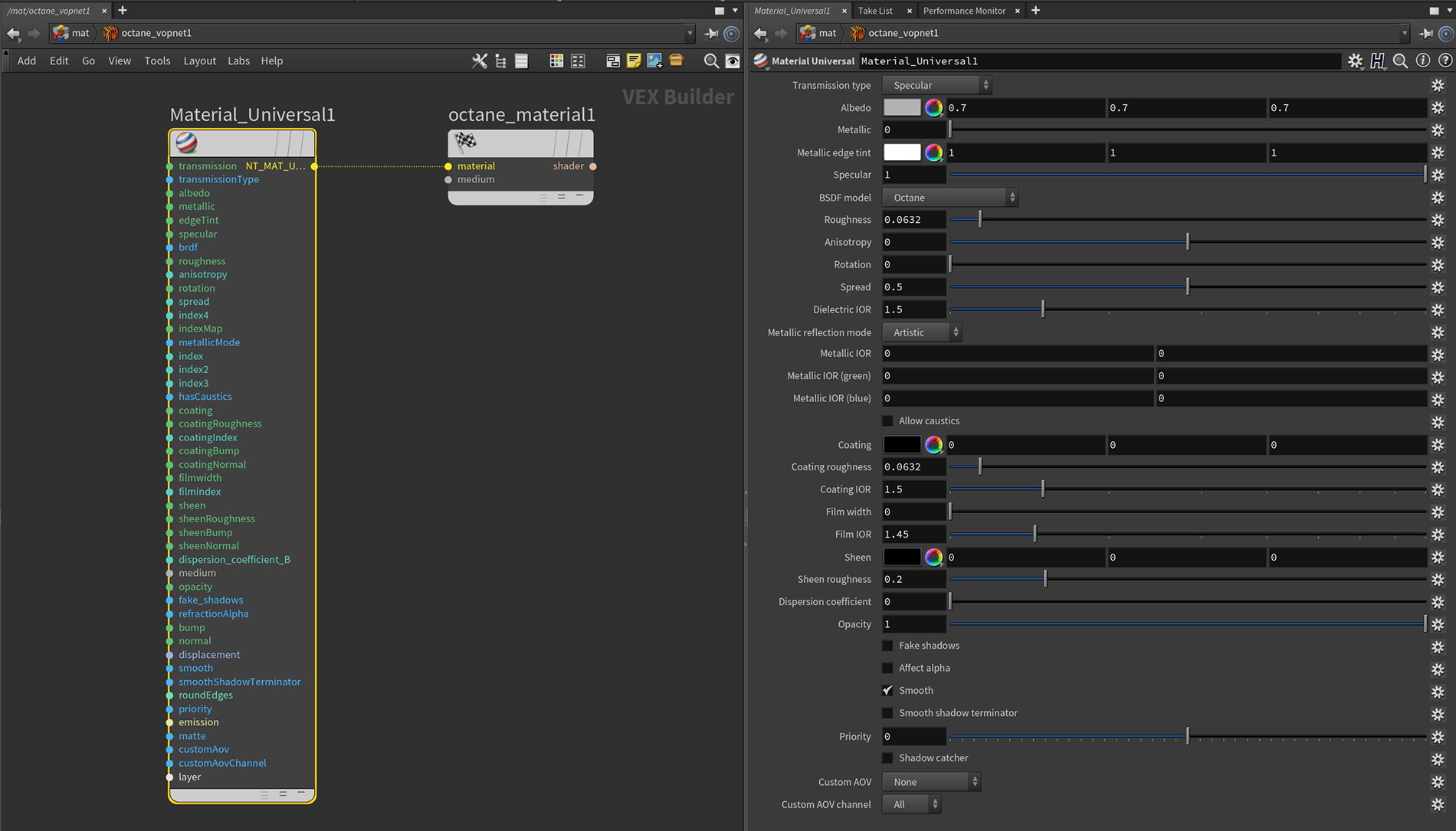
The Universal material is designed to integrate with PBRA contemporary shading and rendering process that seeks to simplify shading characteristics while providing a more accurate representation of lighting in the real world. (Physically Based Rendering) workflows, such as Substance Designer. Where the DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters., SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water., GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals., and Metallic materials isolate parameters to design specific material types, the Universal material can design material characteristics associated with any of the other MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. types (Figure 1).

