The layered material system lets you construct complex materials that consist of a base layer and up to eight MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. Layers. The layers are based on components used in previous Octane materials. Using this set of unique layers, OctaneRender® now lets you recreate complex materials in a physically-based manner, as opposed to manually mixing materialsUsed to mix any two material types. together.
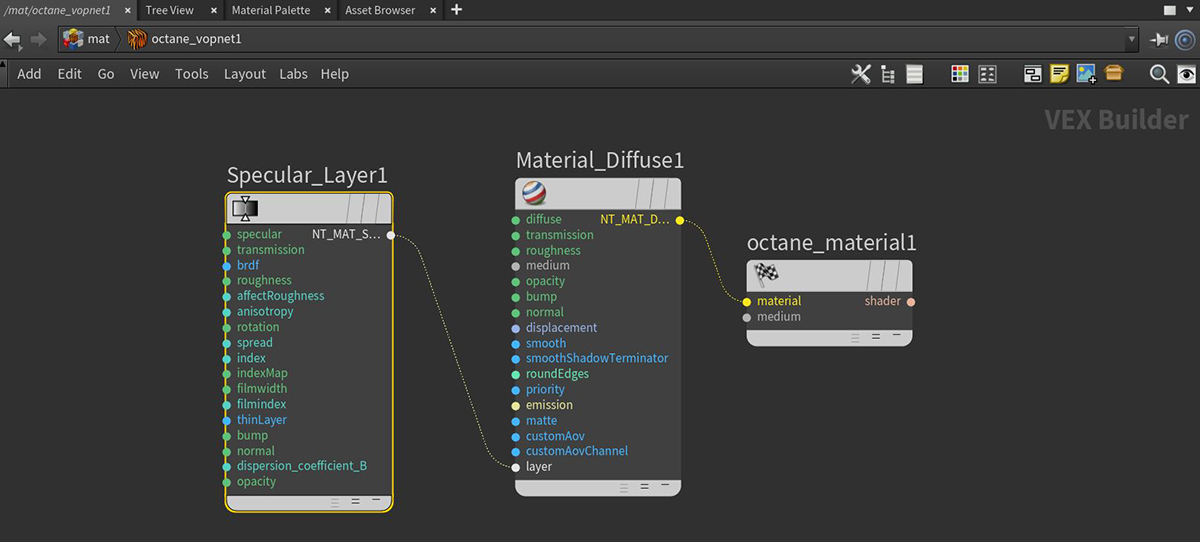
The Specular layer is used for shiny materials like plastics, or clear materials like glass. Refer to the GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals., Specular, and Universal Material topics in this manual for more information. Material Layers can connect to the Material Layer, Layer Group, or Layer pin on standard materials (Figure 1).

Figure 1: A Specular Layer mode connected to the Layer pin on a DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. Material node
Specular Layer Parameters
Specular - The layer's coating color.
TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. - The layer's transmission color.
BRDF - The BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) determines the amount of light that a material reflects when light falls on it. For Glossy materials, you can choose from six BRDF models. Specific geometric properties (the micro-facet distribution) of the surface affects each BRDF, which describes the surface's microscopic shape (i.e. micro-facet normals) and scales the brightness of the BRDF's reflections. Refer to the topic on BRDF Models in the Standalone documentation for more information.
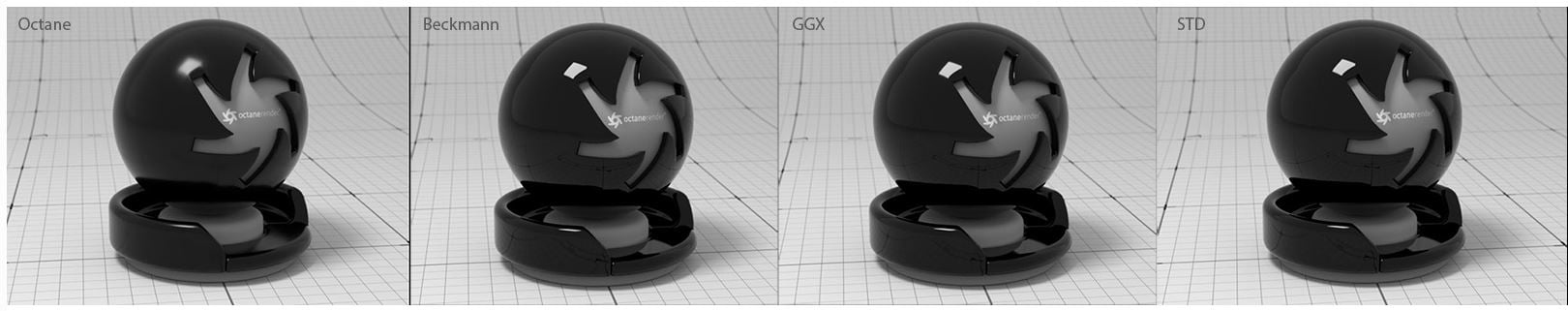
Figure 2: Examples of the BRDF types
Roughness - The layer's roughness.
Affect Roughness - The percentage of roughness affecting subsequent layer roughness.
Anisotropy - The layer's anisotropy. A value of -1 is horizontal, while 1 is vertical. A value of 0 is Isotropic.
Rotation - The rotation of the specular anisotropic reflection.
Spread - Determines the tail spread for the specualr BSDF (Bidirectional ScatteringDefines how fast light gets scattered when traveling through the medium. Distribution Function) model of the specular layer.
IOR - Controls the Fresnel effect of the reflection and refraction of light when it enters or exits the material. You can find standard values of Index Of Refraction (IOR) by searching the internet. Glass has a value of 1.53, and water has a value of 1.33.
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through the object.
Film Width - Sets the film coating's thickness.
Film IOR - Sets the film coating's Index Of Refraction.
Thin Layer - Makes the layer very thin so it reflects, or goes straight though the layer.
Bump Input - Simulates a relief by using a Greyscale texture interpreted as a Height map for the layer.
Normal Input - Distorts layer normals using an RGB image.
Dispersion Coefficient - This is the B parameter of the Cauchy dispersion model. Increasing this value increases the coloration amount and dispersion in the layer’s transmission and caustics.
Opacity - Controls the layer's opacity with a Greyscale texture.