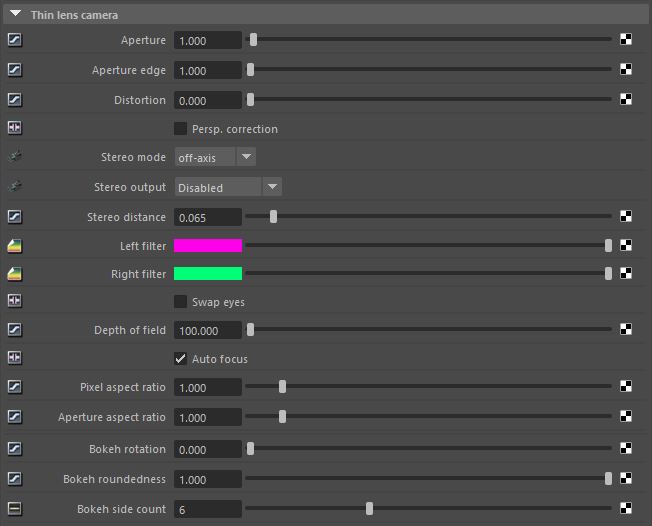
Figure 1: The Thin Lens Camera attributes
The Thin Lens camera is the same as a standard photographic camera used to render Maya® scenes.

Figure 1: The Thin Lens Camera attributes
ApertureDetermines how much light enters a camera lens. A large aperture produces a narrow depth of field and a small aperture produces a wide depth of field. - The radius of the camera's lens opening, measured in centimeters. Low values create a wide depth of fieldThe distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions. source: wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field) (DOFThe distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions. source: wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field)), where everything is in focus. High values create a shallow depth of field, where objects in the foreground or background are out of focus, depending on what the camera focuses on.
Aperture Edge - Controls aperture edge detection at all points within the aperture and modifies the lens's bokeh effect. Lower values give more pronounced edges to out-of-focus objects affected by a shallow DOF. High values increase the contrast towards the edge.
Distortion - Adjusts the spherical and cylindrical distortion. The rendered image displays the entire sphere and uses equidistant cylindrical projection.
Perspective Correction - If the up-vector is vertical, enabling this option keeps vertical lines parallel. This is useful for architectural rendering, where you want to render images of tall buildings from a similar height as the human eye but keep the vertical lines parallel.
Stereo - Chooses between two types of stereo camera: Off Axis or Parallel. This option only applies when you enable Stereo rendering.
Stereo Output - Specifies the output rendered in Stereo mode. Disabled is the default choice.
Stereo Distance - The distance between the left and the right eyes in Stereo mode, measured in meters.
Left Stereo Filter/Right Stereo Filter - Adjusts the colors that create the anaglyphic stereo effect in the render.
Swap Eyes - This swaps left and right eye positions when Stereo mode shows both images.
Depth Of Field - The depth of the plane in focus, measured in meters.
Auto Focus - Overrides the Focal Depth parameter and focuses on objects towards the center of the camera view.
Pixel Aspect Ratio - Squashes or stretches the DOF plane and renders it to a non-square pixel format like NTSC or PAL.
Aperture Aspect Ratio - Squashes or stretches the DOF plane.
Bokeh Rotation - Bokeh settings adjust the quality of highlights when DOF blurring is apparent. Raising the aperture increases DOF blurring. Bokeh Rotation rotates the blurred highlights' shape. This becomes more obvious when you lower the Bokeh Roundness value.
Bokeh Roundness - Keeps blurred highlights rounded. Lowering this value reduces the roundness and increases the highlight edges.
Bokeh Side Count - Sets the number of edges on blurred highlights.

Figure 2: From left to right, the sphere is rendered with a Bokeh Roundness set to 6, 4, and 3