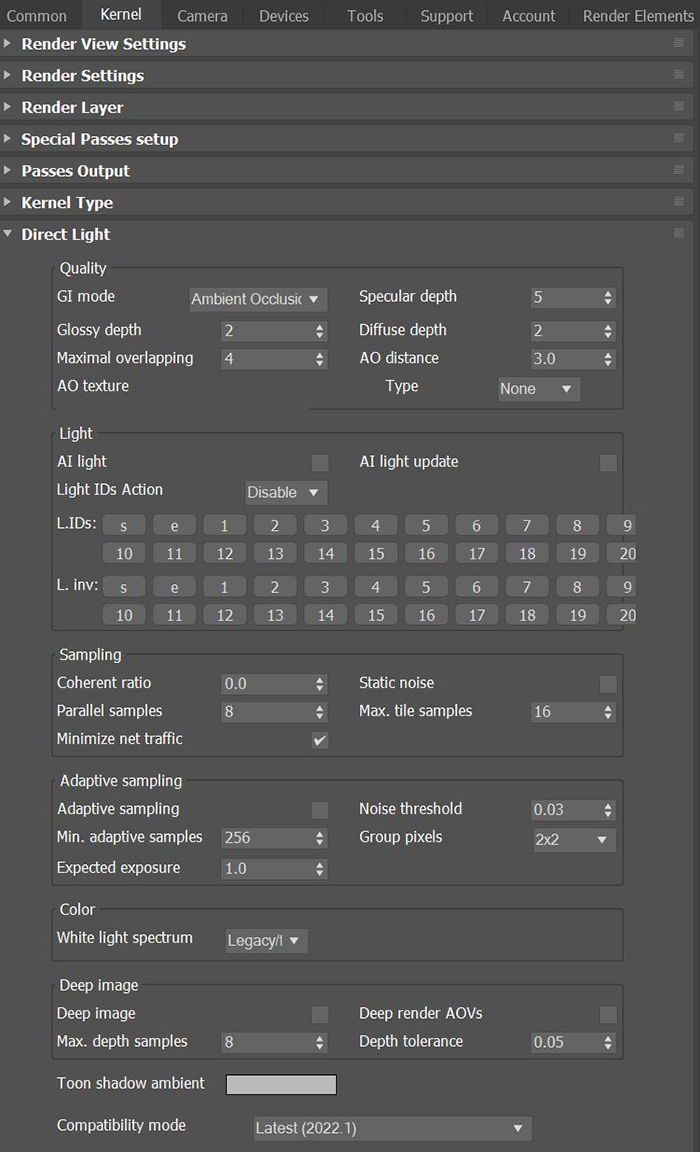
The Direct Light kernel renders previews faster. Direct lighting is not unbiased, and is not meant for photorealism. This Kernel is good for creating quick animations or renders (figure 1).

Figure 1: The Direct Light kernel parameters
GI Mode - There are three different Global Illumination Modes in the Direct Light kernel:
SpecularAmount of specular reflection, or the mirror-like reflection of light photons at the same angle. Used for transparent materials such as glass and water. Depth - Controls the number of times a ray refracts before dying. Higher values mean higher render times, but more color bleeding and more details in transparent MaterialsA set of attributes or parameters that describe surface characteristics.. Low numbers introduce artifacts or turn some refractions into pure black.
GlossyThe measure of how well light is reflected from a surface in the specular direction, the amount and way in which the light is spread around the specular direction, and the change in specular reflection as the specular angle changes. Used for shiny materials such as plastics or metals. Depth - Controls the number of times a ray reflects before dying. Higher values mean higher render times. Values lower than 4 can introduce artifacts or turn some reflections into pure black.
Diffuse Depth - Gives the maximum number of diffuse reflections if GI Mode is set to Diffuse.
Maximal Overlapping - Determines how much space to allocate for overlapping volumes. Ray marching is faster with low values but artifacts can be present where volumes overlap.
AO Distance - The ambient occlusion distance in units. Always check if the amount is correct relative to the scene scale. For example, you don’t need 3 units if your object is a small toy. However, if your model is a house or something large, then increase the value.
