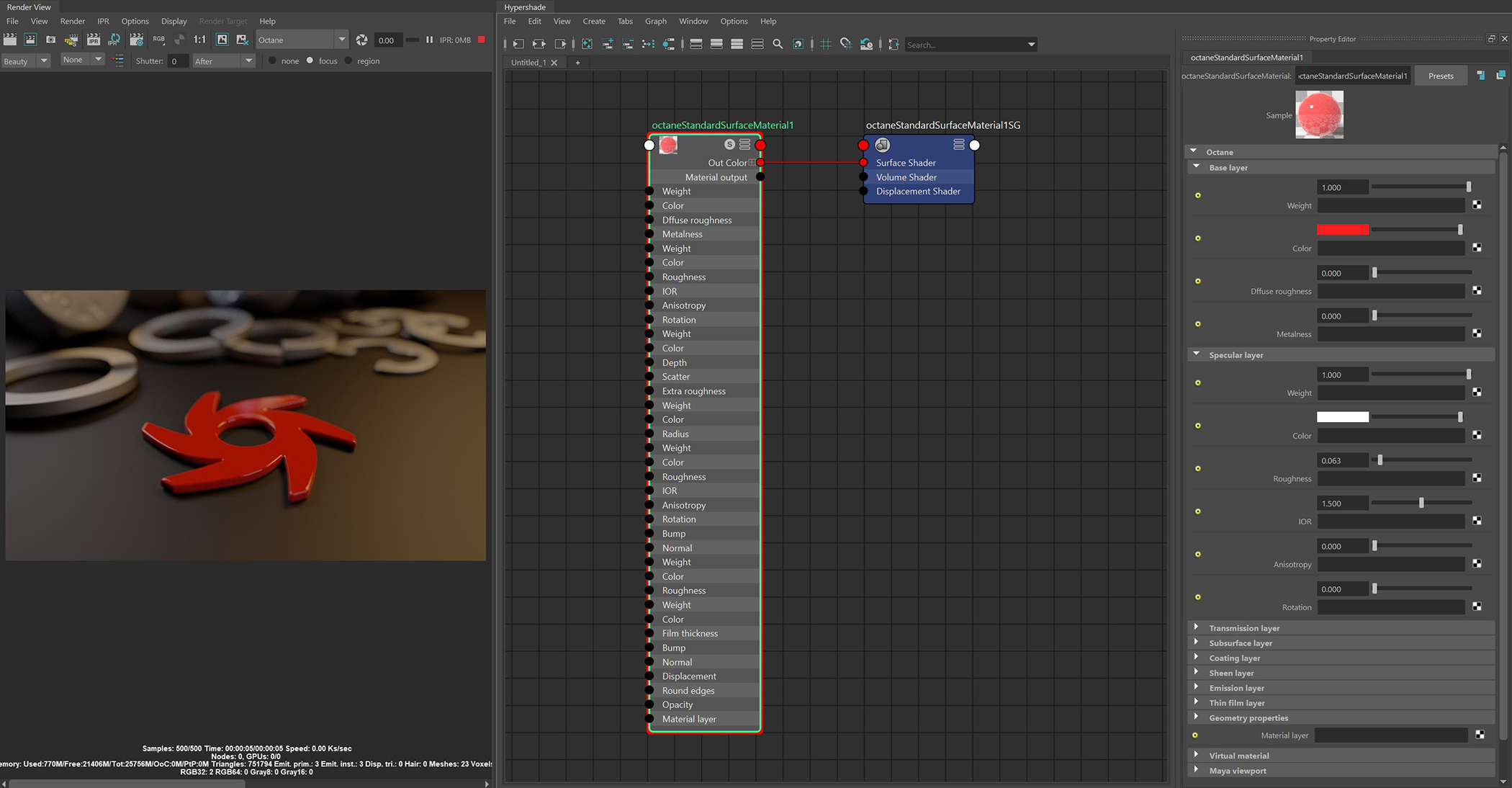
The Standard Surface material closely aligns with the Autodesk Standard Surface shader specification. Much like the Octane Universal MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object., the Standard Surface material is an uber surface shader with multiple layers of BSDF(s). It can address nearly all surface characteristics in one unified material (figure 1).

Figure 1: The Standard Surface material and its associated attributes
Weight - Determines the contribution of the base layer to the shader results.
Color - Determines the base color.
DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. Roughness - Higher values result in a micro-level of roughness being applied to the base layer.
Metalness - Determines whether the material behaves in a dielectric (value of 0) fashion or a metallic (value of 1) fashion.
Weight - Determines the contribution of the specular layer to the shader results
Color - Determines the specular color, however, leaving this parameter at white produces the most physically accurate result.
Roughness - Higher values will introduce roughness to the specular reflection and transmission channels.
IOR - The index of refraction controlling the Fresnel effect of the specular reflection and TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume., if activated.