Figure 1: The Universal material parameters
TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. Pin - Controls how light passes through a transparent surface. It is closely tied with the Dielectric IOR to control the surface's transparency. It accepts a color, texture, or value as an input. However, a color input provides the most control. To create colored glass, change the color input to something other than black and set the Albedo to black. Transmission is not the same as Opacity. Opacity controls the surface visibility, while Transmission controls the transparency. Use Transmission to create a reflective glass surface, and use Opacity to create a hole in the surface.
Transmission Type - Determines how light refracts.
Albedo - The material's base color which controls the overall color of a non-metallic opaque material. It can also color a metallic material which is using the Artistic IOR type.
Metallic - Determines how metallic a surface looks. Lower values make the surface look more dielectric, and higher values make the surface look more metallic.
Metallic Edge Tint - The color of the edges of the metal material, only used with Artistic and IOR+Color modes.
Specular - Determines the color of glossy reflections for Dielectric materials (when the Metallic parameter is set to 0). Set the Dielectric IOR parameter higher than 1.0 for the Specular parameter to contribute to the surface characteristics.
BRDF Model- The BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) determines the amount of light that a material reflects when light falls on it. For Glossy materials, you can choose from six BRDF models. Specific geometric properties (the micro-facet distribution) of the surface affects each BRDF, which describes the surface's microscopic shape (i.e. micro-facet normals) and scales the brightness of the BRDF's reflections.
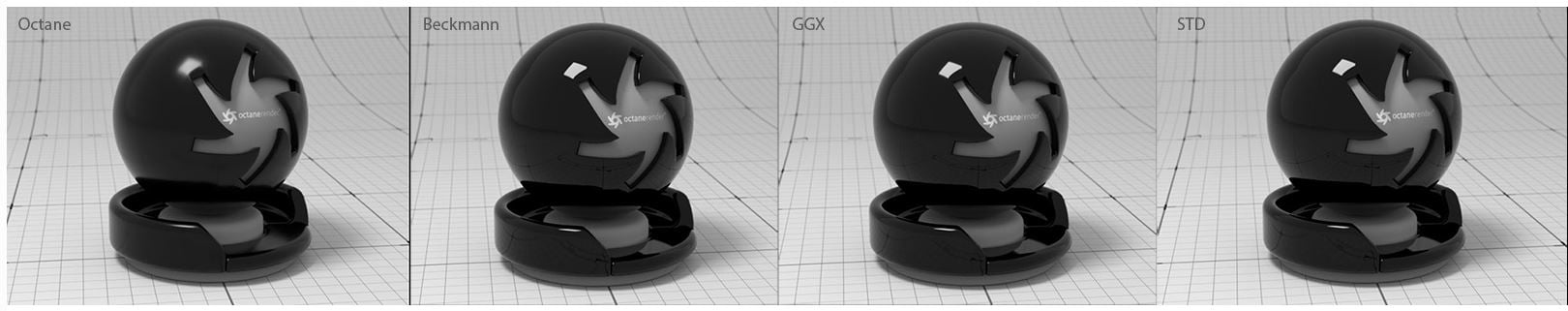
Figure 2: Examples of the BRDF types
Roughness - Determines how much the Specular and Transmission characteristics spread across the surface.
Anisotropy - Determines the shape of Specular and Transmission highlights. A value of -1 creates a horizontal shape, and a value of 1 creates a vertical shape.
Rotation - Controls the Anisotropy shape's rotation.
