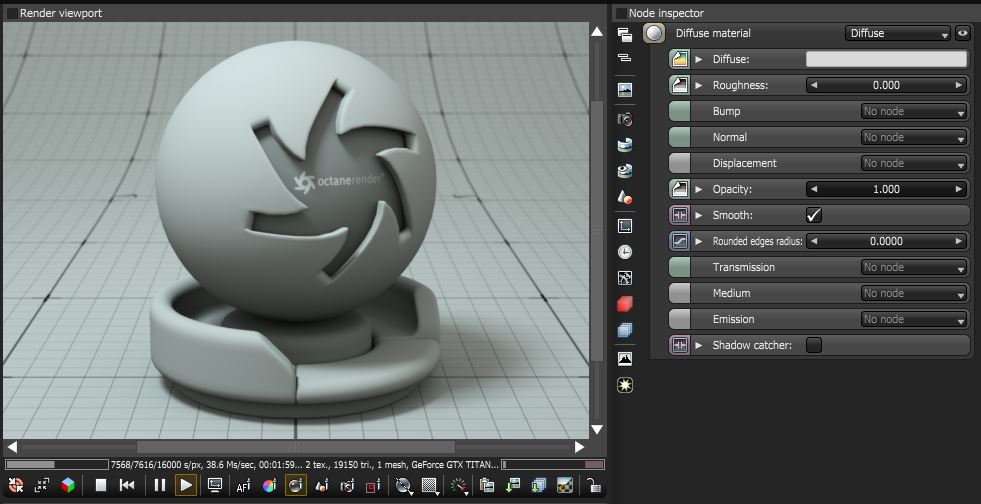
Figure 1: The Diffuse materialUsed for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. and its associated parameters.
The DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. material is used for dull, non-reflecting materials or light emitting surfaces. The Diffuse material simulates a rough surface that reflects light back into the environment in all directions, thus specular highlights and reflections do not appear on diffuse surfaces.

Figure 1: The Diffuse materialUsed for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. and its associated parameters.
Diffuse MaterialsA set of attributes or parameters that describe surface characteristics. have these parameters to adjust:
Diffuse
The Diffuse value gives the material its color.
TransmissionA surface characteristic that determines if light may pass through a surface volume.
The Transmission value gives the basic texture of the material.
Bump / Normal
Both the Bump and Normal channels can load images to control the amount of bump mapping and normal mapping. The Bump channel is set to Greyscale Image to load a bump map. The Normal channel should be set to the image data type to load a full color normal map. The Bump channel simulates a relief using a greyscale texture interpreted as a height map while the Normal Channel distorts normals using an RGB image. Note that Normal maps take precedence over bump maps, therefore you cannot use both a normal map and a bump map at the same time.
Opacity
Opacity sets the transparency of the material. Set the data type to alphaimage (if the image has an alpha channel) or floatimage (for black/white images) to load an image to set the transparency (use the Invert checkbox if necessary to adjust whether black or white regions are considered transparent.
Smooth
Normal Smoothing is a Boolean value that sets whether to smooth the normals of all meshes sharing that material. When off, the materials can be faceted and polygonal.
Emission
The Emission setting controls whether the material acts as a light source.
Medium (AbsorptionDefines how fast light is absorbed while passing through a medium. or ScatteringDefines how fast light gets scattered when traveling through the medium.)
Octane has two types of mediums, absorption and scattering, which can be used to create translucent surfaces. To use these options the Medium input of a SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. material needs to be connected to either the Absorption or Scattering medium nodes.This sets the medium inside the material.
Absorption Medium
Absorption means that the material slightly absorbs light while passing through. The color resulting from this absorption is dependent on the distance light travels through the material. With increased distance it will get darker, and if the absorption is colored it will get more saturated. It works in a subtractive way, so users will need to configure the inverted color instead to get an absorption color desired.
Absorption works in a subtractive way so if the absorption is colored and provided that the transmission value of the material is white (allowing all light to pass through), the resulting color of the material is the complementary color of the absorption node based on the color wheel:
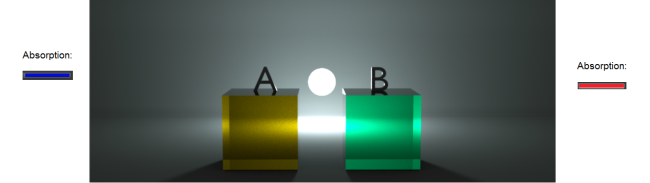
Example 1: The absorption color used in Box A is blue, the absorption color used in Box B is red.
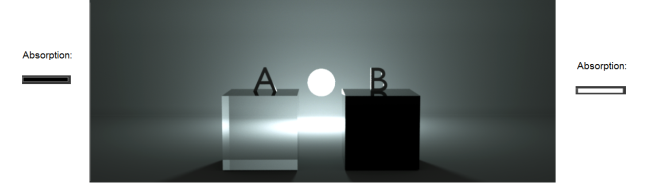
Example 2: The absorption used in Box A is black, the absorption used in Box B is white. Given that the transmission color of the material on both boxes is white, the material in Box B shows no transmission of light at all because this is subtracted entirely by the white absorption.
Scattering Medium
Similar to the absorption medium but with the option to simulate subsuburface scattering. This is a medium with single-scattering SSS, and also absorption. To use this medium, a volume needs to be created and it will not work correctly on simple surfaces. Users can use it to create true unbiased SSS, using various parameters, including scattering texture, emission texture and various other parameters. Note that this is single-scattering SSS, not multiple-scattering. It is much faster than the latter, and much more practical, although it does not allow a few things such as volumetric caustics.
The scale parameter in both mediums multiplies the absorption texture, allowing a wide range of values to be set more easily.
For applying absorption, SubSurface Scattering, and Emission refer to section on Medium Nodes in the Standalone Manual.
Matte
This switches the material to a shadow catcher. The material will be transparent unless there is some (direct) shadow cast onto the material which will make it less transparent depending on the shadow strength.
Edges Rounding
This is the radius of the rounded edges that are rendered as a shading effect. The shading effect is created at render time that easily and efficiently round the sharp edges of geometric objects without modifying and reloading the geometry. The parameter is a float value and requires vertices to be welded prior to applying the round edge value. This is very useful to virtually bevel hard edges during render time especially when using low-polygon models.
DisplacementThe process of utilizing a 2D texture map to generate 3D surface relief. As opposed to bump and normal mapping, Displacement mapping does not only provide the illusion of depth but it effectively displaces the actual geometric position of points over the textured surface.
The displacement mapping allows the height of points on a surface to be adjusted based on an image value to give objects depth and detail. The displacement is a pin in the material nodes that needs to be connected to a displacement node. A displacement texture can be specified in the displacement node, as well as the amount of displacement (in meters), the offset (in meters) and the level of detail (i.e. the maximum resolution of the resampled displacement map). Image textures are supported and of RGBA images the red channel is used as height map.
Displacement only works with the texture image node over a mesh with an UV map. No other Octane nodes can be used for displacement.
Roughness
This parameter allows users to simulate very rough surfaces like sandpaper or clay. It works similar to Oren-Nayer. Roughness is set to the minimum (0) by default.