Mediums
Octane supports participating media inside objects (absorption, subsurface scattering, and volume). These settings are stored in Medium nodes, which are attached to the corresponding input pins of Diffuse, Specular, Universal, or Null material nodes.
There are five types of Medium nodes:
- Scattering - Has parameters for absorption, scattering light passing through the Medium, and emission inside the Medium.
- Random Walk - A newer variant of subsurface scattering that ensures a more realistic result.
- Absorption - Is a simple version with Absorption parameters.
- Standard Volume Medium - A comprehensive node with the flexibility to specify what VDB grid data can be used for the various node channels. This node is covered further under the Effects section of this manual.
- Volume Medium & Ramp - Volume mediums are used on volumetric surfaces such as smoke and clouds, and require a VDB file to create the Volume objects. Volumes are described in more detail under the Effects section of this manual.
To render with Medium nodes, the Path Tracing or PMC render kernels are the best choice. It is possible to render Mediums using the Direct Light kernel, but only if the Medium node is connected to a Diffuse material, and if Diffuse Mode is set to GI.
|
|
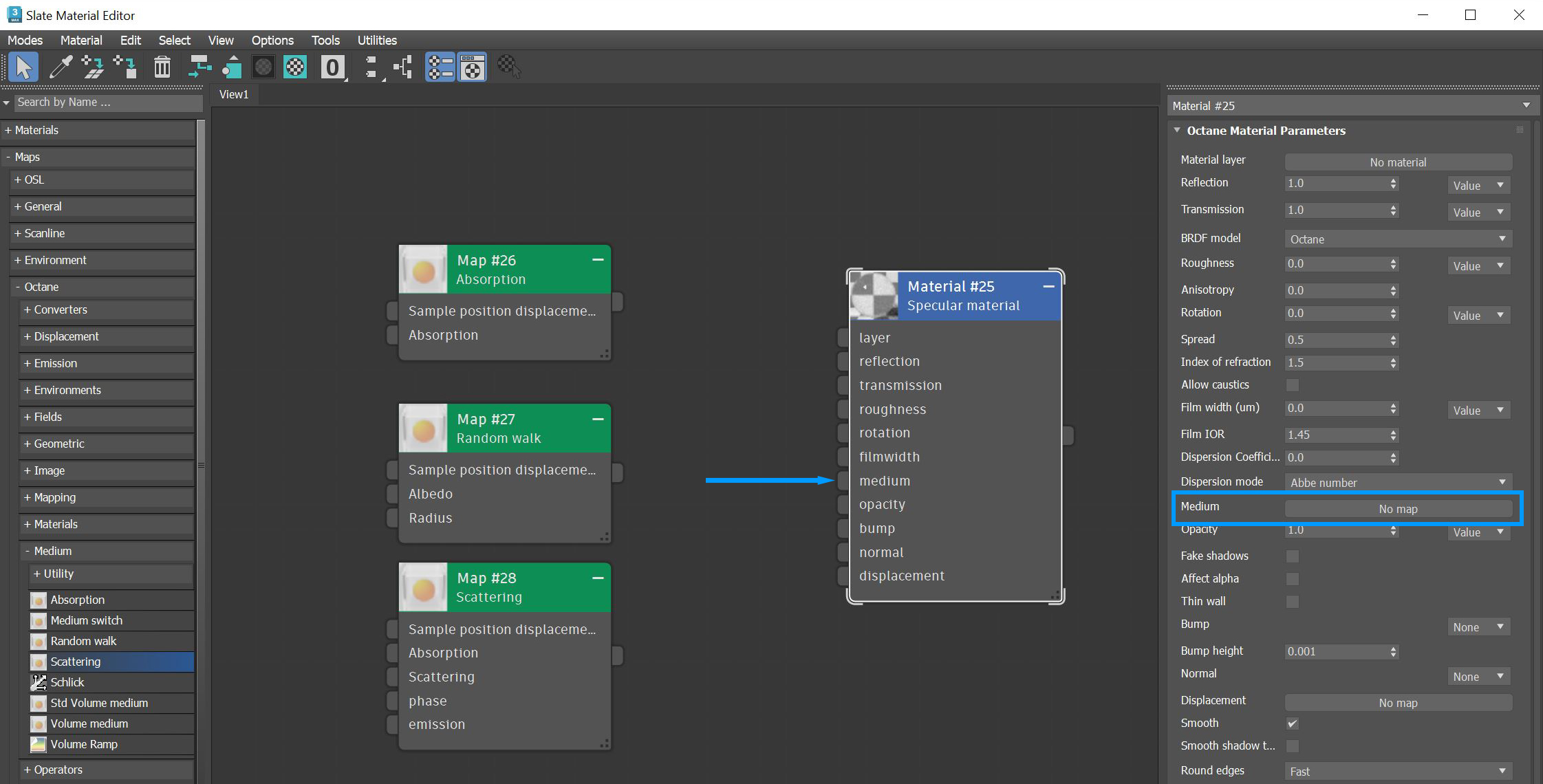
Medium Nodes
|
Figure 1: Medium nodes are connected using the Medium button in the Material's parameters
Add medium nodes to materials applied to meshes that define a closed volume. A single-sided plane will not work. For example, a plane representing a leaf will not work if you apply a material with a medium to it. The one exception is a plane representing the ground. OctaneRender® treats the ground plane as an endless, deep surface.
