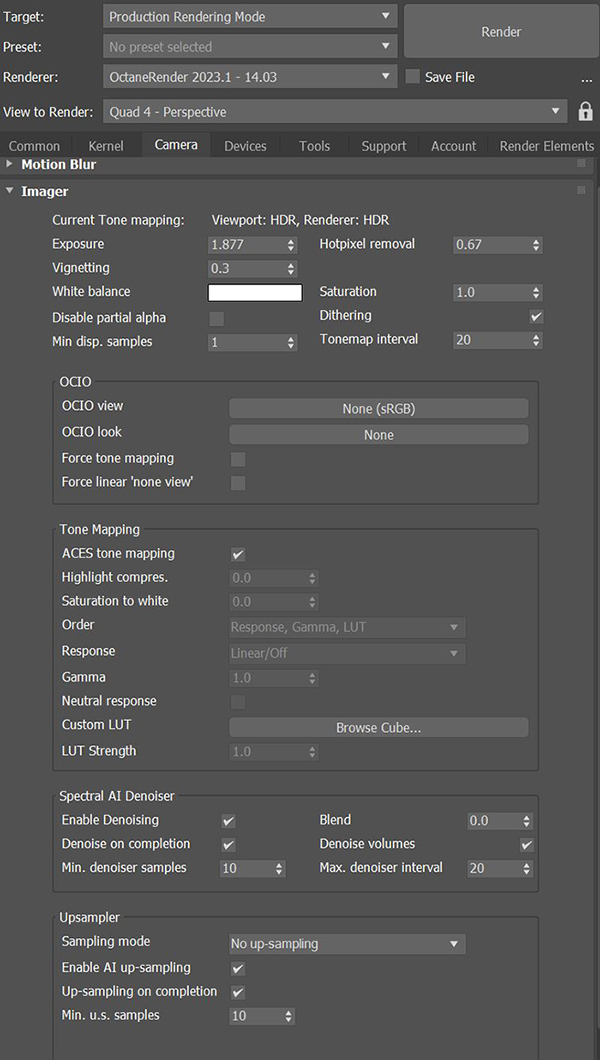
You can access the Camera Imager Settings from the Camera tab in the Render Setup window, or from the Modify panel if you added an OctaneRender® Camera to the scene.

Figure 1: Accessing the Camera Imager settings from the Render Setup window
The Modify panel for Octane Camera and Universal Camera have similar Imager settings.
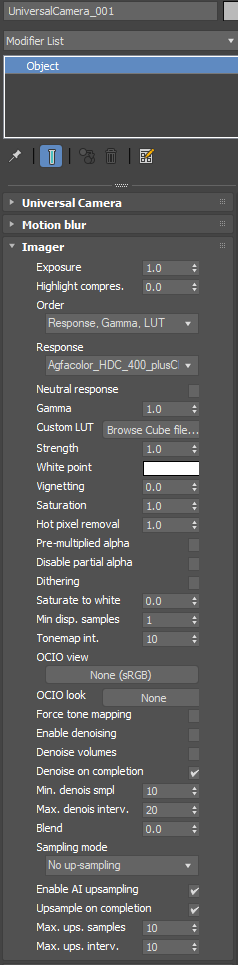
Figure 2: Camera Imager settings from the Modify panel.
Current Tone MappingRefers to applying a curve to an image to reduce dynamic range - Display the dynamic range settings used for the viewport and renderer.
Exposure - Controls the scene's exposure. Low values create a dark scene, while high values brighten the scene. Exposure has no effect on any of the render layer passes.
Hot Pixel Removal - Removes bright pixels (known as fireflies) during the rendering process. Many pixels can disappear if the render progresses, so this feature removes the bright pixels at a much lower sample per pixel.
Vignetting - Darkens the corners of the render, which increases the render's realism. OctaneRender® doesn't apply vignetting to any of the beauty passes except the main pass.
White Balance - Specify the color to adjust the tint for producing and simulating the relative temperature cast throughout the image by different light sources. The white point is white by default.
Saturation - Adjusts the amount of color saturation for the render.
Disable Partial Alpha - Makes semi-transparent pixels opaque (where the Alpha is greater than 0).
Dithering - Adds random noise, which removes banding in very clean images.
