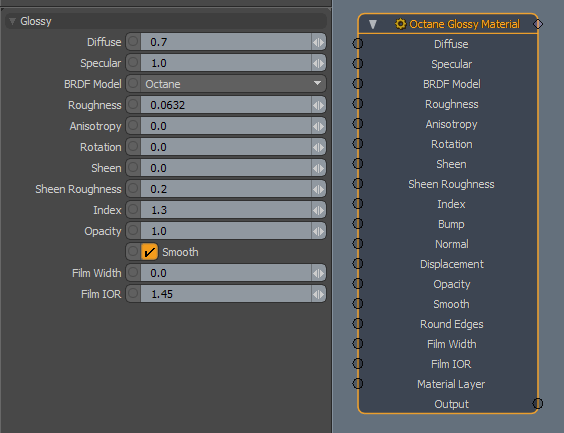
DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. - The material's base color (also known as albedo). You can set the Diffuse color by using a value or connecting a texture.
SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. - Determines the intensity for specular reflections on the surface. This parameter accepts values or textures. In most cases, specular highlights are white or colorless.
BRDF Model - Determines how light is reflected. See BRDF Models for details.
Roughness - Adjusts the Specular reflection channel's roughness.
Anisotropy - Anisotropy values for the Specular channel. Controls the material's reflectance uniformity. A value of -1 is horizontal, while 1 is vertical. A value of 0 is Isotropic.
Rotation - Rotation values for the Anisotropy channel.
Sheen - The material's sheen color.
Sheen Roughness - The Sheen channel's roughness.
Index - Index of refraction. Determines the reflection strength on the surface based on Fresnel's law. With a value greater than 1, reflection is strongest on the surface parts that turn away from the viewer's angle (grazing angles), while the reflection appears weaker on the surface parts perpendicular to the viewing angle. The Glossy Material includes a special case for a value of 1, which disables Fresnel reflections and makes the material 100% reflective. The Specular channel's color determines the reflective highlight's color.
Bump - Creates fine surface detail by simulating a relief using a Greyscale texture interpreted as a height map.
Normal - Creates fine surface detail by distorting normals using an RGB image.
DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface. - Adjusts the height of a surface's vertices at render time using a texture. See Displacement for details.
Opacity - Controls the material's opacity with a Greyscale texture.
Smooth - Smooths surface normals. If this option is disabled, edges between polygons appear sharp, giving the surface a faceted look.
Round Edges - Connects to a Round Edges node. Rounds geometry edges by using a shading effect instead of creating additional geometry. See Round Edges for details.
Film Width - The film coating's thickness. This simulates the look of thin film on a surface, like an oil slick which creates a rainbow effect. Larger values increase the effect's strength.
Film IOR - The film's index of refraction. This value adjusts the visible colors in the film.
Material Layer - Adds a Material Layer above the base material. See Material Layers for details.