Specular and Universal materials are the best choice when using a medium node (figure 2). Set the Transmission and Reflection parameters to a non-zero value, or a color other than black, or a texture map. If the reflection is set to 1.0, all light gets reflected regardless of the Transmission value. If reflection is set to 0.0, all light gets transmitted through the surface. However, the result is an unnatural appearance. Reflection values of 0.1 - 0.2 are good starting points.
|
|
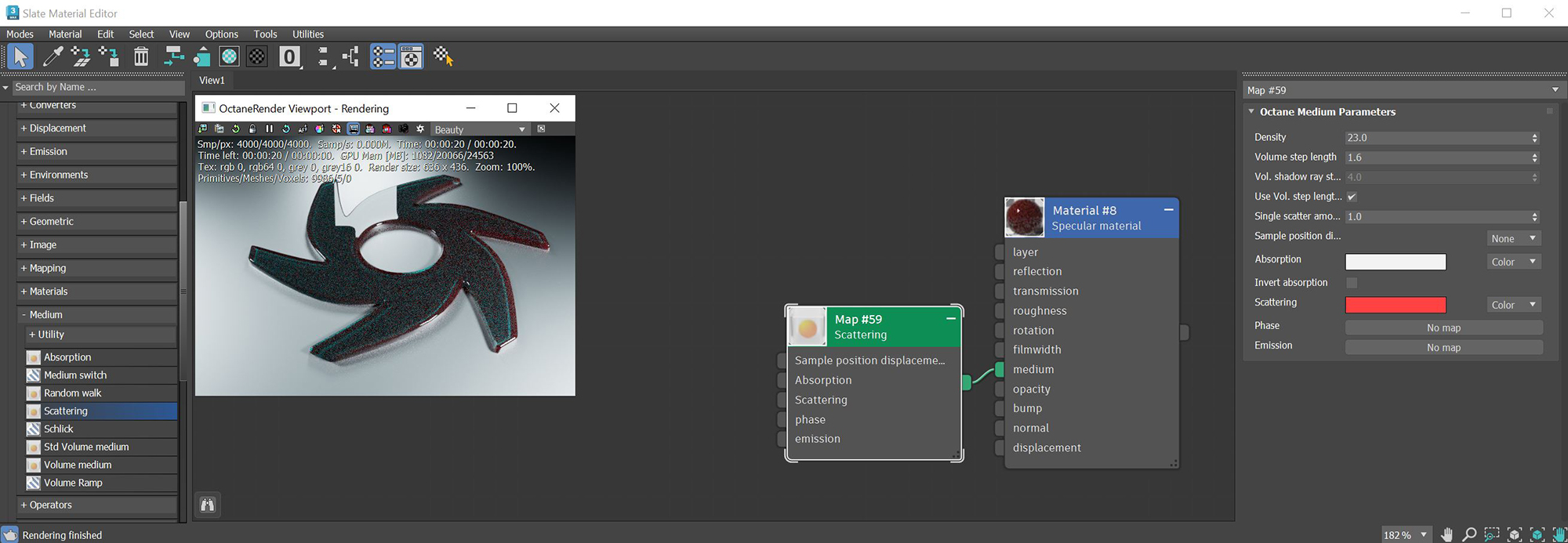
Mediums
|
Figure 2 : A Scattering medium node is connected to a Specular material
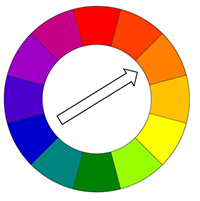
In the physical world, if the Absorption attribute use a color, the light transmitted through the surface is shaded as the complementary color (figure 3). The Invert Absorption parameter can be activated in the Absorption and Scattering nodes which will make the these real-world physical characteristics behave in an opposite fashion.
|
|
Mediums
|
Figure 3: Complementary colors on the color wheel