Anisotropy - Controls the shape/direction of the specular and transmission characteristics, -1 is horizontal and 1 is vertical.
Rotation - Controls the orientation of the anisotropic specular reflection.
Weight - Controls the amount of light scattering through the surface.
Color - Determines the color accumulated as light rays travel deeper inside the surface. For instance, red glass becomes a deeper red where light rays travel through thicker parts of the surface.
Depth - Determines the depth rays have to travel inside the surface for the transmission color to be realized.
Scatter - Determines the scattering of the transmission color inside the surface, not to be confused with subsurface scattering which affects the propagation and decay of light in different directions under the surface.
Scatter Anisotropy - Controls the directional bias of the scattering effect. A value of 0 scatters evenly in all directions.
Dispersion Abbe - Determines how much the index of refraction varies across wavelengths.
Extra Roughness - Adds additional roughness in the refractive areas of the surface volume.
Dielectric Priority - When nested dielectric surfaces overlap, only surfaces with the highest priority contribute.
Fake Shadows - If enabled, light will be traced directly through the material during the shadow calculation, ignoring refraction.
Affect Alpha - If enabled, refractions will be added to the alpha channel data.
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through the object.
Weight - Blends between the diffuse and subsurface scattering. When set to 1, there is only subsurface scattering. When set to 0, there is only diffuse characteristics.
Color - Determines the color that is scattered under the surface of the object.
Radius - Determines the distance light can scatter below the surface before scattering back out.
Scale - Controls the distance the light travels under the surface. It scales the subsurface radius data and multiplies against the subsurface color.
Anisotropy - Controls the direction of the subsurface characteristics, a value of 0 scatters evenly in all directions.
Weight - Controls the amount of coat that is added on top of the base layer and other material characteristics. The coating is reflective and considered to be dielectric.
Color - Determines the color of the coating on top of all colors and characteristics from layers below the coating layer.
Roughness - Controls the glossiness of the coating's specular reflections.
IOR - The index of refraction that defines the Fresnel reflectivity of the coating layer.
Anisotropy - Controls the shape/direction of the coating's specular characteristics.
Rotation - Controls the orientation of the coating's anisotropy effect.
Bump - Allows for a bump texture to be applied to the coating layer.
Normal - Allows for a normal map to be applied to the coating layer.
Weight - Controls the amount of sheen that is added on top of the base layer and other material characteristics. This characteristic is mainly used to simulate surfaces such as velvet or satin.
Color - Determines the color of the sheen on top of all colors and characteristics from layers below the sheen layer.
Roughness - Controls the glossiness of the sheen's specular reflections.
Emission - Allows for either the Blackbody or Texture Emission nodes to be connected to the material.
Weight - Controls the amount of emitted light.
Color - Determines the color of the emitted light.
Film Thickness - The film coating's thickness, mainly used to simulate to look of a thin layer of additional surface material.
Film IOR - The film coating's IOR.
Thin Wall - When enabled, this parameter provides the effect that the surface is translucent. This option should only be used with objects that are single sided.
Bump - Used to simulate surface relief using a greyscale texture map.
Normal - Used to distort the normals of the surface using a normal map generated in texturing applications.
DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface. - Used to distort the actual surface of the object using a greyscale image.
Smooth - If enabled, the mesh's triangles will be smoothed. If disabled, the mesh's surface will appear facetted.
Smooth Shadow Terminator - If enabled, the self-intersecting shadow terminator for low polygon objects is smoothed according to the polygon's curvature.
Round Edges - Smooth sharp edges during render time. When the Round Edges node is connected to this input, the following attributes are available:
Opacity - Controls the transparencey of the surface.
Material Layer - Adds a Material Layer above the base material, which provides greater flexibility for mixing and blending multiple surface characteristics.
Virtual Material - Gives particles random materials. The main material is assigned to the particles. After that, you can create any number of additional materials by adding them to the MaterialsA set of attributes or parameters that describe surface characteristics. List. The particles are assigned materials according to the Virtual Material type chosen. If you select the Non-Permanent Object Material checkbox, materials will not stick to the particles.
TexturesTextures are used to add details to a surface. Textures can be procedural or imported raster files. Resolution (PX) - Assigns a resolution to the Texture. Default setting is 1, which represents a 1 x 1 square. The maximum setting is 1024.
Preview Plane Size (M) - Adjusts the Octane Material preview plane's size, with the default value measured in meters.
Texture Quality (SPP) - The number of samples rendered per pixel. Higher values give finer details at the expense of rendering speed.
Shininess (VP2.0 Only) - Renders roughness in the Viewport. A value of 0 makes the texture totally shiny, and a value of 8 makes the texture totally rough.
Rebuild Textures - Refreshes the Viewport after you adjust any of the parameters in this section.
Swatch Quality (SPP) - The number of samples rendered per pixel on the native Swatch material in Maya®.