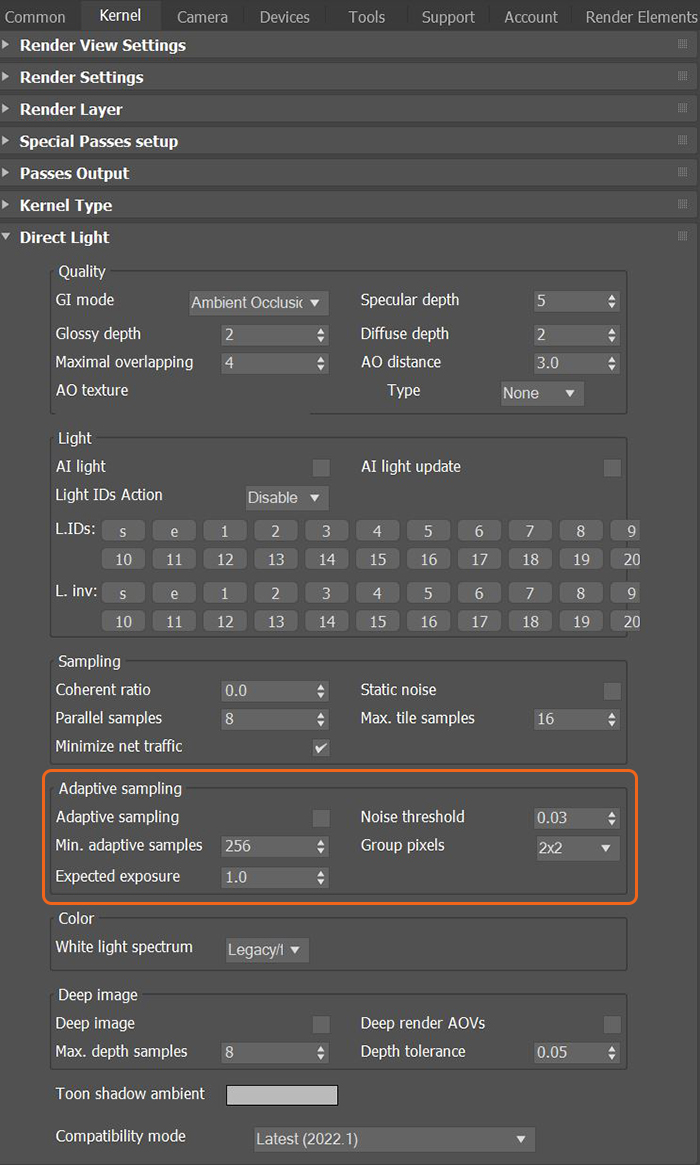
Adaptive SamplingA method of sampling that determines if areas of a rendering require more sampling than other areas instead of sampling the entire rendering equally. disables sampling for pixels that reach a specified noise threshold, which allows the Kernel to focus its processing on areas that still need refinement. You can find the Adaptive Sampling options in the attributes for the Direct Light, Path Tracing, and Photon Tracing kernels.

Figure 1: The Adaptive Sampling parameter of the Direct Light kernel
Adaptive Sampling - Stops sampling pixels that reach a specified noise threshold. This lets the kernel focus its processing on areas that still need refinement.
Min. Adaptive Samples - Specifies the minimum number of samples to calculate before Adaptive Sampling kicks in. The pixel's noise estimate has a large initial error. If you set the noise threshold to a high value, then you should set Min. Adaptive Samples to a high value to avoid artifacts.
Noise Threshold - When Adaptive Sampling is enabled, Noise Threshold specifies the smallest relative noise level. When a pixel's noise estimate is less than this value, OctaneRender® turns off sampling for this pixel. Good values are in the range of 0.01 - 0.03. The default is 0.02, which is pretty clean.
Group Pixels - When Adaptive Sampling is enabled, Group Pixels specifies the number of pixels that are handled together. If all pixels of a group reach the noise level, sampling stops for all of these pixels.
Expected Exposure - This parameter's value should be about the same value as the image exposure, otherwise set it to 0 (the default value) to ignore these settings. Adaptive Sampling uses this parameter to determine what pixels are bright and dark. This depends on the exposure setting in the Octane Imager. If the value is not 0, Adaptive Sampling adjusts the noise estimate of very dark areas of the image. It also increases the Min. Adaptive Samples limit for very dark areas, because they tend to find paths to light sources irregularly, resulting in an over-optimistic noise estimate.