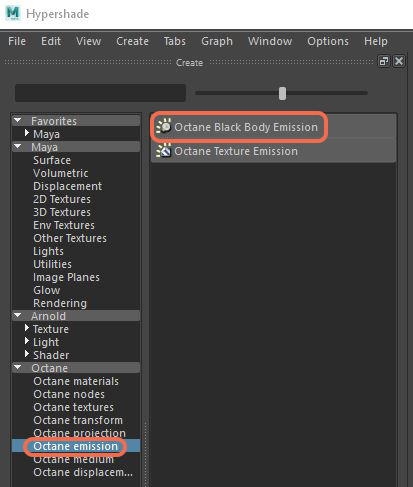
The Black Body emission makes a material emit light. You can use emission nodes with the DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters., Standard Surface, and Universal material types, which can make any surface with these attributes cast light. Figure 1 shows the Black Body emission option in the Create Render Node window of Maya’s Hypershade window.
The Black Body emission type uses Temperature (in Kelvin) and Power to control the light's color and intensity.

Figure 1: The Black body emission option in the Create Render Node window of the Hypershade window
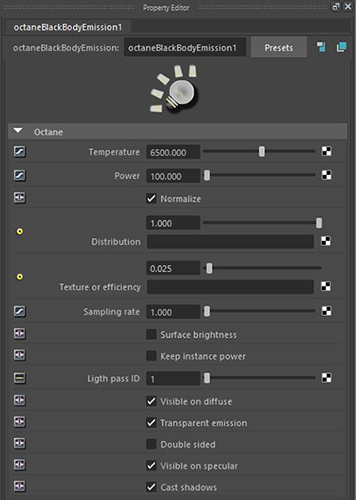
Figure 2: Black BodyAn opaque object that emits thermal radiation. In Octane, this is used to designate illumination properties for mesh emitters. emission parameters
Temperature - The temperature (in Kelvin) of the light emitted by the Black Body emission. Lower values result in warmer colors, and higher values result in cooler colors.
Power - The light source's wattage. Set each light in the scene to its real-world wattage. This power is multiplied by the texture input, where 1.0 means 100% of the power, so 0.025 means 2.5%, which gives 2.5 watts of light).
Normalize - Ensures all the normal vectors have the same length for the Black Body emission to keep the Black Body emitted light's luminance constant if the temperature varies.
Distribution - Controls the light pattern. You can use an Image texture or IESAn IES light is the lighting information representing the real-world lighting values for specific light fixtures. For more information, visit http://www.ies.org/lighting/. profile as an emission pattern. If Distribution is set to 0, the texture doesn't cast light into the scene.
Texture Or Efficiency - Determines how far the light casts into the scene based on its power settings. No light is 100% efficient at delivering power at the specified wattage - a 100-watt light bulb does not deliver 100 watts of light. The Efficiency setting enters the real-world values. These values create very realistic light settings. For example, a standard 100-watt incandescent bulb is 2.0% efficient, whereas a 25-watt compact fluorescent light is 10% efficient. These both produce around the same quantity of light in real life. You can connect this setting to a Texture to alter the emitted light's color.
Sampling Rate - Choose what light sources receive more samples. Adjusting the light source Sampling Rates in the scene leads to a better balance between light sources. You can set the Sampling Rate to 0, which means the Direct Light calculation excludes the emitter.
Surface Brightness - Keeps the Emitters' surface brightness constant, independent of the Emitter surface area.
Keep Instance Power - Enabling this option with Surface Brightness disabled and Uniform Scaling applied to the object causes Power to remain constant.
Light Pass ID - Used with the Light Pass ID AOVs. This parameter renders the light's contribution in a separate AOV, provided the Light ID pass of the same ID value is enabled in the Render AOV Group section of the Octane Render Settings.
Visible On Diffuse - Makes the Black Body or Texture emission light sources visible on Diffuse objects. This is enabled by default. Disabling this option disables emission. It's not visible in diffuse reflections, but is visible in specular reflections. It's also excluded from the Direct Light calculation.

Figure 3: The Visible On Diffuse option when enabled (left) and disabled (right)
Transparent Emission - Makes the light source cast illumination on Diffuse objects, even if the light source is on a Transparent material.
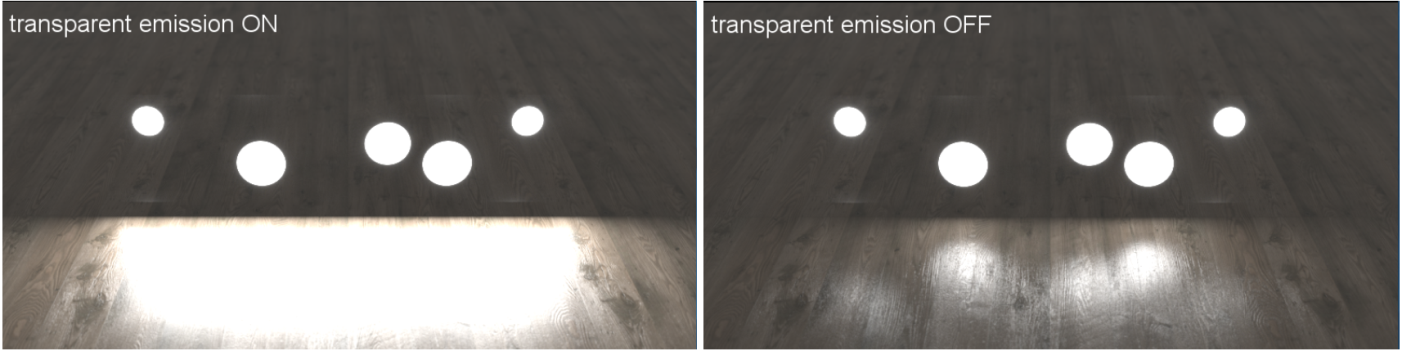
Figure 4: Comparison of the Transparent emission when enabled (left) and disabled (right)
Double Sided Makes the Emitter emit light from both the front and back sides.
Visible On SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. - Makes the light source visible on specular surfaces. This is enabled by default. This lets you hide Emitters on specular reflections and refractions.

Figure 5: The Visible On Specular option when enabled (left) and disabled (right)
Cast Shadows - Makes the light source cast light and shadows on diffuse surfaces, and disables direct light shadows for Mesh emitters. This option has an effect if the Emitter is included in the Direct Light calculation, such as when the Sampling Rate is greater than 0. This option is enabled by default.