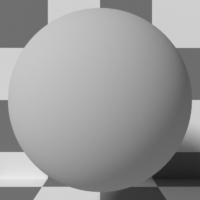
The DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. simulates a rough surface that reflects light in all directions, therefore specular reflections are not visible. This material can also be used to create light emitting surfaces used by Mesh EmittersThe ability for a surface to emit illumination usually described by a Black Body or Texture emission type..

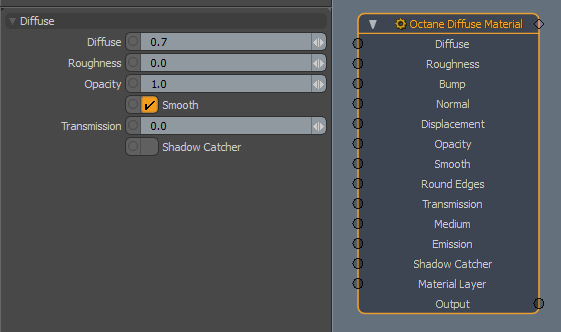
Diffuse - The material's base color (also known as albedo). Can be controlled by a value or texture.
Roughness - Determines the spread of highlights on the surface. A high value can simulate very rough surfaces such as sand paper or clay. Can be controlled by a value or texture.
Bump - Creates fine surface detail by simulating a relief using a Greyscale texture interpreted as a height map.
Normal - Creates fine surface detail by distorting normals using an RGB image.
DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface. - Adjusts the height of a surface's vertices at render time using a texture. See Displacement for details.
Opacity - Controls the material's opacity with a Greyscale texture.
Smooth - Smooths surface normals. If this option is disabled, edges between polygons appear sharp, giving the surface a faceted look.
Round Edges - Connects to a Round Edges node. Rounds geometry edges by using a shading effect instead of creating additional geometry. See Round Edges for details.
TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. - Uses a color or texture that is mixed with the material's Diffuse color, and is most noticeable in areas affected by indirect lighting.
Medium - Connects to a Medium node. See MediumsThe behavior of light inside a surface volume described by scatter, absorption, and transmission characteristics. for details.
Emission - Allows the material to emit light by connecting it to an Emission node. See Mesh Emitters for details.
Shadow CatcherThe Shadow Catcher can be used to create shadows cast by objects onto the surrounding background imagery. The shadows cast are not limited to simply a ground plane but can be cast onto other surfaces of varying shapes. - Makes the material a shadow catcher, which captures shadows cast by other objects. It becomes visible in areas that are in shadows, while other areas become transparent.
Material Layer - Adds a Material Layer above the base material. See Material Layers for details.