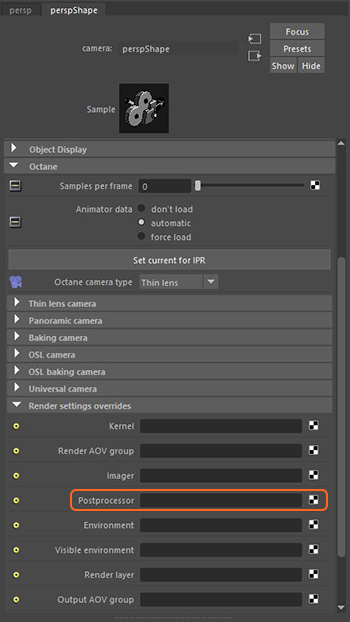
OctaneRender's post-processing effects are accessible from a Camera's Shape node, under the Octane rollout. Figure 1 shows how to add a Postprocessor node in the Attribute Editor. This provides camera-specific control over the post processor attributes.

Figure 1: The Postprocessor settings in the Camera’s Attribute Editor
You can also add Post processor attributes to all cameras in the scene from the Render Settings window (figure 2).
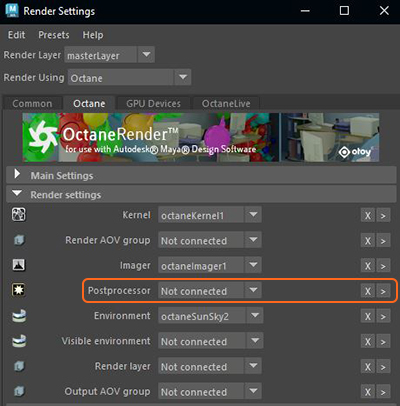
Figure 2: Adding Post processing attributes via the Render Settings window
Enabled - Activates post-processing effects. Post-processing is disabled by default.
Bloom Power - Controls the size of the glow originating from an Emitter, and the size of the halo of light originating from the sun and/or concentrated light on reflective GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals. materials.


Figure 2: A comparison of two images with bloom power disabled (top) and enabled (bottom)
Glare Power - Controls the size of the visible rays originating from an Emitter, and the size of the glare originating from reflective Glossy materials.

Figure 3: Glare power creates a star patterned glare on bright light sources and reflections
Glare Ray Count - Controls the number of visible rays that are radiated or reflected.
Glare Angle - Adjusts the glare's direction relative to the Object.
Glare Blur - Controls the glare's sharpness. Small values result in a crisp linear glare, and large values result in a softer glare.

Figure 4: A render showing a blurred glare
Spectral Intensity - Adjusts the rays' intensity distribution across a source. This affects the radiant energy's brightness.
Spectral Shift - Adjusts the specturm's displacement as the frequency of light emitted from a source changes. The shift is evident by a color change, similar to the Doppler effect, as the distance traveled by the ray from its source increases or decreases.

Figure 5: A render showing spectral shift