AO Texture - Specifies an ambient occlusion color or value. If you select None, OctaneRender® uses the Environment instead.
AI Light - Enables AI lights. AI light functionality learns from the scene, and rendering becomes more efficient as more samples are rendered. When used with Adaptive SamplingA method of sampling that determines if areas of a rendering require more sampling than other areas instead of sampling the entire rendering equally., AI Light becomes even more effective as it learns pixel and light importance in a scene, and some pixels are no longer sampled.
AI Light Update - Enables dynamic updates to the AI lighting.
Light IDs Action - This parameter determines whether the L.IDs (Light IDs) and L. Inv (Light Inverse) buttons enable or disable lights with matching Light Pass ID numbers.
Coherent Ratio - Increasing this value increases the render speed, but introduces low-frequency noise (blotches), which may require a few hundred or even a few thousand samples per pixel to remove, depending on the scene.
Parallel Samples - Controls how many samples OctaneRender® calculates in parallel. Low values require less memory to store the sample's state, but rendering is slower. High values need more graphics memory, making rendering faster. The change in performance depends on the scene and the GPUThe GPU is responsible for displaying graphical elements on a computer display. The GPU plays a key role in the Octane rendering process as the CUDA cores are utilized during the rendering process. architecture.
Minimize Net Traffic - OctaneRender distributes the same tile to the net render nodes until it reaches the max samples/pixel for that tile, and then it distributes the next tile to render nodes. Work done by local GPUs is not affected by this option. A render node can merge all of its results into the same cached tile until the Primary Render Node switches to a different tile.
Static Noise - Makes noise static - it doesn’t change between frames.
Maximum Tile Samples - Controls the number of samples per pixel that OctaneRender will render until it takes the result and stores it in the film buffer. Higher values mean results arrive less often in the film buffer.
Adaptive Sampling - Stops sampling pixels that reach a specified noise threshold. This lets the kernel focus its processing on areas that still need refinement.
Min. Adaptive Samples - Specifies the minimum number of samples to calculate before Adaptive Sampling kicks in. The pixel's noise estimate has a large initial error. If you set the noise threshold to a high value, then you should set Min. Adaptive Samples to a high value to avoid artifacts.
Noise Threshold - When Adaptive Sampling is enabled, Noise Threshold specifies the smallest relative noise level. When a pixel's noise estimate is less than this value, OctaneRender® turns off sampling for this pixel. Good values are in the range of 0.01 - 0.03. The default is 0.02, which is pretty clean.
Group Pixels - When Adaptive Sampling is enabled, Group Pixels specifies the number of pixels that are handled together. If all pixels of a group reach the noise level, sampling stops for all of these pixels.
Expected Exposure - This parameter's value should be about the same value as the image exposure, otherwise set it to 0 (the default value) to ignore these settings. Adaptive Sampling uses this parameter to determine what pixels are bright and dark. This depends on the exposure setting in the Octane Imager. If the value is not 0, Adaptive Sampling adjusts the noise estimate of very dark areas of the image. It also increases the Min. Adaptive Samples limit for very dark areas, because they tend to find paths to light sources irregularly, resulting in an over-optimistic noise estimate.
White Light Spectrum - Controls the appearance of colors produced by spectral emitters. This value determines the spectrum that will produce white in the final image. The D65 setting will produce a reasonable daylight color. The Legacy/Flat setting will preserve the appearance of legacy projects where the spectral emitters appear more blue.
Deep ImageRenders frames with multiple depth samples in addition to typical color and opacity channels. - Enables rendering deep pixel images used for deep image compositing.
Max. Depth Samples - Used when Deep Image is enabled. This sets the maximum number of depth samples per pixel. For more information, see the Deep Image Rendering topic in this manual.
Deep Render AOVs - Includes rendering AOVs in deep pixels.
Depth Tolerance - Used when deep image rendering is enabled. OctaneRender® merges the depth samples whose relative depth difference falls below this tolerance value together. This is covered in the Deep Image Rendering section in this manual.
Toon Shadow Ambient - Modifies the shadow ambient for toon shading.
Compatibility Mode - The Octane version that the behavior of this node should match.