Spread - Controls the spread of the tail of the specular BSDF (STD only).
Dielectric IOR - This IOR controls the specular reflection's or transmission's Fresnel effect. By default, if the Dielectric 1/IOR parameter is empty, then the dielectric specular uses this parameter instead.
Metallic Reflection Mode - This attribute, along with the IOR attributes, provide options for controlling the Index of Refraction across a surface.
IOR attributes associated with the Metallic Refl. Modes. Complex-valued Index Of Refraction controlling the Metallic reflection's Fresnel effect, where n = the refractive index, and k = the extinction coefficient. For the following parameters, the left field is the value for "n" and the right field is the value for "k."
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through the object.
Coating - Provides a second layer of reflection to the surface.
Coating Roughness - Determines how much the Coating characteristic spreads across the surface.
Coating IOR - Controls the Fresnel effect for the surface's Coating characteristics.
Coating Bump Input - Much like a regular Bump map, this creates fine details on the material’s Coating attribute using a Procedural or Image texture.
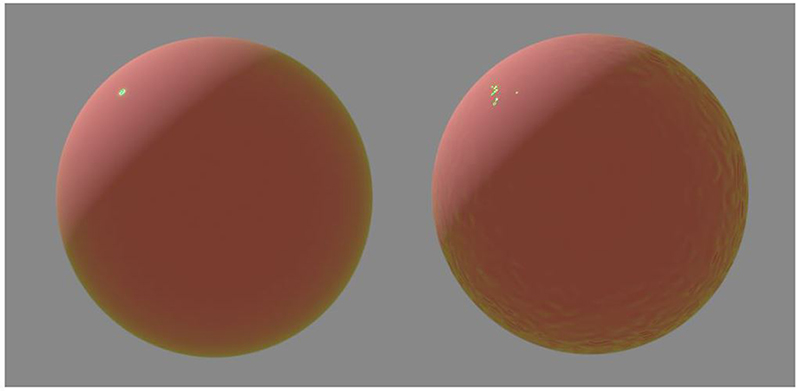
Figure 3: The sphere on the right has an Octane Turbulence texture connected to the Coating Bump attribute
Coating Normal Input - This attribute also creates fine details on the surface's coating. A Normal map is a special type of image texture that uses red, green, and blue color values to perturb the normals of the surface at render time, giving the appearance of added detail. They can be more accurate than Bump maps, but require specific software, such as ZBrush®, Mudbox®, Substance Designer, XnormalTM, or others to generate.
Film Width - Simulates the look of thin film material on a surface, like creating a rainbow color effect that appears on an oil slick's surface. Larger values increase the effect's strength.
Film IOR - Controls the film's IOR by adjusting its visible colors.
Sheen - Provides a second layer of glossiness to the surface.
Sheen Roughness - Determines how much the sheen characteristic spreads across the surface.
Sheen Bump Input - The sheen layer's Bump map. If you don't specify a Bump map, the sheen layer uses the default shading normal. Otherwise, it applies the bump-mapped surface to the sheen layer.
Sheen Normal Input - The sheen layer's Normal map. If you don't specify a Normal map, the sheen layer uses the default shading normal. Otherwise, it applies the normal-mapped surface to the sheen layer.
Dispersion Coefficient - This is the B parameter of the Cauchy dispersion model, where normal dispersion is derived through the relationship between the Index Of Refraction and the wavelength of light passing through transparent materials. Increasing the Dispersion value increases the amount of coloration and dispersion in the object’s transmission and in caustics.
Medium Input - OctaneRender® has three types of mediums to create translucent surfaces: Absorption, Scattering, and Volume. To use these options, connect the Diffuse materialUsed for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters.'s Medium input to either the Absorption or Scattering medium nodes.
