The PortalA technique that assists the render kernel with exterior light sources that illuminate interiors. In interior renderings with windows, it is difficult for the path tracer to find light from the outside environment and optimally render the scene. Portals are planes that are added to the scene with the Portal material applied to them. MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. option should be used with the Path Tracing and PMC kernels, it will not work when rendering with the Direct Light kernel (not direct-lighting/ambient occlusion).
Portal MaterialsA set of attributes or parameters that describe surface characteristics. are a used to optimize the rendering of light sources, they accomplish this by helping the render kernel find important light sources in the scene. For example, in the case of interior scenes illuminated by an outside light source that comes in through windows, it can be difficult for the path tracer to optimize the light as it enters the interior environment. To help the path tracer find these light sources a polygon plane can be placed outside the window and then a Portal Material can be applied to the plane, thus creating a ‘portal plane’ (AKA Portals). This set-up will improve the quality of the light and increase the efficiency of the render.
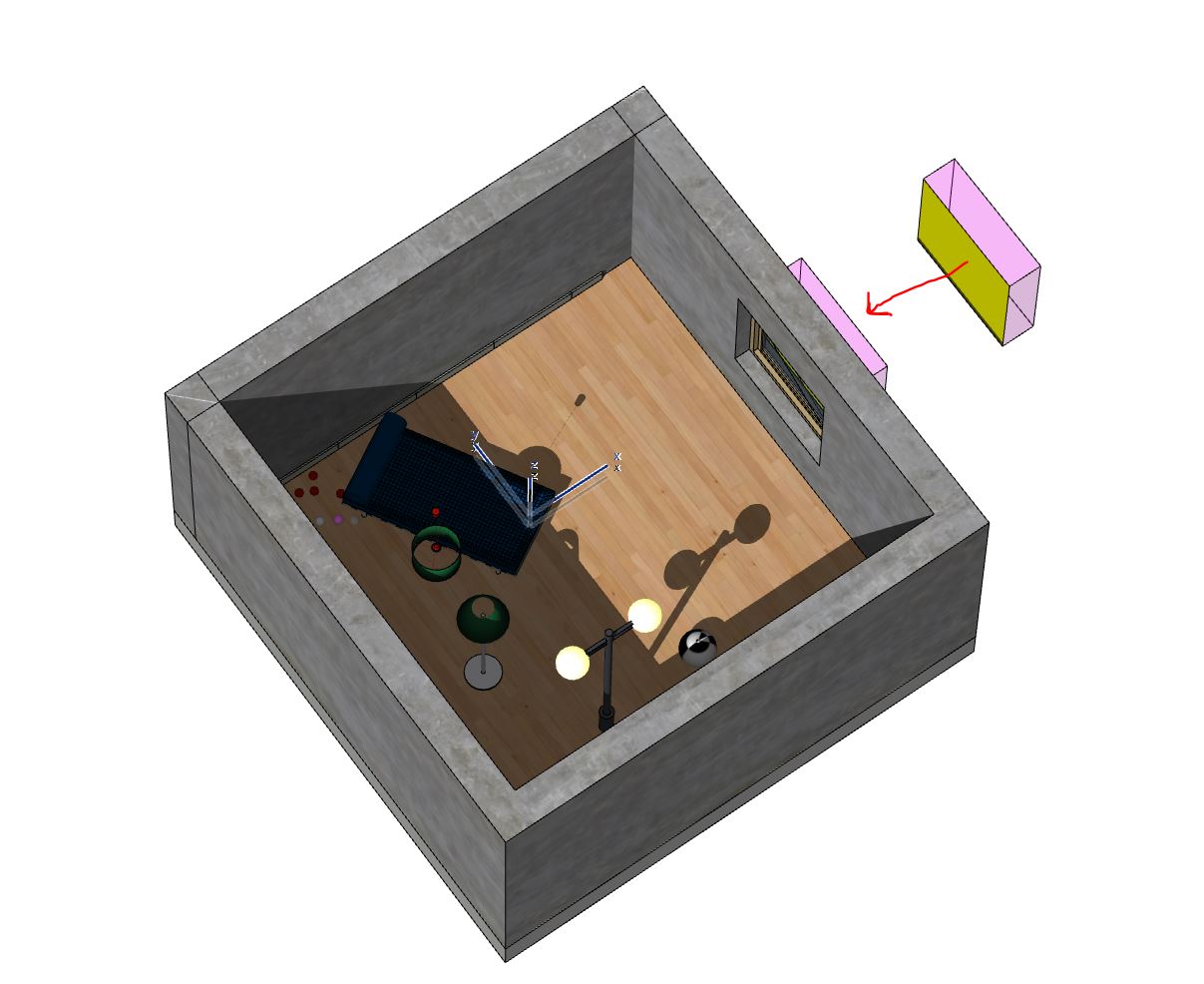
In the image below a room is being prepared with a small, single window. This would be a difficult scene to light with a sun/sky or HDRIAn image which presents more than 8 bit per color channel unlike most common image formats. file with no lighting on the interior of the room.
A plane is placed outside an opening in a polygon room, this plane will serve as a surface for the portal material. A single plane was placed as one side of an ArchiCAD wall object with a unique material name (yellow plane). The pink material is another ArchiCAD material in the plugin set as a 100% transparent material so that it will not be seen in the rendering.

Portal nodes can be accessed by navigating to the Materials category then choosing Portal and can be enabled in the Node Parameters.
