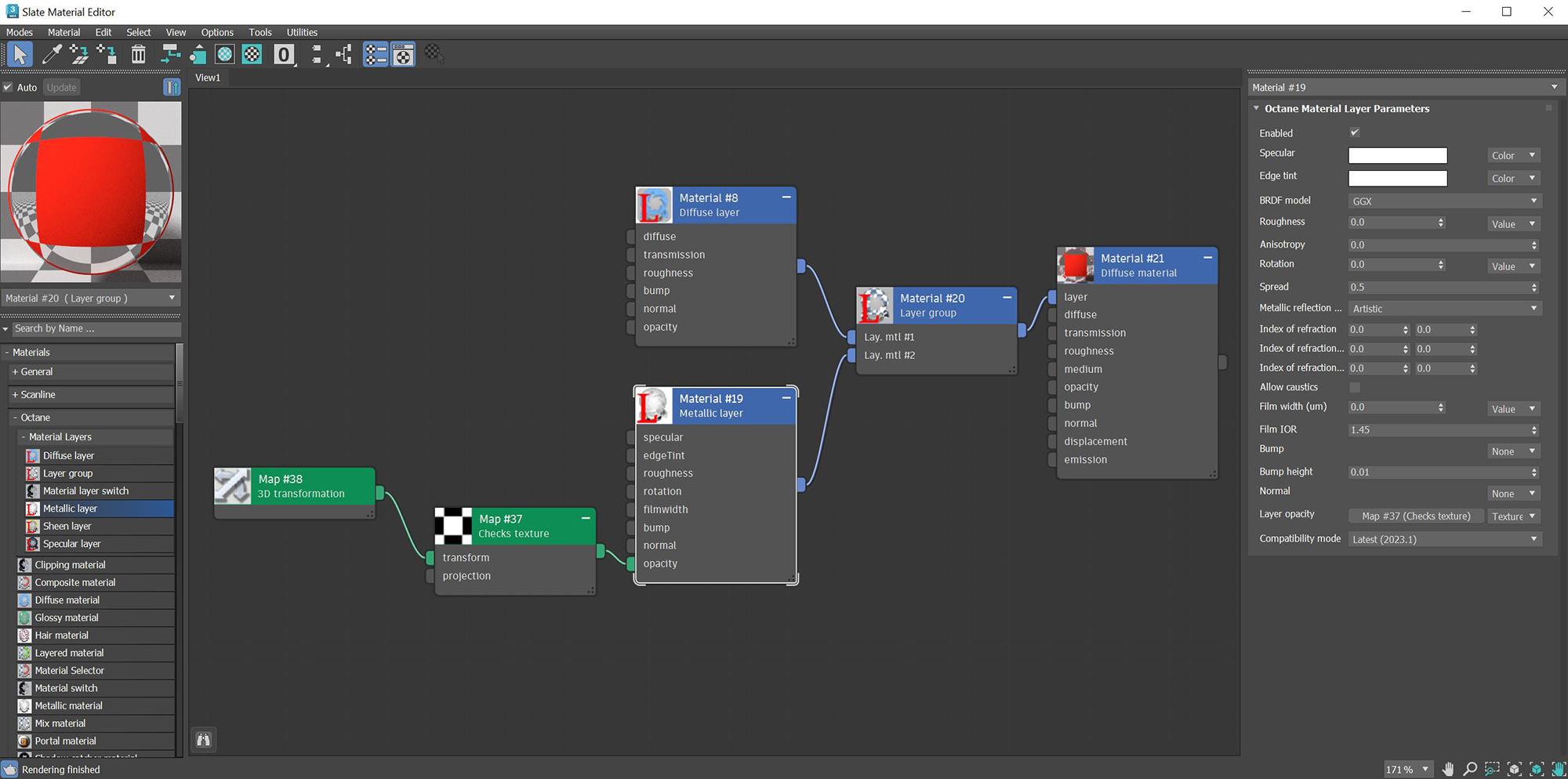
The layered material system lets you construct complex materials that consist of a base layer and up to eight MaterialThe representation of the surface or volume properties of an object. Layers. The layers are based on components used in previous Octane materials. Using this set of unique layers, OctaneRender® now lets you recreate complex materials in a physically-based manner, as opposed to manually mixing materialsUsed to mix any two material types. together.
