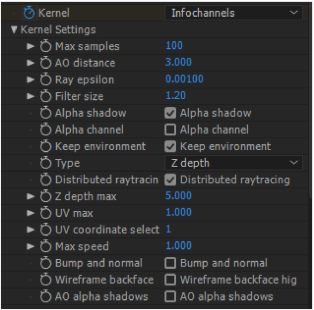
The Info Channel creates false-color images of the scene according to types that contain various information about the scene (Figure 1).

Figure 1: The Info Channel Kernel Settings.
The following Info channel types are available:
Info Channel Kernel parameters:
Max. Samples
This sets the maximum number of samples per pixel before the rendering process stops. The higher the number of samples per pixel, the cleaner the render. For quick animations and scenes with predominantly direct lighting, a low amount of samples (500-1000) may suffice. In scenes with lots of indirect lighting and mesh lights, a few thousand samples may be required to obtain a clean render.
AO Distance
- The distance of the ambient occlusion in units.
Ray Epsilon
- The ray epsilon is the distance to offset new rays so they don’t intersect with the originating geometry. If the scale of a scene is too large, precision artifacts in the form of concentric circles may appear. In that case, increasing the ray epsilon can make these artifacts disappear.
Filter Size
This sets the pixel size for filtering the render. This can improve aliasing artifacts in the render. Noise can also be reduced this way, but if the filter is set too high, the image can become blurry.
Alpha Shadows
Opacity is now taken into account in the AO calculation and this may be used by render passes to specify if shadows cast by Ambient Occlusion should be rendered as transparent (zero alpha). This can be useful to composite the render over another image and does not want the AO shadows to be present.
Alpha ChannelA greyscale image used to determine which areas of a texture map are opaque and which areas are transparent.
- This option removes the background and renders it as transparent (zero alpha). This can be useful to composite the render over another image without the background being present.
Keep Environment - This option is used in conjunction with the Alpha Channel setting. It allows the background to be rendered with zero alpha but is still visible in the final render. This allows even further flexibility in compositing images.
Type
- This drop list contains the various Info Channel types specified previously.
Distributed Raytracing
- This option allows Motion BlurAn optical phenomenon that occurs when a camera’s shutter opens and closes too slowly to capture movement without recording a blurring of the subject. and DOFThe distance between the nearest and farthest objects in a scene that appear acceptably sharp in an image. Although a lens can precisely focus at only one distance at a time, the decrease in sharpness is gradual on each side of the focused distance, so that within the DOF, the unsharpness is imperceptible under normal viewing conditions. source: wikipedia (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Depth_of_field) sampled.
Z-DepthA measure of object distances from the camera typically represented as a grayscale image. Max
- Gives the maximum z-depth that can be shown.
UV Max
Gives the maximum value that can be shown for the texture coordinates.
UV Coordinate Selection
Determines which set of UV coordinates will be used.
Max Speed
Speed mapped to the maximum intensity in the motion vector channel. A value of 1 means a maximum movement of 1 screen width in the shutter interval.
Bump and Normal Mapping
- Option to calculate or not calculate the bump and normal maps.
Wireframe Backface Highlighting
Option to highlight backface in wireframe channel.
AO Alpha Shadows
Opacity is now taken into account in the AO calculation and this may be used by render passes to specify if shadows cast by Ambient Occlusion should be rendered as transparent (zero alpha). This can be useful to composite the render over another image and does not want the AO shadows to be present.