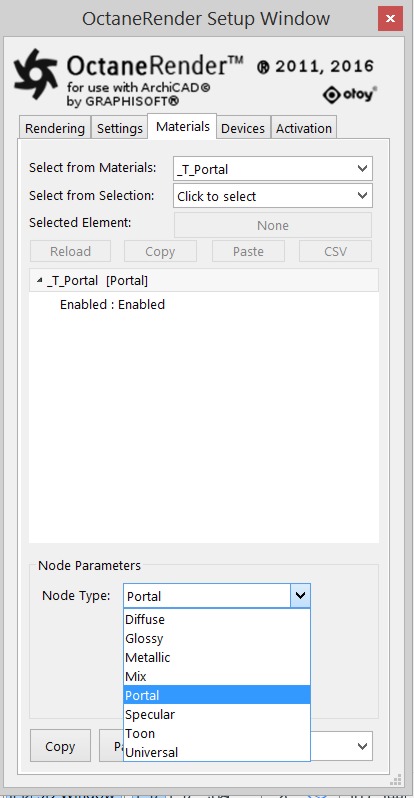
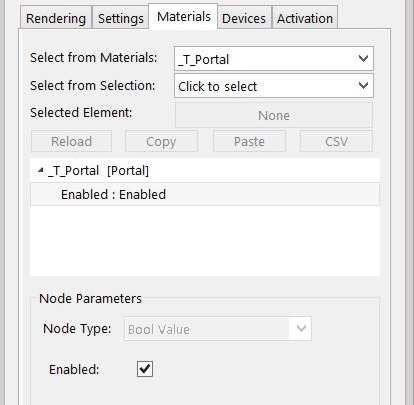
To set up a scene using Portal Materials it is important to make sure that every window or opening in the environment is covered by a portal plane. It will not work if only one window has a portal over it when all other windows do not have a portal over them. And the normal direction of the portal plane should be facing inwards towards the interior or the scene will not render properly. Portal planes should not be blocked by other geometry such as a glass surface. Objects with the Portal material applied will not be visible in the rendering as geometry.
Note: You can either set the glass material with 100% transparency not to block the portal or either find settings for the glass to compromise.
It is best to try to use the least amount of geometry for portals, e.g. only a few simple rectangular planes are best, dense geometry used for portal planes can slow down rendering. It is possible to use a single piece of portal geometry to cover several openings such as multiple windows on a single wall however if the geometry is too large that can reduce rendering efficiency. It’s important to strike a balance between coverage of openings and the size of the geometry that uses the portal material.
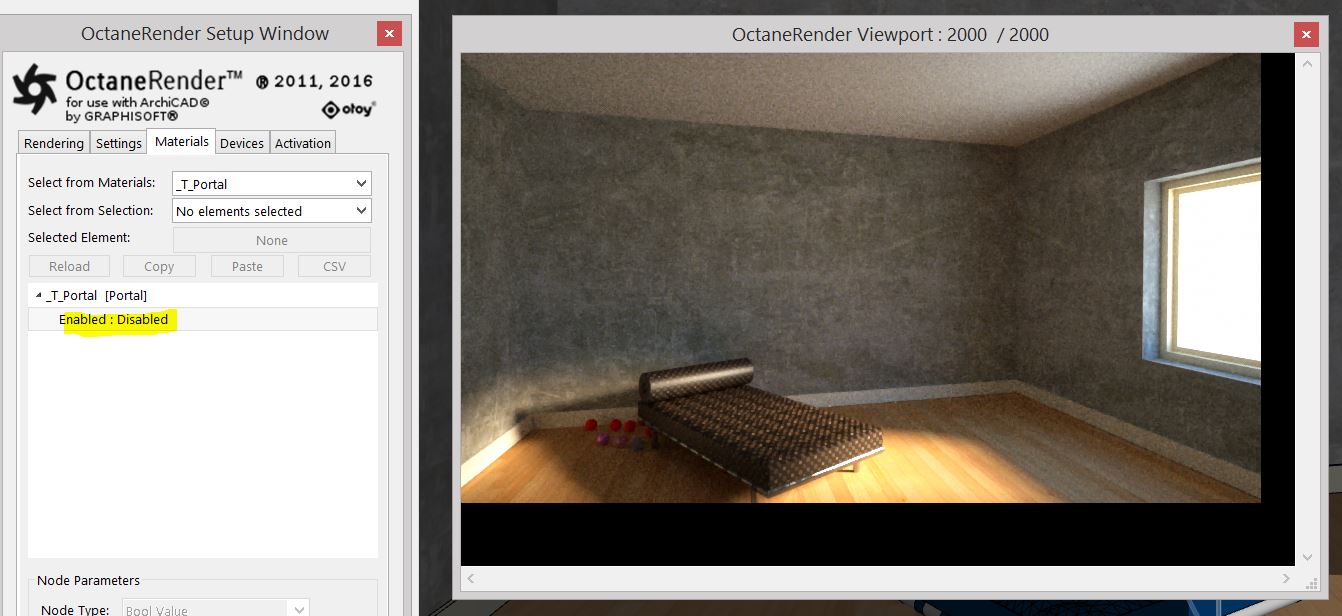
The two images in below show the results of rendering without and with a portal material. The scene shows scene rendered in a room lit by light coming through a window. The scene is rendered using 2000 samples. Notice the first image, that does not have a portal plane placed over the opening, is noisier than the second image which does use a portal plane.