Opacity - Determines what surface parts are visible in the render. Dark values indicate transparent areas, and light values indicate opaque areas. Values between light and dark indicate semi-transparent areas. Lowering the Opacity value fades the object's overall visibility, or you can use a Texture map to vary the surface's opacity. For example, if you want to make a simple polygon plane look like a leaf, you connect a black-and-white image of the leaf's silhouette to the Diffuse shader's Opacity channel. When you use an Image texture map, set the Data type to Alpha Image if the image has an Alpha ChannelA greyscale image used to determine which areas of a texture map are opaque and which areas are transparent., or Grayscale image for black-and-white images, to load an image for setting transparency. Use the image's Invert checkbox to invert the transparency regions.
Fake Shadows - Activates the Architectural glass option for all Meshes sharing that Material. When enabled, Specular materials exhibit Architectural glass characteristics with its transparent feature, allowing light to illuminate enclosed spaces or frame an exterior view.
Affect Alpha - Lets refractions affect the Alpha Channel, as long as you enable the Alpha Channel in the Render settings’ Kernel parameters.
Bump Input - Creates fine details on material surfaces using a Procedural or Image texture. When you connect a Grayscale image texture to this parameter, light areas appear as protruding bumps, and dark areas appear as indentations. You can adjust the Bump map strength by setting the Power or GammaThe function or attribute used to code or decode luminance for common displays. The computer graphics industry has set a standard gamma setting of 2.2 making it the most common default for 3D modelling and rendering applications. values on the Grayscale image texture node. These attributes are covered in more detail under the Octane TexturesTextures are used to add details to a surface. Textures can be procedural or imported raster files. section of this manual.
Normal Input - Creates fine details on the surface. A Normal map is a special type of Image texture that uses red, green, and blue color values to perturb the surface normals at render time, giving the appearance of added detail. They can be more accurate than Bump maps, but require specific software, such as ZBrush®, Mudbox®, Substance Designer, xNormalTM, or others to generate. To load a full-color Normal map, set the Normal channel to the RGB Image data type. Note that Normal maps take precedence over Bump maps, so you cannot use a Normal map and a Bump map at the same time.
DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface. Input - Adjusts the surface vertices' height at render time using a Texture map. Displacement maps differs from Bump or Normal maps in that the geometry is altered by the texture, as opposed to just creating the appearance of detail. Displacement mapping is more complex than using a Bump or Normal map, but the results are more realistic, especially along the silhouette of the surface. Displacement mapping is covered in more detail under the Octane Textures section of this manual.
Smooth - Smooths the transition between surface normals. If this option is disabled, the edges between the polygons of the surface are sharp, giving the surface a faceted look.
Smooth Shadow Terminator - If enabled, self-intersecting shadows are smoothed according to the polygon's curvature.
Round Edges Pin -
Emission Input - Create a surface that emits light (also known as a Mesh emitter). To use this option, connect the Diffuse material's Emission input to either a Blackbody or Texture emission node. These nodes are covered in more detail under the Mesh EmittersThe ability for a surface to emit illumination usually described by a Black Body or Texture emission type. topic under the Lighting category of this manual.
Priority - Used to resolve the ambiguity in overlapping surfaces, the surface priority control allows artists to control the order of preference for surfaces. A higher number suggests a higher priority for the surface material, which means it is preferred over a lower priority surface material if a ray enters a higher priority surface and then intersects a lower priority surface while inside the higher priority surface medium.
Shadow CatcherThe Shadow Catcher can be used to create shadows cast by objects onto the surrounding background imagery. The shadows cast are not limited to simply a ground plane but can be cast onto other surfaces of varying shapes. - Makes the material a shadow catcher. The material becomes transparent unless there is some direct shadow cast onto the material, which makes it less transparent, depending on the shadow strength.
Custom AOV - Writes a mask to the specified custom AOV.
Custom AOV Channel - Determines whether the custom AOV is written to a specific color channel (R, G, or B) or to all the color channels.
Layer Input - Connects any of the Octane Material layers, which provide greater flexibility for mixing and blending multiple surface characteristics.