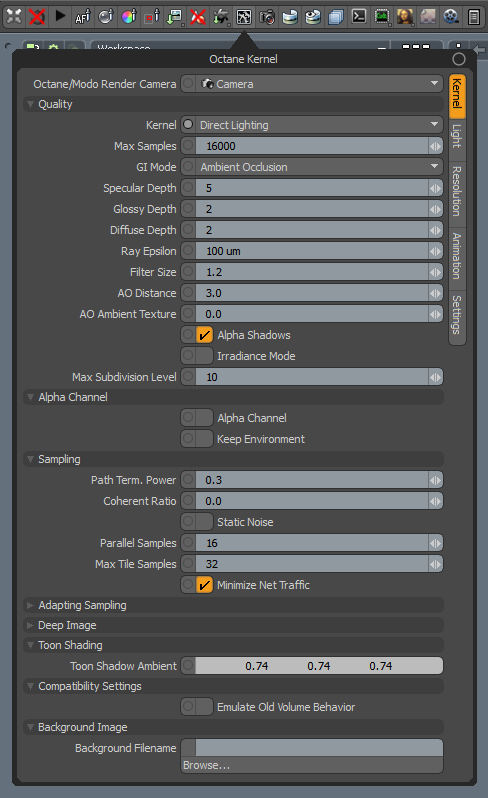
The Direct Lighting Kernel is generally used for faster preview rendering. Direct Lighting is not unbiased and will not yield photorealistic results, but because of its speed, it's ideal for rendering animations or stills, depending on the project's demands.
Direct Lighting Kernel settings can be accessed from the Render Toolbar > Kernel Button > Kernel.

Octane/Modo Render Camera - Select the camera used for rendering.
Kernel - Allows you to select the kernel type.
Max Samples - Sets the maximum number of samples per pixel before the rendering process stops. Higher values result in cleaner renders. There is no rule as to how many samples per pixel are required for a good render - it depends on the content and complexity of the scene being rendered.
GI Mode - There are three types of Global Illumination modes in the Direct Lighting kernel:
None - Includes direct lighting from the sun or area lights. Shadowed areas receive no contribution, and will be black.
Ambient Occlusion - Standard ambient occlusion. This mode provides realistic images, but offers no color bleeding.
DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. - This gives a GI quality that is in between Ambient Occlusion and Path Tracing, but without caustics. The advantage is much faster rendering than Path Tracing and PMC. It is similar in some ways to brute force indirect GI in other engines.
SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. Depth - Controls the number of times a ray refracts before dying. Higher numbers mean higher render times, but more color bleeding and more details in transparent materials. Low numbers introduce artifacts or turn some refractions into pure black.
GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals. Depth - Controls the number of times a ray reflects before dying. Higher numbers mean higher render times. Values lower than 4 can introduce artifacts, or turn some reflections into pure black.
Diffuse Depth - The maximum number of diffuse reflections if GI Mode is set to Diffuse.
Ray Epsilon - The distance between the geometry and the light ray when calculating ray intersections for lighting and shadowing. Larger values push rays away from the geometry surface. Lower values are more accurate, but cause artifacts on large or distant objects. Ray Epsilon is similar to ray tracing bias in other rendering engines. Adjust Ray Epsilon to reduce artifacts in large-scale scenes.
Filter Size - Sets the filter size in terms of pixels. This improves aliasing artifacts in the render. However, if the filter is set too high, the image can become blurry.
AO Distance - The distance of the ambient occlusion shadowing spread in units. This setting provides realistic results, depending on the scale of the objects in the scene. Small values are more appropriate for small objects like toys, and larger values are more appropriate for something like a house.
AO Ambient Texture - Specifies an Ambient Occlusion texture, which is used for the AO calculation instead of the environment. If not specified, the environment will be used instead. To add a texture, drag this property into a schematic workspace, and attach a texture node to it.
Alpha Shadows - This enables direct light through Opacity maps. If disabled, ray tracing is faster, but it renders incorrect shadows for alpha-mapped geometry or Specular materials with fake shadows enabled. Alpha Shadows allows any object with transparency (Specular materials, materials with Opacity settings, and Alpha Channels) to cast a shadow instead of behaving as a solid object.
Irradiance Mode - This renders the first surface as a white Diffuse material. Irradiance Mode is similar to Clay Mode, but it applies to just the first bounce. It disables the Bump channel and makes samples that are blocked by back faces transparent.
Max Subdivision Level - The maximum subdivision level applied on the scene's geometry. A value of 0 disables subdivision.
Alpha ChannelA greyscale image used to determine which areas of a texture map are opaque and which areas are transparent. - Removes background images or environment colors from the rendered image, without affecting lighting cast by the environment. This is useful if you want to composite the render over another image without the background being present.
Keep Environment - Used in conjunction with the Alpha Channel setting. It makes the background visible in the rendered image while also keeping the Alpha Channel.
Path Term. Power - Tweaks samples-per-second vs. convergence (how fast noise vanishes). Increasing this value causes the kernels to keep paths shorter and spend less time on dark areas, which means they stay noisy longer, but it also increases samples-per-second. Reducing this value causes kernels to trace longer paths on average and spend more time on dark areas. In short, high values increase the render speed, but they may lead to higher noise in dark areas.
Coherent Ratio - Increasing this value increases the render speed, but it introduces low-frequency noise or blotches. Eliminating the blotchy appearance requires a few hundred or even a few thousand samples per pixel, depending on the scene's contents.
Static Noise - Keeps noise patterns static between rendered frames in a sequence. The noise is static as long as the same GPUThe GPU is responsible for displaying graphical elements on a computer display. The GPU plays a key role in the Octane rendering process as the CUDA cores are utilized during the rendering process. architecture is used for rendering. Different architectures produce different numerical errors, which manifest as small differences in the noise pattern.
Parallel Samples - Controls how many samples OctaneRender® calculates in parallel. Smaller values require less memory to store the sample's state, but cause slower renders. High values require more memory, but reduce the render time. The change in performance depends on the scene and the GPU architecture.
Max Tile Samples - Controls the number of samples per pixel that OctaneRender® will render before storing the result in the render buffer. Higher values mean that results arrive less often in the film buffer.
Minimize Net Traffic - Distributes the same tile to the net render slaves until OctaneRender® reaches the maximum number of samples per pixel for that tile, and then it distributes the next tile to slaves. This option doesn't affect work done by local GPUs. A slave can merge all of its results into the same cached tile until the master switches to a different tile.
Adaptive SamplingA method of sampling that determines if areas of a rendering require more sampling than other areas instead of sampling the entire rendering equally. Parameters - See Adaptive Sampling for more details.
Deep ImageRenders frames with multiple depth samples in addition to typical color and opacity channels. Parameters - See the Deep Image topic for more details.
Toon Shadow Ambient - This is the ambient modifier of Toon Shadowing.
Emulate Old Volume Behavior - This is for previous scenes with Volume geometry that are set up using the former volume rendering system in earlier versions of OctaneRender®. When enabled, older scenes built with earlier versions render using the former volume rendering system. When disabled, OctaneRender® renders volumes using the new volume rendering system, and any pre-existing volumes must be set up again in order to render correctly.
Background Filename - Full path and filename of the background texture map. Delete the filename in order to clear the background image from the Octane Viewport.