The Metallic layer is used for highly reflective materials that have colored reflections. See the Metallic Material topic in this manual for more information. Material Layers can connect to the Layered Material, Layer Group, Material Layer Switch, or a Material Layer pins on the standard Octane materials (Figure 1).

Figure 1: DiffuseAmount of diffusion, or the reflection of light photons at different angles from an uneven or granular surface. Used for dull, non-reflecting materials or mesh emitters. and Metallic layers are mixed by using the Layer Group node and a Checks texture
Enabled - Enables or disables this node in a material layer network.
SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. - The Layer's coating color.
Edge Tint - The color of the edges of the metal material, only used with Artistic and IOR+Color modes found under the Metallic Refl. Mode.
BRDF Model - The BRDF (Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function) determines the amount of light that a material reflects when light falls on it. For glossy materials, you can choose from six BRDF models. Specific geometric properties (the micro-facet distribution) of the surface affects each BRDF, which describes the surface's microscopic shape (i.e. micro-facet normals) and scales the brightness of the BRDF's reflections (figure 2).
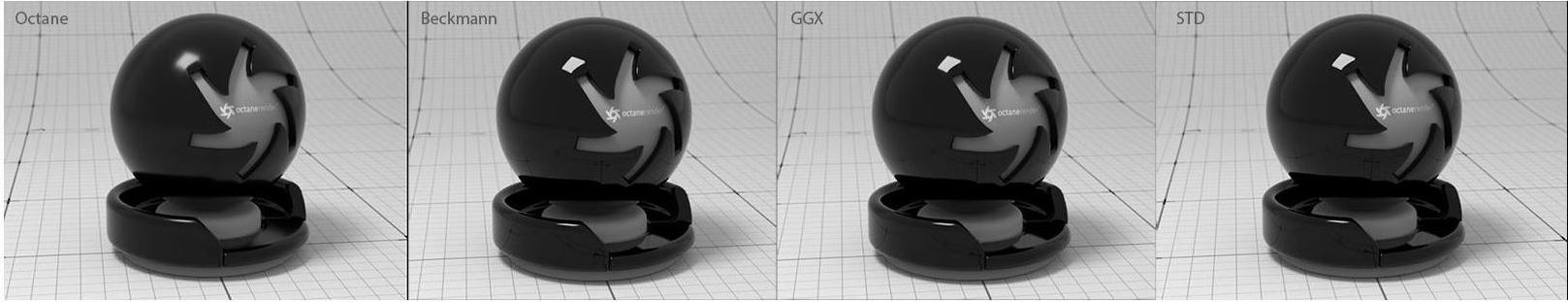
Figure 2: The various BRDF models available for specularity
Roughness - Adjusts how rough the Metallic layer looks.
Anisotropy - The Metallic layer's anisotropy. A value of -1 is horizontal, while 1 is vertical. A value of 0 is isotropic.
Rotation - The Metallic anisotropic reflection's rotation.
Spread - Determines the tail spread of the specular BSDF.
Metallic Reflection Mode - This changes how OctaneRender® calculates reflectivity.
Index Of Refraction - Complex-valued IOR (n-k*i) controlling the specular reflection's Fresnel effect, where n = the refractive index and k = the attenuation or extinction coefficient. For RGB mode, the IOR for red light (650nm).
Index Of Refraction (Green) - For RGB mode, the IOR for red light (550nm).
Index Of Refraction (Blue) - For RGB mode, the IOR for red light (450nm).
Allow Caustics - If enabled, the photon tracing kernel will create caustics for light reflecting or transmitting through objects with this material applied.
Film Width - Sets the film coating's thickness.
Film IOR - Sets the film coating's Index Of Refraction.
Bump - Simulates a relief using a Greyscale texture interpreted as a Height map for the Layer.
Bump Height - Determines the strength of the bump map. A value of 0 provides no bump height and negative values will invert the bump map.
Normal - Distorts the Layer normals using an RGB image.
Layer Opacity - Controls the Layer's opacity with a Greyscale texture.
Compatibility Mode - The Octane version that the behavior of this node should match. The default is Latest (2023.1). The 2022.1 compatibility mode is the legacy behavior where Bump map strength is active but Bump Map Height is ignored.