The layered material system lets you construct complex materials that consist of a base layer and up to eight MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. Layers. The layers are based on components used in previous Octane materials. Using this set of unique layers, OctaneRender® now lets you recreate complex materials in a physically-based manner, as opposed to manually mixing materialsUsed to mix any two material types. together.
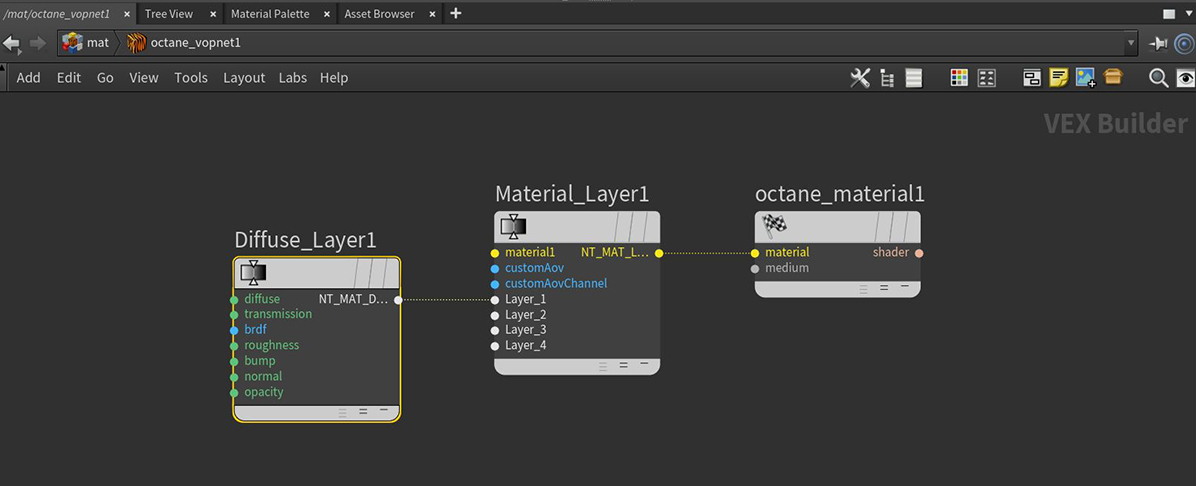
The DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. layer is used for dull, non-reflective materials. See the Diffuse Material topic in this manual for more information. Material Layers can connect to the Layered Material, Layer Group, or Material Layer pins on standard materials (Figure 1).

Figure 1: A Diffuse Layer node is connected to the Layer 1 pin on a Material Layer node
Diffuse Layer Parameters
Diffuse - The layer's diffuse color.
TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume. - The layer's transmission color. This can be used for thin translucent objects.
BRDF Model - Determines how light reflects or refracts using either the Octane or Lambertian models.
Roughness - The Diffuse layer's roughness. High values simulate very rough surfaces like sandpaper or clay.
Bump - Simulates a relief, using a Greyscale texture interpreted as a Height map for the layer.
Normal - Distorts layer normals using an RGB image.
Opacity - Controls the layer opacity with a Greyscale texture.