Minimum Display Samples - The minimum amount of samples that OctaneRender® calculates before displaying the image. This feature reduces the noise when navigating, and it's useful for real-time walkthroughs. When using multiple GPUs, we recommend setting this value as a multiple of the number of available GPUs for rendering - if you’re rendering with four GPUs, set this value to 4 or 8.
Tonemap Interval - Maximum interval between tonemapping operations (in seconds).
OCIO View - OCIO View to use when displaying in the Render Viewport. OCIO Config file is set in Octane preferences.
OCIO Look - OCIO Look to apply when displaying in the Render Viewport, if using an OCIO view. OCIO Config file is set in Octane preferences.
Force Tone Mapping - Whether to apply Octane's built-in tone mapping (before applying any OCIO look(s)) when using an OCIO view. This may produce undesirable results due to an intermediate reduction to the sRGB color space.
Force Linear None View - When OCIO view is set to None, use Linear sRGB instead of sRGB. This can be useful to save as EXRAlso known as OpenEXR. This image file format was developed by Industrial Light & Magic and provides a High Dynamic Range image capable of storing deep image data on a frame-by-frame basis. via 3ds max saving format, but note that no tone mapping can be applied in this mode. It is preferred to use an OCIO config with a Linear Raw view.
ACES Tone Mapping - Use the ACES 1.2 RRT + sRGB ODT. If enabled, all other tone mapping settings will be ignored.
Highlight Compression - Reduces burned out highlights by compressing them and reducing their contrast.
Saturation To White - Creates multicolored reflections when the sun is too bright. Increasing this value changes the colors to white. This is also applicable to all sources of light.
Order - Determines the order that OctaneRender®applies the Response, GammaThe function or attribute used to code or decode luminance for common displays. The computer graphics industry has set a standard gamma setting of 2.2 making it the most common default for 3D modelling and rendering applications., and Custom LUT (Custom Look Up Table) to the scene. 3D LUTs are defined for sRGB input values - you should apply the custom LUT last, but if there are 3D LUTs for linear input data, then apply the Custom LUT first.
Response - Select the use of measured camera response curves, which provides various pre-defined color grades to a rendering.
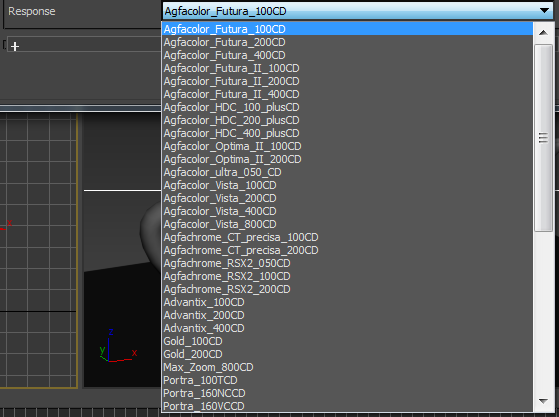
Figure 2: Listing the various types of response curves available in OctaneRender®
Gamma - Adjusts the render's gamma and controls the image's overall brightness.
Neutral Response - The camera response curve doesn't tint the render result.
Custom LUT - Choose a custom LUT.
LUT Strength - Controls the influence of the LUT.
Enable Denoising - Enables the spectral AI denoiser. This applies denoise to some beauty passes, including the main beauty pass, and writes the outputs into separate denoiser render passes.
Blend - Accepts a value between 0 and 1 to blend the original image with the denoised results. A value of 0 results in a total denoised image, and a value of 1 results in an image without any denoising.
Denoise On Completion - The beauty pass denoises once at the end of a render. Disable this option while rendering with the Interactive Region tool.
Denoise Volumes - The spectral AI denoiser denoises Volumes in the scene.
Min. Denoiser Samples - The minimum number of samples taken per pixel before the denoiser begins processing.
Max. Denoiser Interval - The maximum interval between denoiser runs (in seconds).
Sampling Mode - Selects the upsampler mode for rendering. The image renders at a lower resolution divided by the sampling mode, then it upscales to the final resolution.
Enable AI Up-Sampling - When you have an Upsampler Mode selection made and you enable this option, the render scales by using AI upsampling. Otherwise, scaling is done using traditional methods.
Up-Sampling on Completion - Beauty passes upsample once at the end of a render.
Min/Max U.S. Samples - The minimum and maximum number of samples per pixel until the upsampler activates. This parameter does not apply if you select No Upsampling in Upsampler Mode.